According to our Antimicrobial Guidelines, what would you prescribe for a young, healthy patient diagnosed with CAP in the outpatient setting?
Amoxicillin 1000 PO TID OR Cefuroxime 500 PO BID for 5 days
Beta lactam allergy: Doxycycline 100 PO BID for 5 days
Spirometry finding required for COPD diagnosis per GOLD guidelines
Post bronchodilator FEV1/FVC <70%
Liver disorder associated with platypnea and orthodeoxia
Hepatopulmonary syndrome
Imaging follow up for ≤ 5 mm solid pulmonary nodule in low risk patient
None
People in which pneumococcal vaccine is indicated (TWO GROUPS)
What is >65 year olds OR what is <65 year old with history of heart disease, pulmonary disease, alcoholic cirrhosis, SCD, asplenia
levofloxacin
Diagnosis suggested by TLC <80% of predicted
Restrictive lung disease
Type of shock with low CO, low wedge, high SVR.
Per GINA guidelines, what should be first choice step-up therapy for adults with mild persistent asthma?
ICS-formoterol
This POCUS finding excludes pneumothorax when seen on lung ultrasound
Sliding lung sign (movement of the visceral pleura against the parietal pleura)
Name 2 bacteria that are implicated in causing "atypical CAP"
Legionella, Mycoplasma, Chlamydophila
Spirometry measure of the air remaining in the lungs at the end of passive expiration
Functional residual capacity (accept FRC)
Change in stress that occurs with each breath, difference in plateau pressure and PEEP
What is the driving pressure
This lung disease can present with small upper lobe nodules and cause Caplan's syndrome when associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
What is Coal worker's pneumoconiosis (black lung disease)?
Pulmonary hypertension is defined as mean pulmonary arterial pressure of ______ Mm Hg at rest.
What is 20mm Hg at rest?
Name one regimen to treat latent TB in an HIV-negative individual
Rifampin daily for 4 months
INH and rifampin daily for 3 months
INH and rifapentine for 3 months
INH daily for 6-9 months
A 51-year-old woman with unrefreshing sleep is evaluated with overnight polysomnography.
A representation of the polysomnogram is shown.

Obstructive sleep apnea
the antidote to cyanide toxicity
What is hydroxycobalamin
2 radiologic findings you would see in a ILD patient
Bilateral Reticulonodular pattern, Irregular Shaped Opacities, Granulomas, Cavity Formation, Honeycombing, Pleural Effusion, Pleural thickening
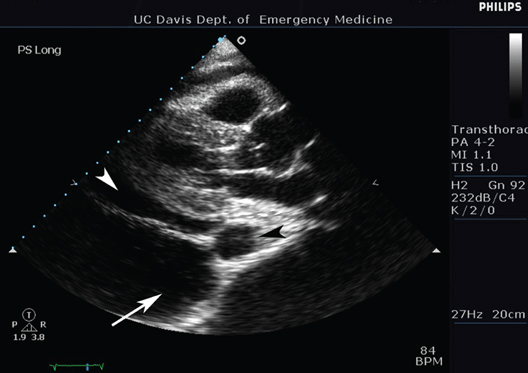 Two white arrows and black arrow
Two white arrows and black arrow
White arrowhead: pericardial effusion
Black arrowhead: descending aorta
White arrow: pleural effusion
Treatment for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
voriconazole, isavuconazole, or posaconazole
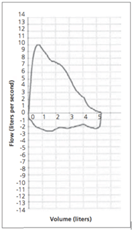
Difficulty getting air "in", chronic cough, voice changes
Vocal cord dysfunction – (flattening of the inspiratory/bottom flow volume loop)
A young woman ingests a mystery substance at a party and becomes wild and altered and starts having diarrhea. Brought in by EMS.
A blood gas is drawn.
ABG 7.3 / 15 / 200
Na 140, Chloride 120, Bicarb 10
Acid base disorder?
1. Non anion gap metabolic acidosis – diarrhea
2. Respiratory Alkalosis – wild and hyperventilating beyond the compensatory response
ABG 7.3/15, AG 10, Bicarb 10
Winter’s expected pCO2 = 1.5 * 10 + 8 +/- 2 = 23 +/- 2
Measured pCO2 = 15 thus there is a respiratory alkalosis
List 4 of the 5 most common opportunistic fungal lung infections
pneumocystis pneumonia
mucormycosis
cryptococcus neoformans
candida albicans
aspergillus fumigatus
Clinical triad associated with Churg-Strauss syndrome
Asthma, hypereosinophilia, necrotizing vasculitis