The system that is responsible for gas exchange & how
What is:
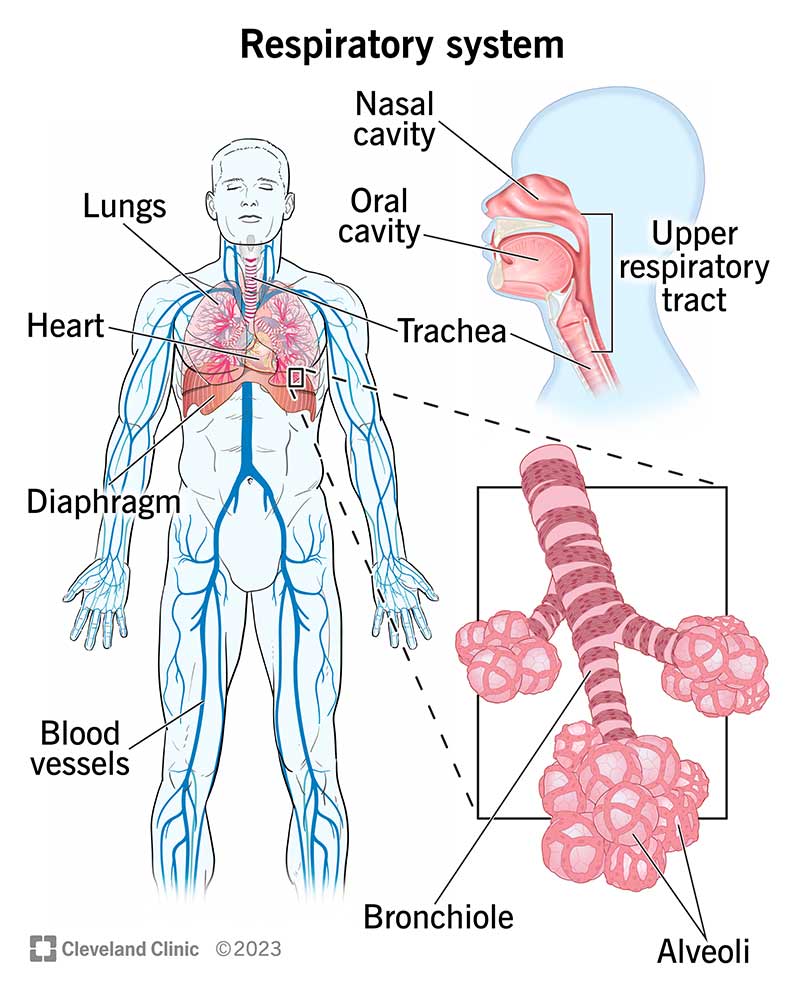
- the respiratory system
- Absorption of O2 & excretion of CO2
the reflex that causes a decrease in heart rate when stimulated from bronchoscopy, ET intubation, or tracheal suctioning
what is:
-Vasovagal reflex

the route of fluid transport to and from the lungs
What is:
-traveling through the bronchial & pulmonary circulation along with the lymphatic system
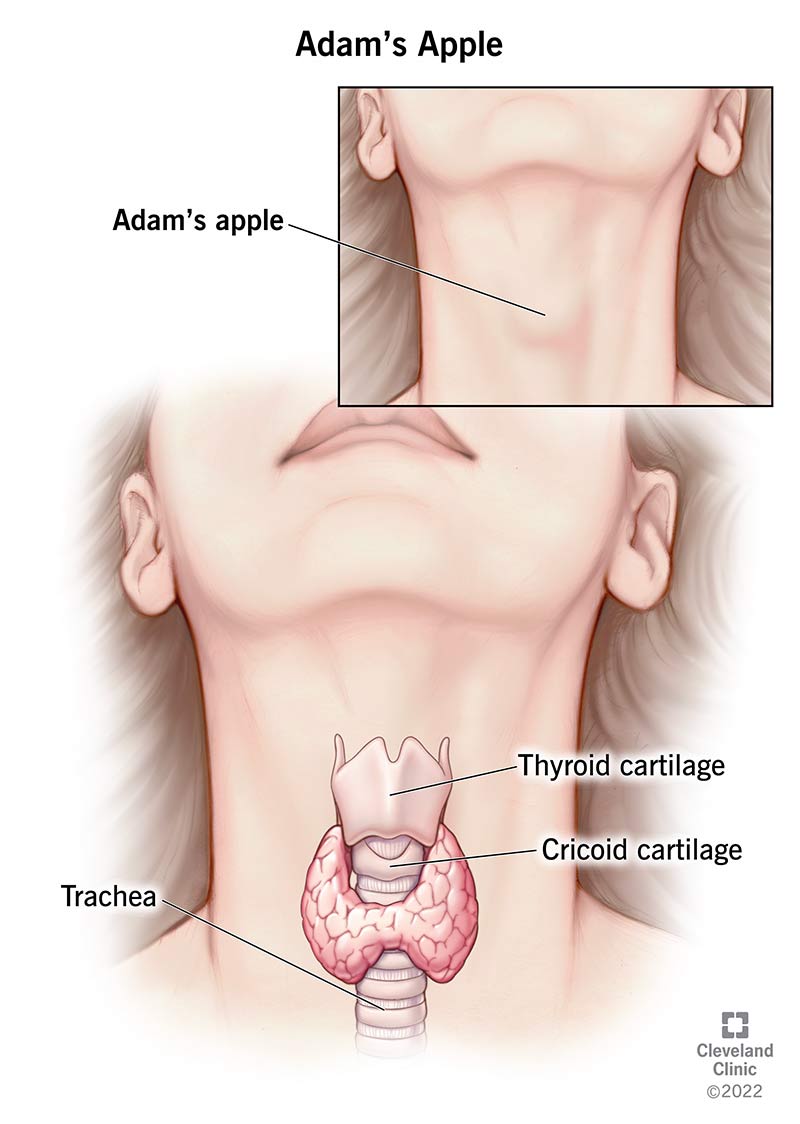
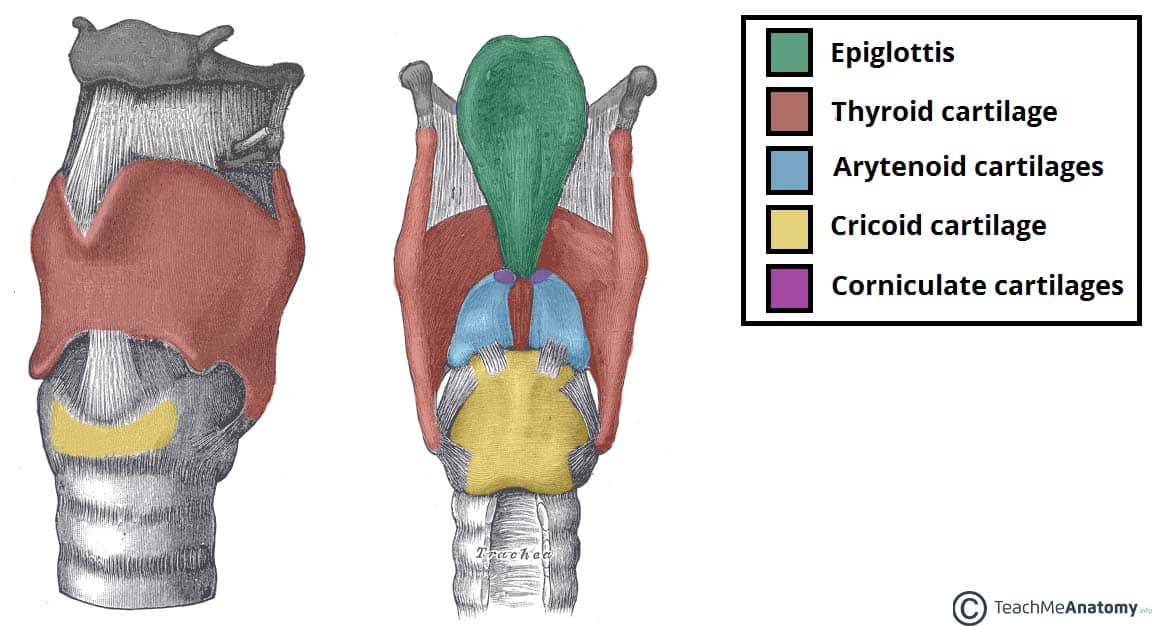
the unpaired cartilage of the upper airway that contains the Adam's apple
what is:
-the thyroid
the pair of ribs that are posterior only and do not connect to anything in the front
What is:
-11,12
-floating ribs, blue in pic
the breathing sound that is soft, muffled sounds heard during inspiration over parenchyma (normal breath sounds)
What is:
-vesicular

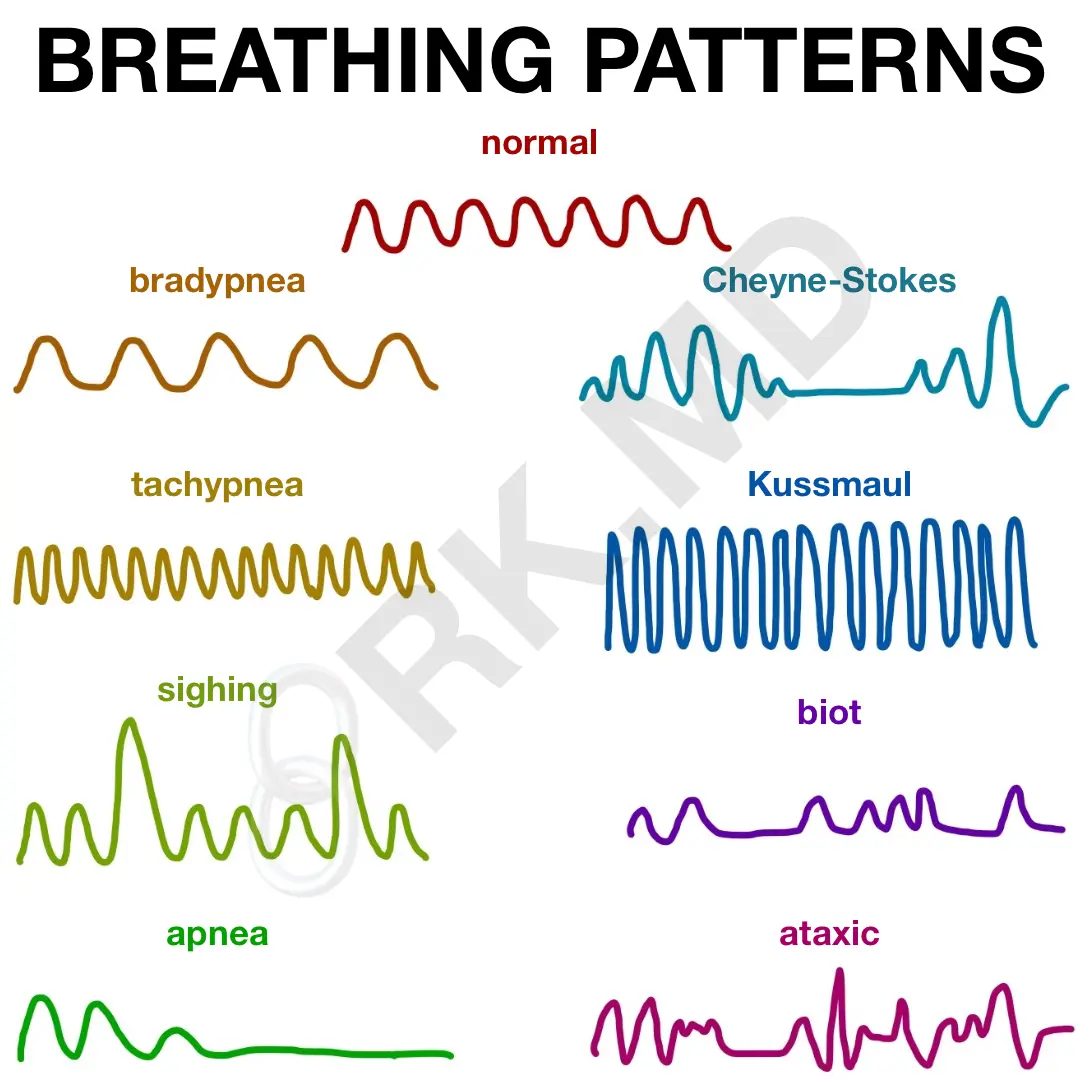
the breathing pattern that depth and rate increase then decrease then a period of apnea (caused by Brain injuries and CHF)
what is: Cheyne stokes
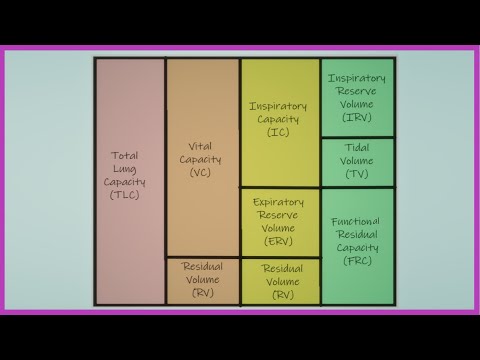
the chart for volumes & capacities

how to calculate smoking pack history in years
Packs smoked per day # X # of years smoked
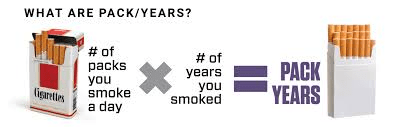
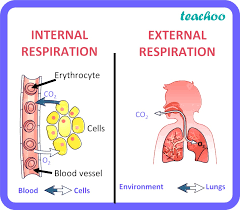
The gas exchange between tissue cells & systemic capillary blood (tissue level)
What is:
-Internal respiration
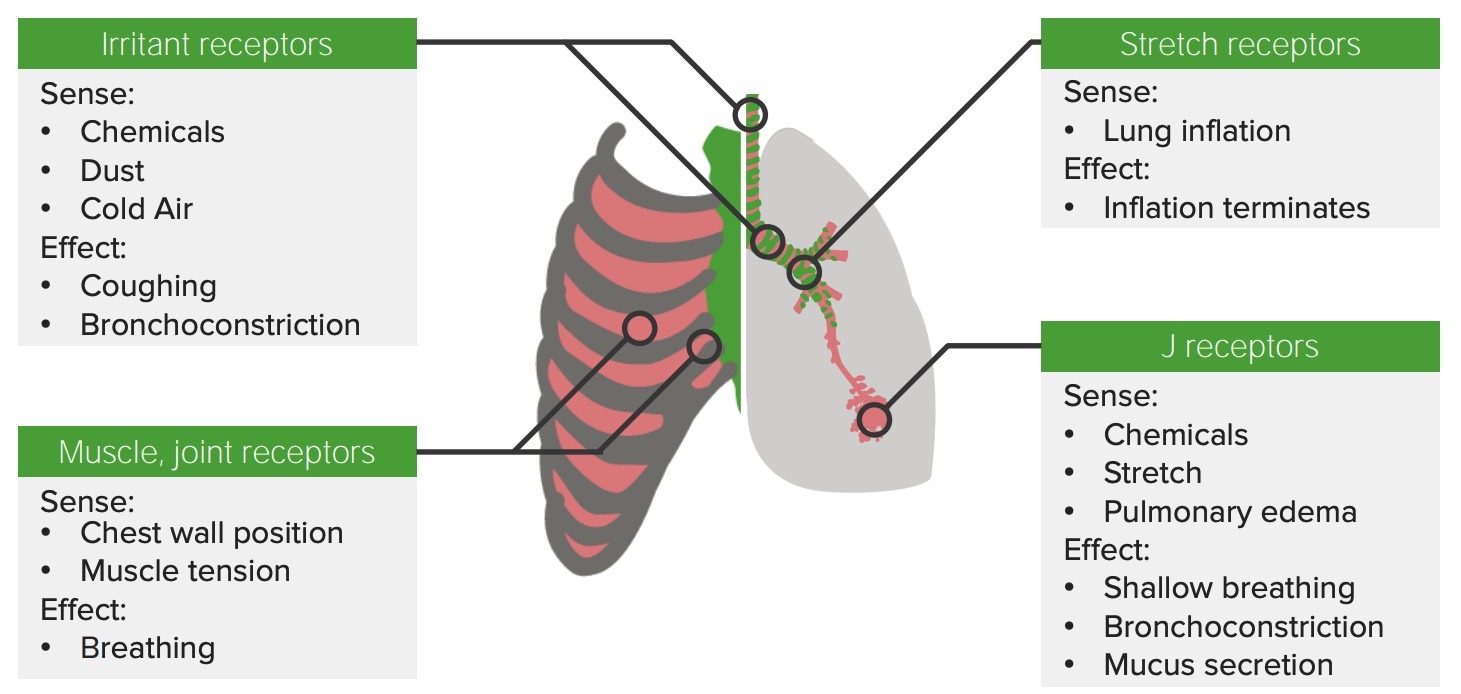
the receptors that cause rapid shallow breathing patterns (stimulated by pulmonary disease/congestion and inflammatory processes such as narrowing of glottis )
what is:
J receptors
the three functions of the lung's pulmonary circulation(3 parts)

what is:
- Gas exchange at the AC membrane (pick up oxygen and drop off CO2)
- AC membrane controls fluid exchange in the lung
- Production, processing, and clearance of a variety of chemicals and blood clots
the unpaired cartilage of the upper airway that is the only complete ring
what is:
-the Cricoid
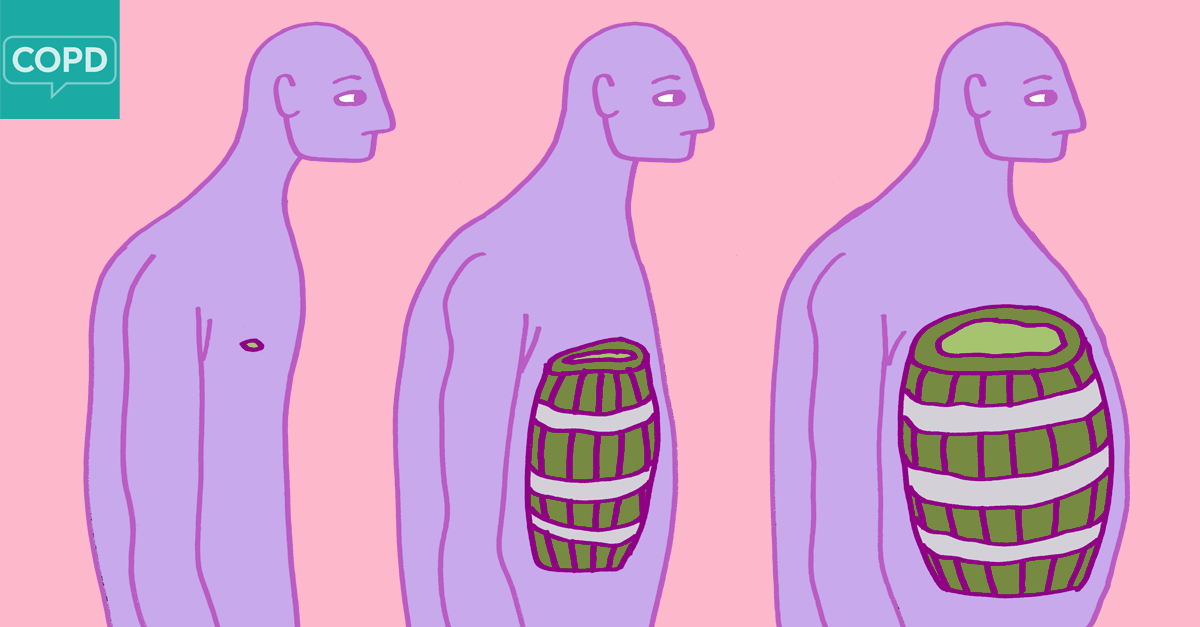
the chest and spine configurations with increased AP diameter of the chest, the cause is emphysema.
what is:
-barrel chest
Side note: Emphysema is a chronic lung condition that damages the air sacs in the lungs, called alveoli, making it difficult to breathe. Over time, the walls of the alveoli weaken and break, creating larger air spaces instead of many small ones. This reduces the surface area of the lungs, which in turn reduces the amount of oxygen that reaches the bloodstream

the breathing sound that is a harsh hollow(normal)
What is:
-Tracheal

the breathing pattern that is caused by damage to the pons
what is: Apneustic breathing/Biot-breathing

the Tidal Volume (TV) capacity(normal, quiet breathing involves inspiration and expiration of TV)
what is:
-TV ~ 500-700 ml
the coughing up of blood-streaked sputum is called
Hemoptysis
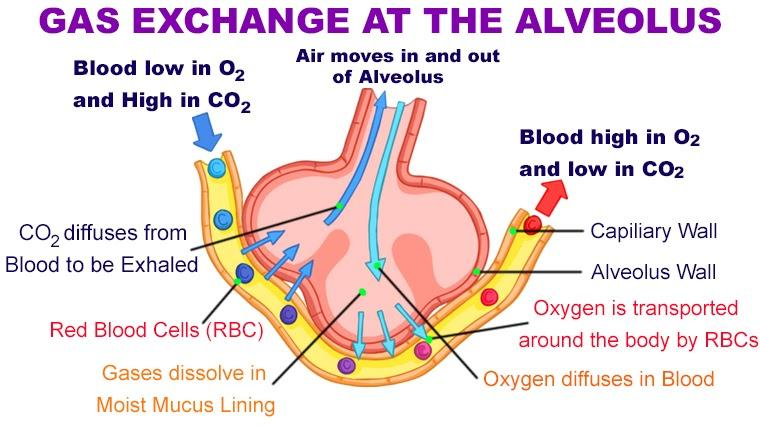
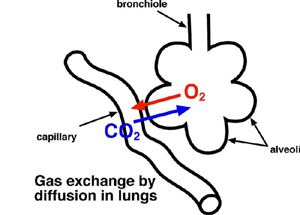
the exchange of gases in the alveoli of the lungs(between gas of the atmosphere & body)
What is:
-external respiration
the receptors responsible for the initial increase in ventilation at the beginning of exercise
what is
-Proprioceptors

the VRG sends signals to which structures during inspiration(3 parts)
what is: the Diaphragm, larynx, and pharynx


the leaf-shaped cartilage extends from the base of the tongue to the thyroid cartilage
What is:
-the Epiglottis

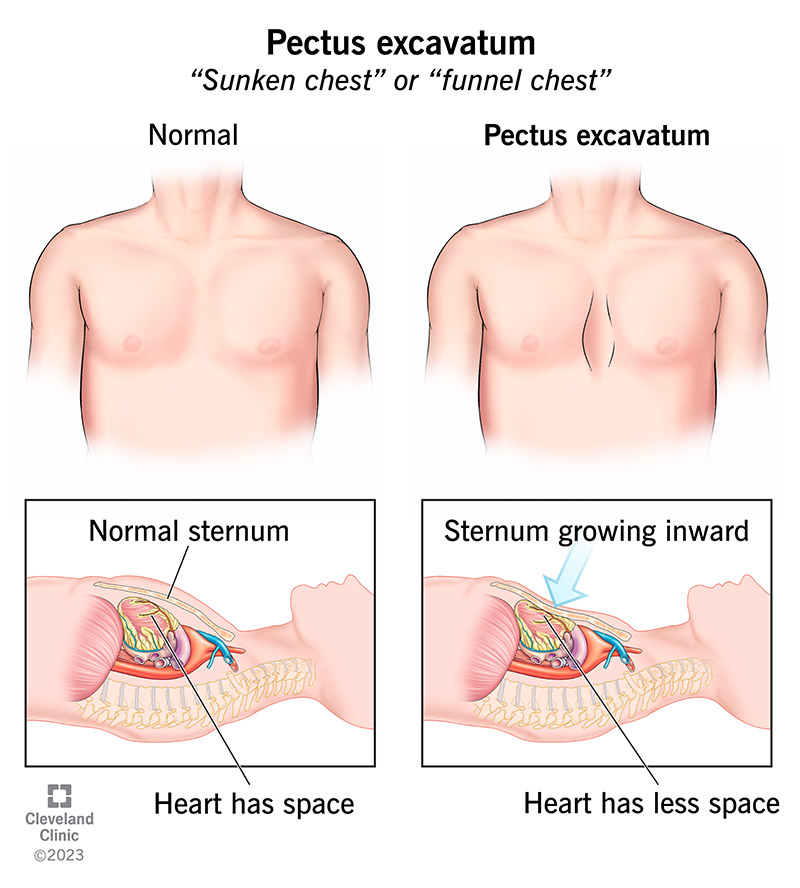
the different chest and spine configuration where the chest protrudes OUTWARD causing the lungs to be less effective( believed to be caused by cartilage growth of costal cartilage that grows faster than the bones)
what is:
-pectus carinatum

the loud breathing sound, tubular breath sounds equal during inspiration and expiration (normal)
what is:
-Bronchial

the breathing pattern of the deep gasping type of respiration caused by DKA(Diabetic ketoacidosis)
what is:
-Kussmaul

the Inspiratory Reserve Volume (the additional volume of gas that can be inspired above TV on maximal inspiration)
what is:
-IRV ~ 3,100 mL

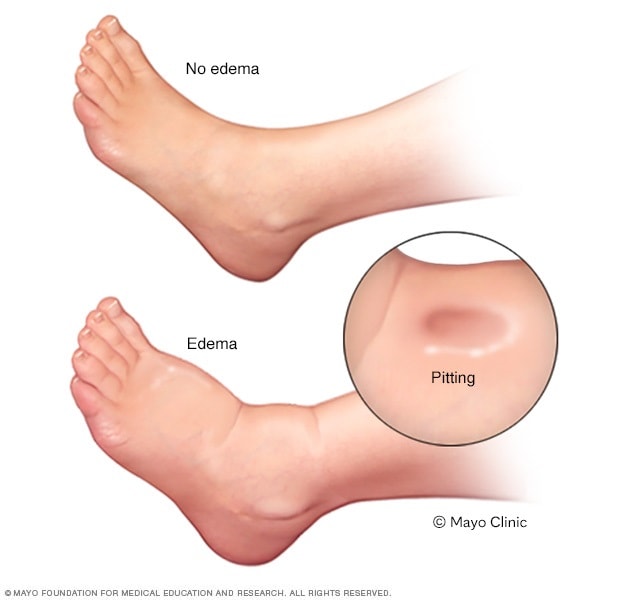
what is pedal edema and what is it associated with
Is swelling in the lower extremities, most often due to right ventricular heart failure
the term for gas exchange across the lungs, in which the alveoli & capillary (A/C) membrane are responsible for the exchange of O2 for CO2
What is:
-simple diffusion
The receptors in the special nerve cells detect changes in the chemical composition of the blood and send information to the brain to regulate cardiovascular and respiratory functions. There are two major types.
what is: Chemoreceptors
Central - Responds to changes in CO2 (by H ions)
Peripheral - Respond to decrease in PaO2, changes in PaCO2

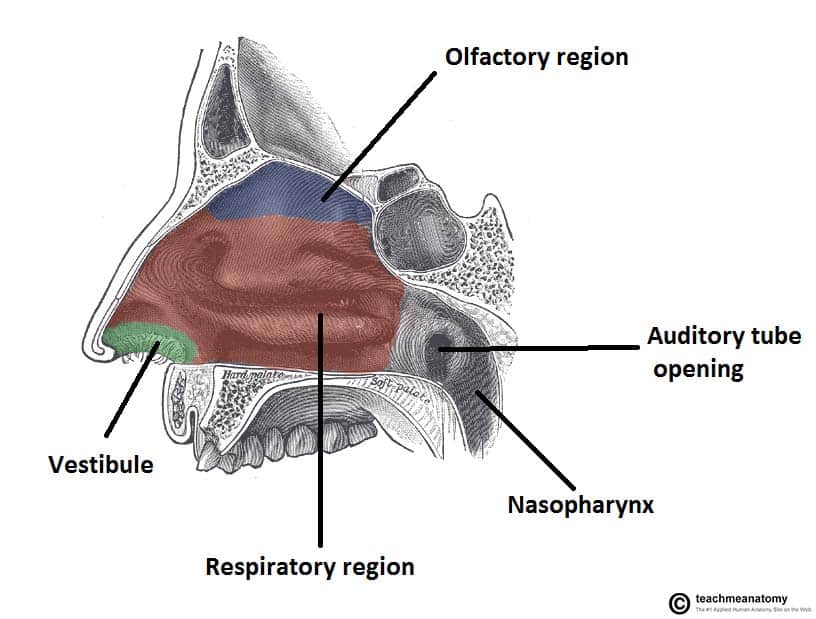
the 3 parts that make up the pharynx
what is:
-Nasopharynx- (nasal cavity to uvula) adenoids lie right where many particles impact
-Oropharynx- (uvula to tip of the epiglottis) palatine tonsils (removed as kid tonsillectomy)
- And Laryngopharynx- (tip of epiglottis to the larynx) is an anatomic location where respiratory & digestive tracts divide, also called the hypopharynx

the paired cartilages of the upper airways
what is
- Arytenoid, Corniculate, and Cuneiform (paired)

the chest and spine configuration in which the chest protrudes out is caused when the sternum(cartilage that connects ribs to the breastbone) grows INWARD, resulting in a depression in the chest that may appear deep. The chest may have a "sunken in" or "funnel chest" appearance.
What is:
- Pectus excavatum
the breathing sound that is a high-pitched noise by bronchoconstriction(adventitious)
what is:
-wheezing
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-bronchoconstriction-200966-FINAL-4b7cac4fd70942b3b44e5959f1b8e148.jpg)

the breathing pattern that has prolonged expiration
what is: Asthmatic

what is Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)(additional volume of gas that can be expired below TV on maximal expiration)
what is:
-ERV ~ 1,200 mL

palpation vs percussion
palpation is touching and percussion is tapping
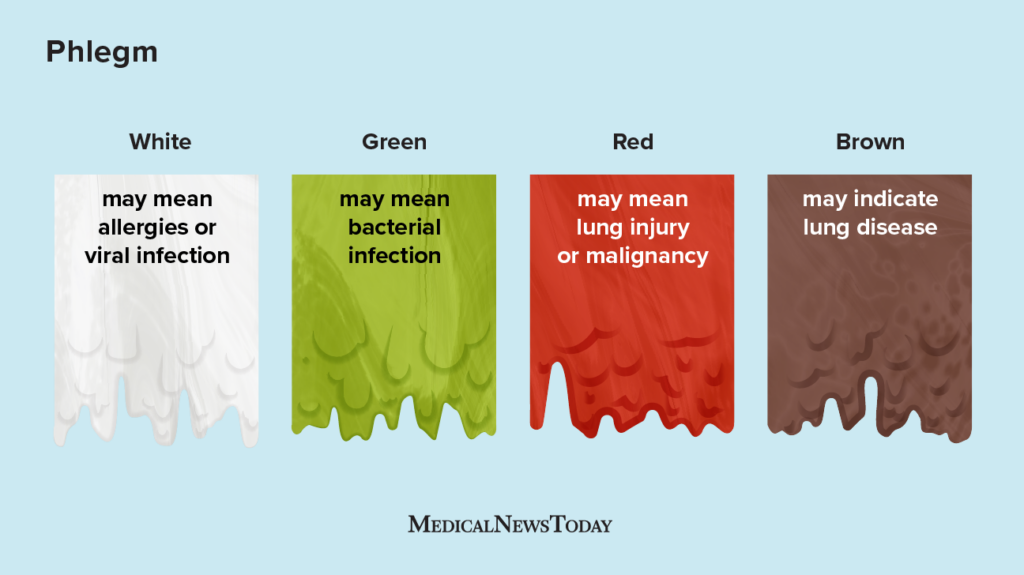
the mucus from the lower airways but is ejected through the mouth
what is:
Sputum

the occurrence of oxygen causing worsening V/Q mismatch in patients with chronically high CO2? And what other complications can occur from excessive O2 in this type of patient? (COPD, asthma)
-improving blood flow to poorly ventilated alveoli (not a lot of new air moving into lungs because of lack of elasticity while there is increased blood flow, less 02 available, and CO2 would continue to rise)
-02 induced hypoventilation
-Decreased hypoxic drive (removes stimulus - low 02)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-vq-mismatch-in-the-lungs-914928-v1-b4d9d6af14a54347bc4cc06d2304308f.jpg)
What is the primary function of the larynx?
what is: Protect the airway during eating or drinking (epiglottis movement)
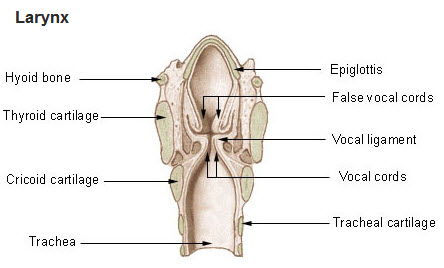
the unpaired cartilage of the upper airways
what is:
-Thyroid, Cricoid, & Epiglottis

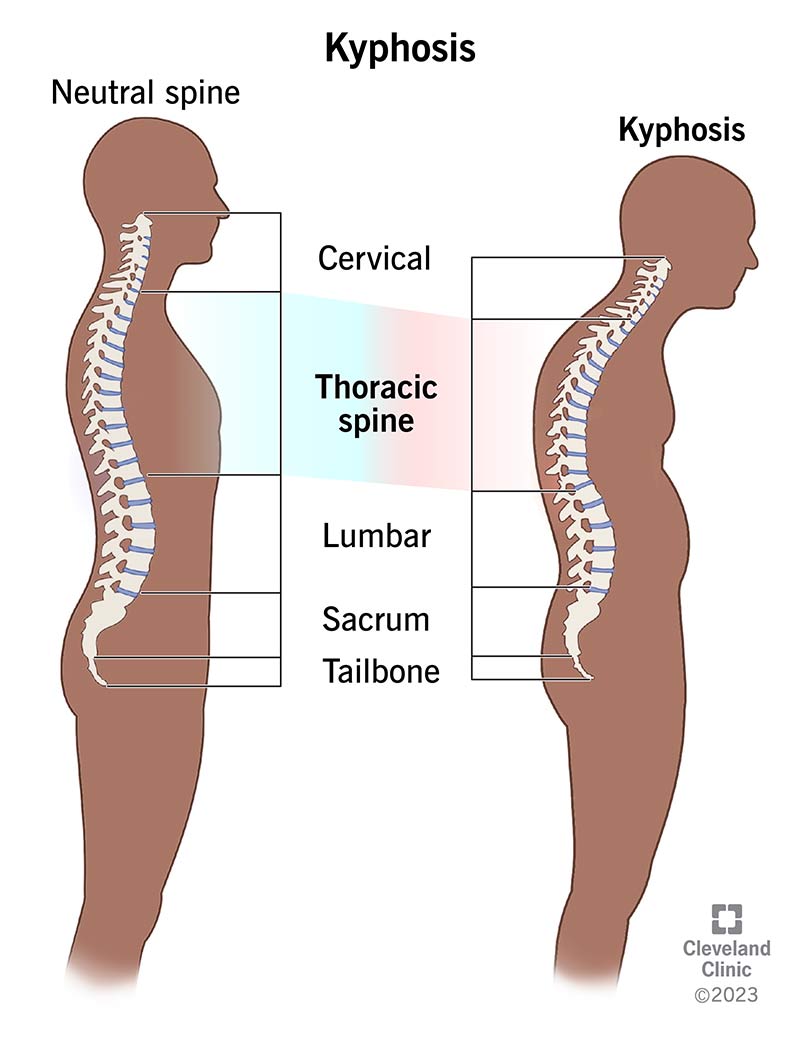
the chest and spine configuration that increases AP(anteroposterior) curvature of the spine
what is:
-Kyphosis

the low breathing sound caused by mucus. A cough or suction can improve this
what is:
-Rhonchi (coarse crackle)


the decrease in pulse during inspiration, caused by hyperinflation (asthma, COPD), pericarditis, cardiac tamponade
what is: the Pulsus paradoxical
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pulsus-paradoxus-4587588-v1-593d02d7f4ab4380894939e7ce04c44d.png)
The residual Volume (RV) (volume of gas that remains in the lungs following maximal expiration), cannot be measured by spirometry
what is:
RV ~ 1,200 mL

what is central cyanosis
bluish color around the oral mucosa(makes torso blue as well) indicates respiratory failure due to low O2 levels
the mucus from TB(Tracheobronchial) tree not contaminated by oral secretions
what is:
Phlegm
the stretch receptors at high lung volumes during inhalation are sent to DRG through the vagus nerve (for adults active at Vt greater than 800ml)
what is:
-Hering-Breuer inflation reflex

the cause of Hypoxemia-mediated/ Hyperventilation
what is:
-pons are damage, Functions only when vagus nerve is served
What is the key landmark for oral intubation
What is:
- the Vallecula

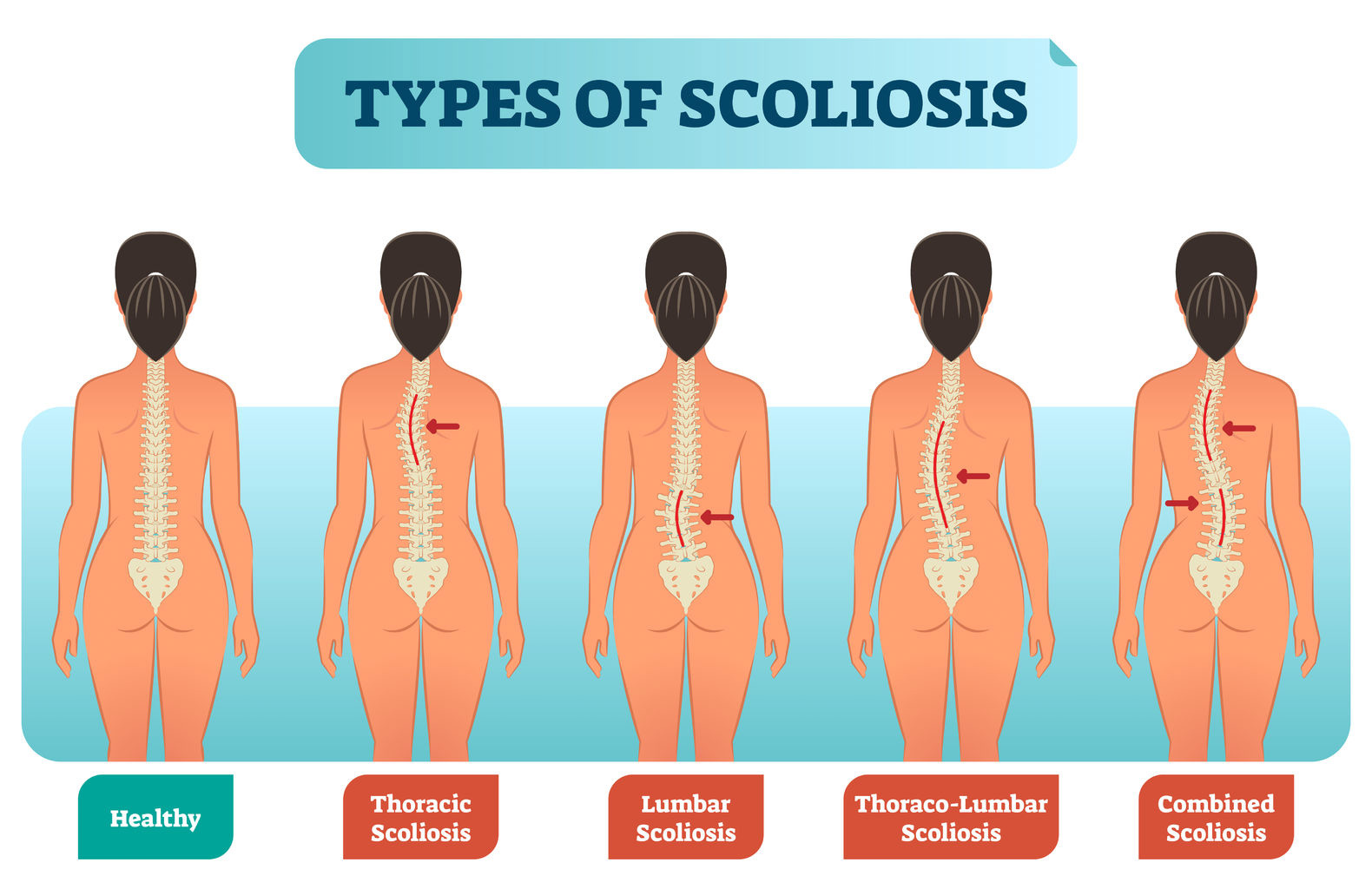
the chest and spine configuration that is a lateral curve of the spine "S shaped"
what is:
-scoliosis
the breathing sound of popping caused by alveoli opening or fluid (overload), is discontinuous, and is an adventitious breath sound "bubbling"
What is:
-Crackle(rales)

the alternating strong and weak pulse; Caused by heart failure
what is: the Pulsus alternan

the lung capacity(greater than 2 volumes) for Inspiratory Capacity (IC), TV + IRV, amount of air inhaled after normal exhalation
what is:
IC ~ 3,600 mL

the hypothalamus's responsibilities and regulation
Feeding, Fighting, Fleeting, Fahrenheit, fornication
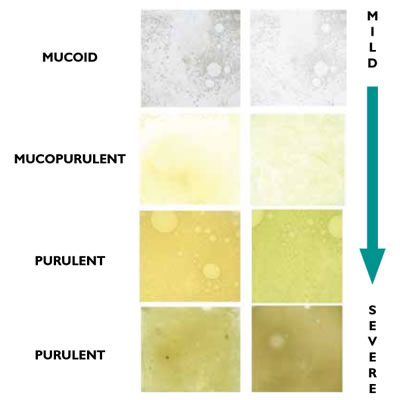
the Sputum that contains pus cells
what is:
Purulent sputum
the reflex that causes a strong inspiratory effort
what is:
-Deflation reflex

the possible causes of tachypnea and diaphoresis(sweating)
what is:
-Exertion, Fever, hypoxemia, Anxiety, Atelectasis, and Pain

The internal point that separates the left and right bronchus?
what is:
-the Carina

the ribs that connect directly to the sternum
what is:
-1-7
-true ribs
the breathing sound of upper airway obstruction, high-pitched and continuous heard over trachea during inspiration
what is:
-Stridor

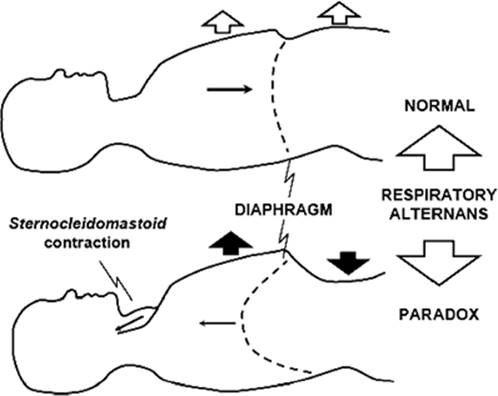
the occurrence of abdomen and chest "see-saw" opposite of each other, Caused by diaphragm weakness
what is: the Abdominal paradox
the lung capacity Functional Residual Capacity (FRC), ERV + RV, the volume of gas that remains in the lungs following normal TV expiration (equilibrium volume of lungs)
what is:
-FRC ~ 2,400 mL

Systolic pressure range and diastolic, hypertension/hypotension range
Systolic- contractions of the left ventricle 90-140MMHG
diastolic- relaxation of ventricles 60-90MMHG
with pulse pressure between 30-40
hyper- >140/90
hypo- <90/60
the sputum that is smelly
what is:
-Fetid sputum(foul smelling)

the reflex that stimulates a deeper breath upon inspiration (sigh)
what is:
-Head's paradoxical

The type of cells secretes pulmonary surfactant? What is the purpose of surfactant?
What is:
- Type II pneumocytes
- Surfactant reduces friction and promotes lung stability

the different zones of the lungs
what is:
a. Respiratory bronchioles- Gas Exchange takes place
b. Transitional airways -Between respiratory and conducting zones, gas is moved and participates in gas exchange
c. Conducting airways-Terminal bronchioles are the smallest of the conducting airways, (Nares to terminal bronchioles)

the ribs that do not articulate directly with the sternum
what is:
-false ribs
-8-10(do not articulate directly with the sternum. The costal cartilages of ribs eight to ten connect with the costal cartilages of the ribs above) pic green ribs
the breathing sound that is creaking or grating gets louder with deep breathing, not affected by cough
what is:
-pleural friction rub

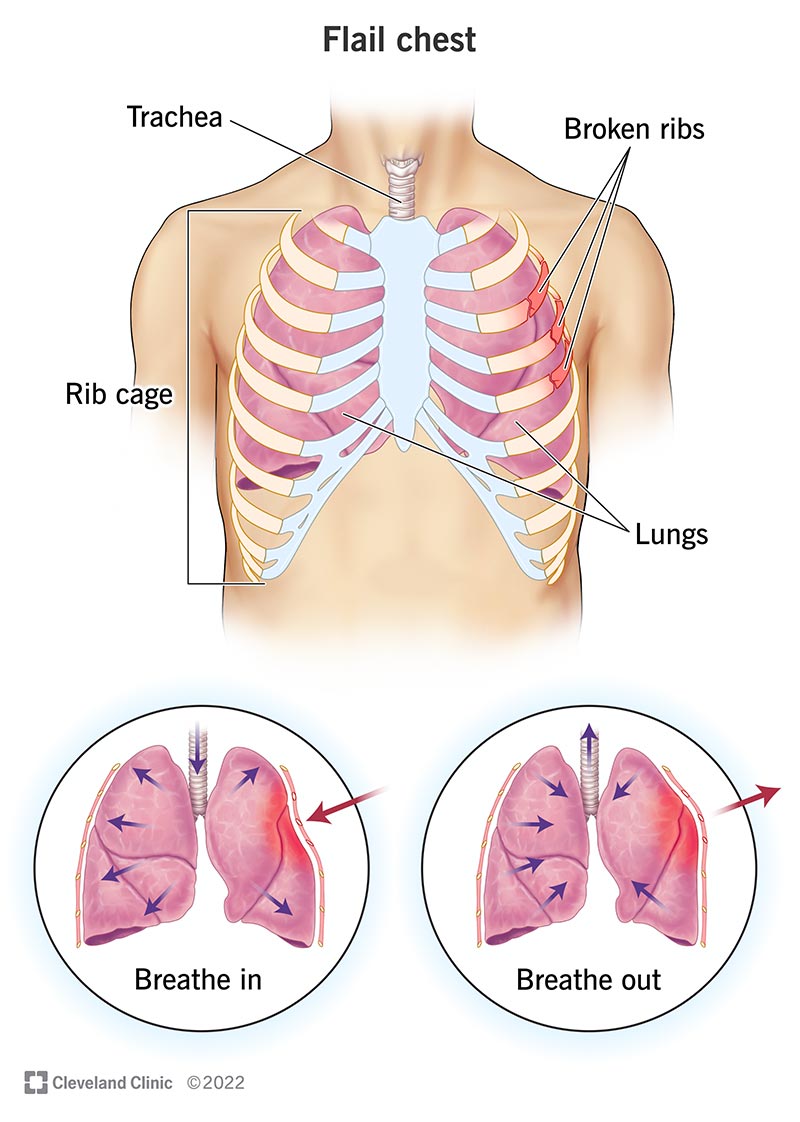
the flail chest of one side of the chest inflates the other, does not, Caused by trauma, rib fx, severe pneumothorax
what is: the Chest paradox
the lung capacity Vital Capacity (VC), measures the maximum amount of air that can be inhaled and exhaled during breath.
IC + ERV = TV + IRV + ERV
what is:
-VC ~ 4,800 ml

SPO2 level in normal adult
92-100%
the sputum that has the presence of blood after coughing it up
what is:
-Hemoptysis


the receptors that cause coughing, sneezing, and tachypnea
what is:
- the irritant receptor
s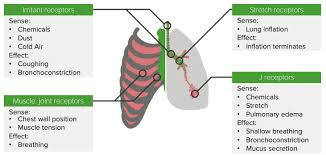
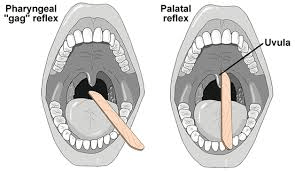
the purpose of gag reflex
what is:
prevent aspiration of bacteria & food
-if the patient is not conscious then intubate or they might aspirate
the medulla contains
what is: Dorsal & ventral respiratory groups
the angle of the right & left bronchi
what is:
right- 20-30 degrees, easier to turn down, and is 60% capacity
left- 45-55 degrees, not easy to turn into, and due to the heart is 40% capacity(thinner)

the breathing sound of little or no air movement (decreased aeration) caused by pleural effusion, hyperinflation, mucus plugging (reabsorption atelectasis), and shallow breathing (passive compressive atelectasis)
what is:
-diminished
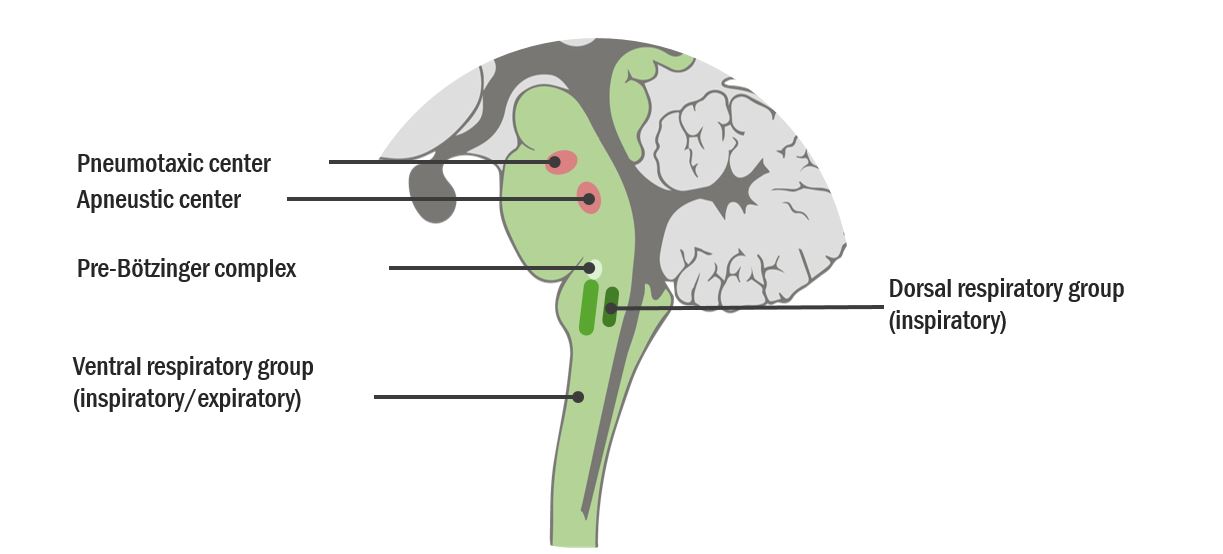
the two centers that exist in the pons below the medulla? Describe both
what is: Pneumotaxix center & Apnesustoc center.
The pneumotaxic center controls IT and shuts off inspiration (normal breathing center)
-Apneustic center- only works when damage to pons; gasping breathing - not life-sustaining
the Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
-VC + RV = TV + IRV + ERV + RV
what is:
-TLC ~ 6 mL

decrease and increase in tactile fremitus(chest palpation) is caused by
decrease- air & fluid in pleural space, bronchus obstruction, emphysema, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, obesity, asthma(w/hyperinflation)
increase- consolidation in the lungs & pneumonia or atelectasis
the nerves that send signals from lungs, airways, and peripheral chemoreceptors to DRG
what is:
-the Glossopharyngeal
-& vagus nerves

the irritant receptors' response in the lungs and airway
what is:
-Bronchospasm, cough, sneeze, tachypnea, narrowing of glottis (laryngospasm), or vasovagal

the pores of Kohn & the canals of Lambert purpose
what is:
-the Pores of Kohn are responsible for allowing communication between alveoli(also if there is a mucus obstruction it gives an alternate route for repair)
-the Canals of Lambert are responsible for allowing communication between alveoli & bronchioles

the nasal cavity and its defenses
what is: sinuses
cilia, nose hairs, heats & humidifies
the amount of lobes on the right and left lung
what is:
right- 3
left -2

the primary muscle of ventilation
what is:
-the diaphragm
- & intercostals
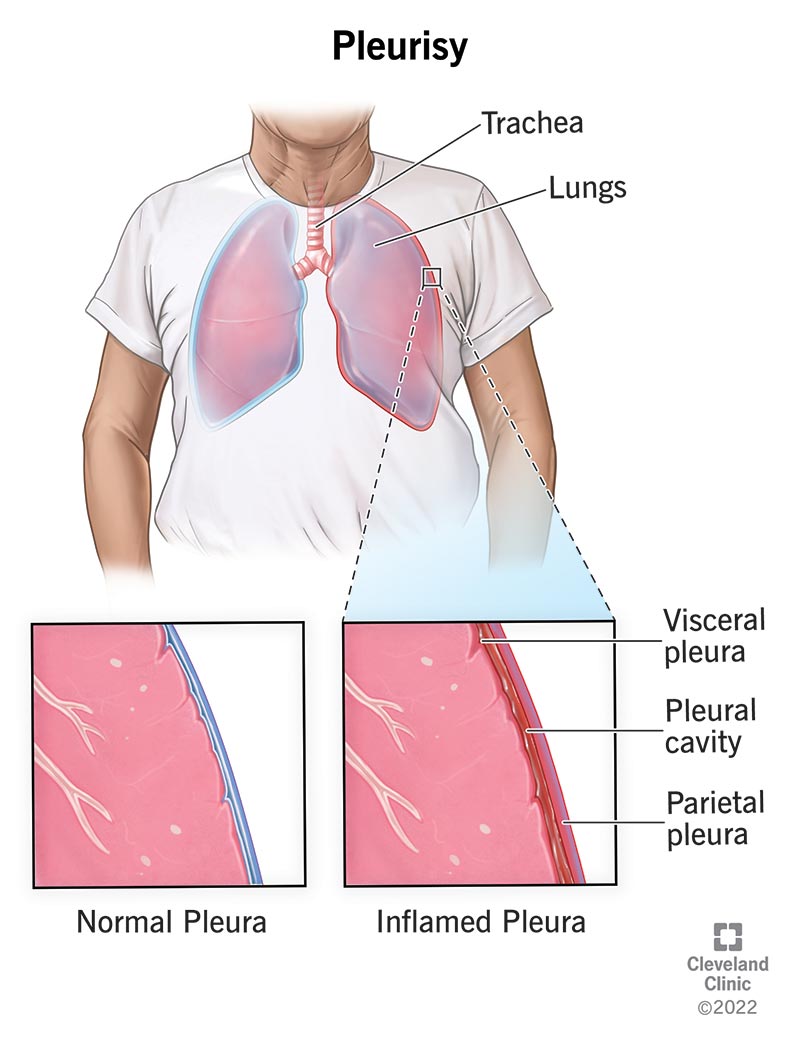
the term pleuritic vs non-pleuritic pain, & causes
what is:
Pleuritic-lateral stabbing pain increased on inspiration; caused by pleuritis, PNA, PE
Nonpleuritic pain - Angina (chest pain caused by coronary artery obstruction) radiating down the shoulder
the when PaO2 falls to 60mmHg, the receptors located in aortic arch & bifurcation of common carotid arteries & condition
what is: PCR and Hypoxic
obstructive diseases CBABE
c- cystic fibrous(genetic)
b- bronchitis
a- asthma
b- bronchiectasis
e- emphysema
the cardiac output formula
what is: SVxHR
5-10 L/min
The Type II pneumocytes and their role(4 parts)
what is:
-only covering 7%,
-reduce surface tension w/surfacant &
- are like stem cells to help repopulate/repair damaged alveolar surfaces with type I,
- will increase compliance and decrease WOB

term for airways that participate in gas exchange & the term for those that don't participate but help facilitate it
What is:
-respiratory zone
-conducting zone
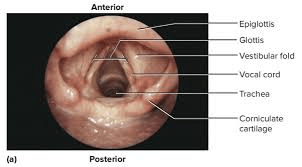
the opening between vocal cords
what is the glottis
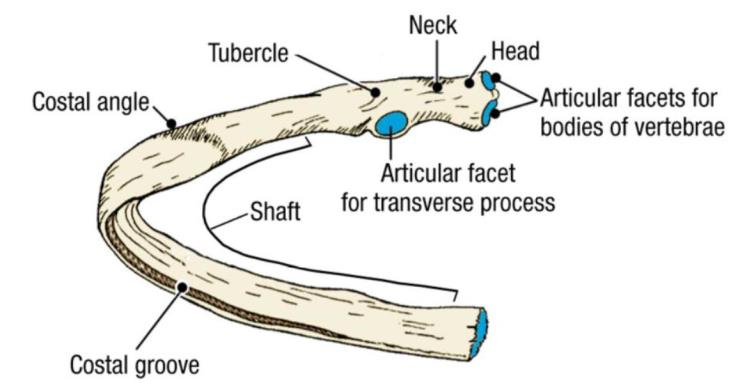
the arteries, veins, and nerves are located where in each ribs
What is:
-Costal groove on the bottom of each rib
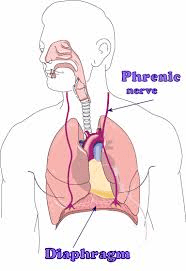
the breathing signal to the diaphragm from the brain
What is the Phrenic nerve
the purpose of a small amount of fluid in the pleural space
what is:
-to reduce friction
the VE=
what is:
-5-10 L/min
serve pulmonary hyperinflation will cause?
an increase in lung volume & flattens diaphragm domes