Pulmonary Edema
Pulmonary edema is a condition in which the lungs fill with fluid. It’s also known as lung congestion, lung water, and pulmonary congestion.
What are some symptoms of pulmonary edema
Name 3
Shortness of breath
coughing up blood (classically seen as pink, frothy sputum)
excessive sweating, anxiety, and pale skin
Shortness of breath can manifest as orthopnea (inability to lie down flat due to breathlessness) and/or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
Self-Care treatment for pulmonary edema
Low sodium diet
no more than 1,500 to 2, 2400 mg per day
What is the first line of treatment for pulmonary edema
Oxygen is always the first line of treatment for this condition
The body does not struggles to get enough oxygen during pulmonary edema
What is false
When pulmonary edema occurs, the body struggles to get enough oxygen and you start to have shortness of breath.
Causes of Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
list 2
Left ventricle failure
Dysrhythmia
left ventricle hypertrophy and cardiomyopathy
volume overload
myocardia infractions
Left ventricular outflow obstruction
What are the two classifications of pulmonary edema
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema
region of the body deprived of adequate oxygen supply at the tissue level
What is Hypoxia
Hypoxia may be classified as either generalized, affecting the whole body, or local, affecting a region of the body.
sensation that your heart has skipped a beat or added an extra beat. It may feel like your heart is racing, pounding, or fluttering
What is Palpitations
The best way to try and prevent pulmonary edema is by doing this
- Get a pneumonia vaccine.
- Get the flu vaccine, especially if you have heart problems or if you are an older adult.
- Remain on diuretics after an episode of pulmonary edema to prevent a reoccurrence.
What are preload reducers
These help decrease pressures from the fluid going into your heart and lungs.
Diuretics also help reduce this pressure by making you urinate, which eliminates fluid.
Acute pulmonary edema can cause drowning
True
Acute pulmonary edema develops suddenly. If left untreated, the fluid in your lungs can cause you to drown
The most common cause of pulmonary edema
What is Congestive heart failure
Heart failure is when the heart can no longer pump blood properly throughout the body. This creates a backup of pressure in the small blood vessels of the lungs, which causes the vessels to leak fluid.
In a healthy body, the lungs will take oxygen from the air you breathe and put it into the bloodstream. But when fluid fills your lungs, they cannot put oxygen into the bloodstream. This deprives the rest of the body of oxygen.
Increased pressure in the pulmonary capillaries because if cardiac abnormalities
Hydrostatic pressure is increased and fluid exit capillary at increased rate
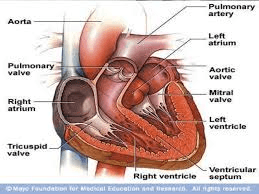
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
is a common and potentially fatal cause of acute respiratory distress. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema is most often a result of acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF).
High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE)
HAPE can occur when people travel to or exercise at very high altitudes
attacks of severe shortness of breath and coughing that awakens the person from sleep at night, and may be quite frightening.
What is Proxy Nocturnal Dyspnea
You can also decrease your risk for heart failure by doing this
- Visit your doctor regularly.
- Don’t smoke or use recreational drugs.
- Get regular exercise.
- Eat healthy foods.
- Maintain a normal weight.
These medications dilate your blood vessels and take pressure off your heart.
Afterload reducers
- an increased heart rate
- rapid breathing
- a crackling sound from your lungs
- abnormal heart sounds
- fluid buildup in neck, legs and abdomen
- pale or blue-colored skin.
All of they above should be checked for pulmonary edema
True
What are some external causes of pulmonary edema
Name 3
- high altitude exposure
- illicit drug use or drug overdose
- lung damage caused by inhalation of toxins
- severe trauma
- major injury
- near drowning
Negative pressure pulmonary, Neurogenic causes, acute respiratory distress syndrome is what type of pulmonary edema
Non-cardiogenic
- Negative pressure pulmonary edema is significant negative pressure in the chest ruptures capillaries and floods the alveoli.
- Negative pressure causes a significant increase in preload, thereby increasing pulmonary blood volume. There is also a significant increase in left ventricular afterload, which causes a decreased cardiac output. The increase in pulmonary blood volume along with a decrease in cardiac output will increase the pulmonary transudative pressures. With all this occurring, pulmonary vascular resistance increases causing a shift of the intraventricular septum. The ventricular septal shift to the left causes a left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, which further increases pulmonary hydrostatic pressures.
- Neurogenic causes such as seizures, head trauma, strangulation, electrocution.
Define Orthopnea
Hard is breath when lying down
When these symptoms happens over time it is called what?
Tiredness
weight gain
swollen feet
wheezing
Chronic pulmonary edema
Name some medication that can help prevent high altitude pulmonary edema
Dexamethasone and Sildenafil is used as a preventive treatment for altitude-induced
These will control your pulse, reduce high blood pressure, and relieve pressure in arteries and veins
Heart medications
The initial management of pulmonary edema, irrespective of the type or cause, is supporting vital functions
True
Name some risk factors that may cause pulmonary edema
People with heart problems or heart failure.
Other factors that may put a person at risk include:
- history of pulmonary edema
- history of lung disease, such as tuberculosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD)
- vascular, or blood disorders
rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs.
Symptoms include shortness of breath, rapid breathing, and bluish skin coloration.
Wikipedia
Define
Coughing up blood
What are some symptoms of congestive heart failure
What are loop diuretics
Loop diuretics such as furosemide or bumetanide are administered, often together with morphine or diamorphine to reduce respiratory distress

 is
is
the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs.
mechanical means is used to assist or replace spontaneous breathing.
What is tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation.
if the level of consciousness is decreased it may be required to proceed to tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation to prevent airway compromise.
Short term pulmonary edema resolves within days to months
False
Within days to weeks
Blood clot from one part of the body that travels to the lung
What is pulmonary embolism
List some other types of pulmonary edema
List 3
Injury
Inhalation of hot or toxic gases
Pulmonary contusion, i.e., high-energy trauma (e.g. vehicle accidents)
Aspiration, e.g., gastric fluid
Reexpansion, i.e. post large volume thoracocentesis, resolution of pneumothorax, post decortication, removal of endobronchial obstruction, effectively a form of negative pressure pulmonary oedema.
Reperfusion injury, i.e. postpulmonary thromboendartectomy or lung transplantation
Swimming induced pulmonary edema also known as immersion pulmonary edema
Transfusion Associated Circulatory Overload (TACO) occurs when multiple blood transfusions or blood-products (plasma, platelets, etc.) are transfused over a short period of time.[11]
Transfusion associated Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) is a specific type of blood-product transfusion injury that occurs when the donors plasma contained antibodies against the donor, such as anti-HLA or anti-neutrophil antibodies.[12]
Severe infection or inflammation which may be local or systemic. This is the classical form of ALI-ARDS.