-typically occurs in children <5yrs, gradual onset and preceding upper airway sxs
-non-toxic appearing
-may have associated with rash
what is viral pneumonia?
CXR findings: bilateral, multifocal, patchy or ground-glass opacities are commonly found in this type of pneumonia.
What is viral pneumonia?
this influenza antiviral medication is used to treat exposed patient deemed high risk, however it has been associated with wheezing & been connected to severe bronchospasm with subsequent death in pt's with underlying lung disease.
What is Zanamirvir (Relenza)?

increased mortality rates 5,000 - 50,000.
greatest risk: very young - very old & chronic medical conditions (ex. COPD, CHF, CKD, immunocompromised)
complications include
(PNA, worsening chronic respiratory disease, myocarditis, meningitis, bacterial superinfection)
What is influenza?

-infectious disease of America recommends treating...
-age < 5yo (esp age <2yo), age > 65yo
-pregnant woman up to 2 weeks postpartum
-nursing homes & LTACs
-chronic lung conditions (ex. asthma, COPD, CAD, CHF, DM, CKD, extreme obesity - BMI >40, chronic liver disease & immunocompromised)
Most common cause of viral pneumonia in age <5 years old.
What is Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)?

clinical features frequently have an indolent course w/ weeks of cough, fever, chest pain, hemoptysis, weight loss and night sweats
What is a lung abscess?

this infection can cause opacification of dependent lung segments.
What is aspiration pneumonia?
most often RLL or recumbent posterior
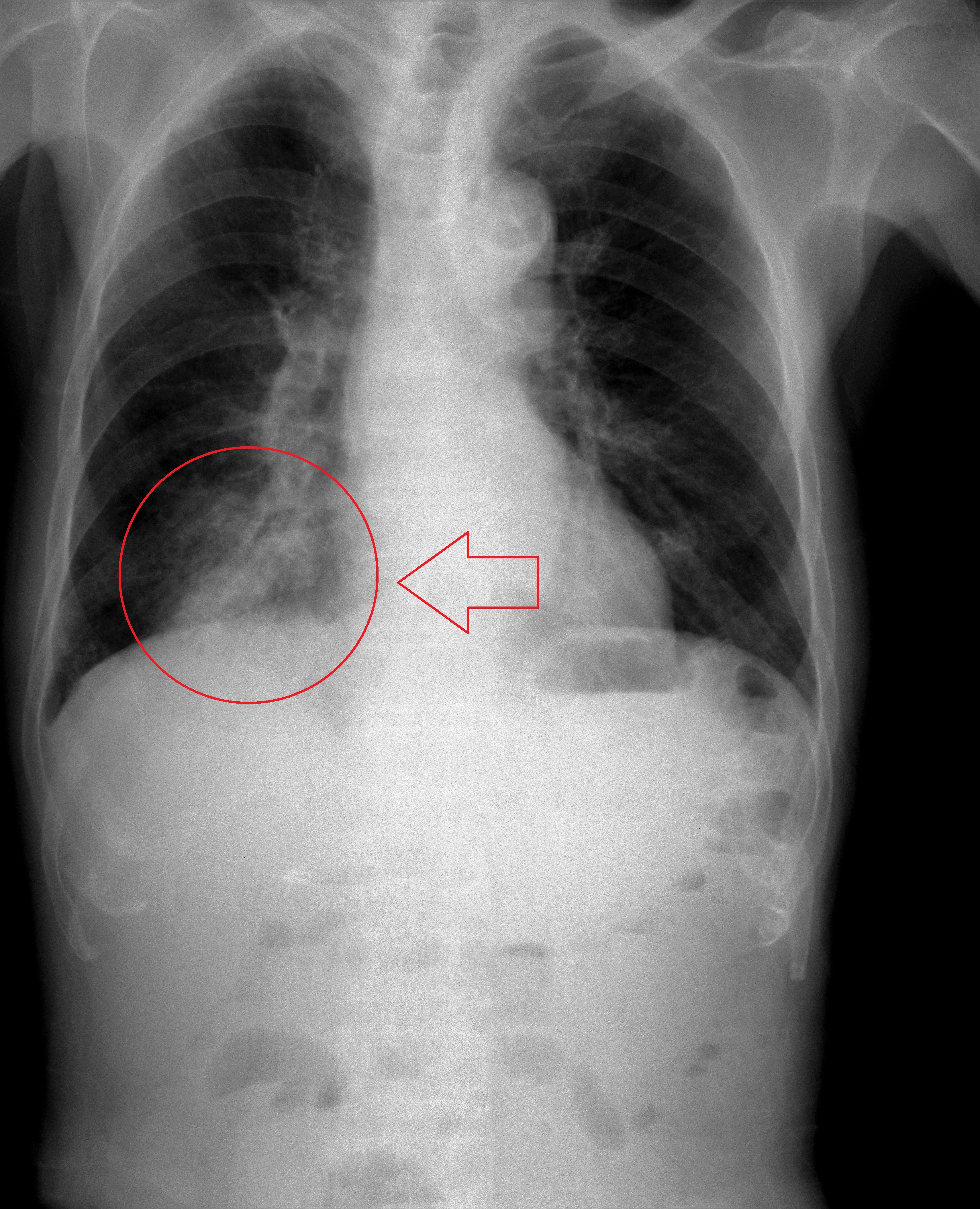
children with abrupt onset of fevers while recovering from a viral infection is presumed to have this.
What is bacterial pneumonia?

this should be suspected when pneumonia do not resolve despite appropriate therapy.
What is empyema?

this type of pneumonia is often associated with impaired consciousness, dysphagia or esophageal disease.
What is aspiration pneumonia?

this type of pneumonia has been associated with the development of adult-onset asthma?
What is Chlamydia pneumonia?

diagnostic of this type of pneumonia is typically clinically although CXR can note patchy infiltrates with occasional hilar adenopathy & pleural effusions.
What is Legionella pneumoniae?

this type of pneumonia typically is described on CXR as having bilateral interstitial infiltrates with "bat wing" appearance.
What is Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia (PJP)?

pt with arterial partial pressure of oxygen <70mm Hg or an alveolar-arterial gradient >35mm Hg should also be treated with this?
What is corticosteroids?

this type of pneumonia occurs in children born to women colonized/infected by this STD? it typically presents between 4-12 weeks of age with an insidious cough, and tachypnea but no fever.
What is Chlamydia Trachomatis?

this type of pneumonia is highly contagious compared to CAP. CT findings typically display a different pattern differentiation - Ground-glass opacities peripherally, posteriorly and multi-lobular distribution vs central or peri-bronchovascular GGO and pure consolidation.
What is Covid-19?
this type of infection typically produces a peripheral multifocal infiltrates, ground-glass and reticular opacities. in severe cases, there maybe diffuse bilateral infiltrates consistent with ARDS.
What is Covid-19?

treatment of covid-19 with this medication was noted to have a faster wean off of supplemental oxygen, a faster improvement of infiltrates on CXR and possibly reduce mortality.
What is corticosteroids?
complications from this type of infection can include..
-ARDS, dysrhythmias, acute cardiac injury, shock, PE, acute stroke
What is Covid-19?

Adults 18+yo with prespecified risk factors for progression to severe disease or 60yo+ regardless of prespecified chronic medical conditions noted significant decrease in hospitalization or death after receiving this medication when diagnosed with covid-19.
What is Paxlovid?
(EPIC-HR clinical trial)
Paxlovid significantly reduced the proportion of people with COVID-19 related hospitalization or death from any cause through 28 days of follow-up by 86% compared to placebo among patients treated within five days of symptom onset and who did not receive COVID-19 therapeutic monoclonal antibody treatment.
symptoms for this infection typically involve cough, hemoptysis, fever, weight loss and night sweats.
What is Tuberculosis (TB)?

black eschar that begins as a papule or vesicle is a characteristic clinical finding.
What is anthrax?

when ingested in large amounts, this medication can result in intractable seizures that may not resolve with traditional BZD.
What is isoniazid (INH) toxicity?

in immunocompromised patients, rapidly progressive reactived or fulminant disease may arise with fever, malaise, pleuritic chest pain & cough.
CXR often demonstrates infiltrate in the upper lobes with hilar or mediastinal adenopathy, sometimes with cavitation.
What is TB?

this is the world's 2nd leading cause of infectious death, with more than 8 million people acquiring this annually.
What is tuberculosis (TB)?