Spirometry finding required for COPD diagnosis per GOLD guidelines
Post bronchodilator FEV1/FVC <70% (or 0.70)
Preferred method to establish a diagnosis of exercise-induced bronchospasm
Exercise challenge test
Protein that protects the lower airways from damage by elastase
Alpha-1 antitrypsin
Liver disorder associated with platypnea and orthodeoxia
Hepatopulmonary syndrome
Another name for Pickwickian syndrome
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
Preferred study for evaluation of lung nodule
CT chest WITHOUT contrast
Effect of early intra-pulmonary hemorrhage on diffusing capacity measurement
Increased diffusing capacity (DLCO)
Other than poor quality study, indication for repeat spirometry in COPD patient
Change in symptoms
Condition associated with ECG J waves (Osborne waves)
Hypothermia
The most common interstitial lung disease
IPF/ UIP
Diagnosis suggested by TLC <80% of predicted
Restrictive lung disease
Diagnosis suggested by asthma, sinusitis, nasal polyp
Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD)
Spirometry measure of the air remaining in the lungs at the end of passive expiration
Functional residual capacity (accept FRC)
Most common acid-base disorder associated with malignant hyperthermia
Respiratory acidosis
Preferred outpatient empiric antibiotic therapy for community-acquired pneumonia in low-risk patients per current ATS guidelines
Monotherapy with doxycycline or amoxicillin
This substance in blood can decrease the accuracy of pulse oximetry
Carboxyhemoglobin (CO poisoning). Also accept methemoglobin (caused by nitrates) and methylene blue
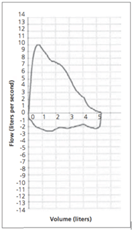
Difficulty getting air "in", chronic cough, voice changes
Vocal cord dysfunction – (flattening of the inspiratory/bottom flow volume loop)
Drug class for an oral enzyme inhibitor used in severe COPD to prevent exacerbations
Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) inhibitor (accept roflumilast)
Symptoms following ICU care, grouped according to the area that they affect (physical impairment, mental health, and cognitive impairments
Post–intensive care syndrome
Diseases categorized under PHTN (pulmonary hypertension) group 2
Left-side heart diseases
This POCUS finding excludes pneumothorax when seen on lung ultrasound
Sliding lung sign (movement of the visceral pleura against the parietal pleura)
Humanized interleukin-5 antagonist monoclonal antibody FDA approved for severe asthma
Mepolizumab, reslizumab, or benralizumab (accept any)
COPD patients with this sea-level oxygen saturation threshold are candidates for in-flight supplemental oxygen
Oxygen saturation less than 92% (accept 92%)
In a patient with refractory septic shock requiring high-dose vasopressors, this syndrome, caused by relative adrenal insufficiency, is diagnosed by a low random serum cortisol level or a suboptimal response to a cosyntropin stimulation test
Critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency (CIRCI)
Clinical triad associated with Churg-Strauss syndrome
Asthma, hypereosinophilia, necrotizing vasculitis