What is a galaxy or the universe?
What emits light as they convert hydrogen into helium using nuclear fusion?
Stars
What are the 6 main layers of the Sun?
Inner Layers C__, R__, C__
Outer Layers P__, C__, C__
The Sun has six main layers: the core, radiative zone, and convection zone (internal layers), and the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona (atmospheric layers).
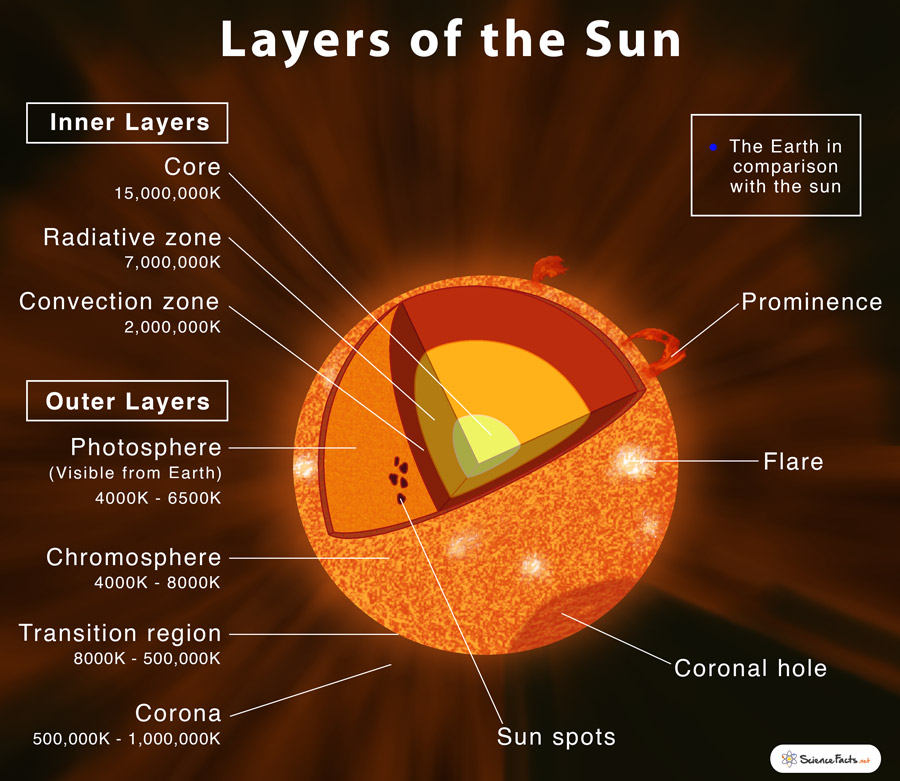
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Layers-of-the-Sun.jpg
What causes the seasons on Earth?
The tilt of Earth's axis (23.5°) and its revolution around the Sun cause seasons (different parts of Earth receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year, leading to seasonal changes).
Which type of radiation from the Sun has the greatest potential to harm human skin?
A) radio B) infrared C) ultraviolet D) visible light
C) ultraviolet
This object is smaller than a star, spherical in shape, and orbits a planet.
What is a moon?
These are 4 characteristics are used to classify stars.
What are color, temperature, size, composition, brightness?
Identify the feature of the Sun labeled "H" in the image below.
Solar Prominence
What phase of the moon would be seen from Earth in the diagram?
Full Moon or Lunar Eclipse.
Which wave has a HIGHER frequency?
Wave N
This is a major difference between comets and asteroids.
(Answers will vary. Accept all reasonable/accurate answers related to composition, size, appearance, and/or motion.)
This is how absolute brightness/magnitude is different from apparent brightness/magnitude.
Apparent brightness/magnitude is how bright a star APPEARS from Earth; Absolute brightness/magnitude is how bright a star actually is, regardless of distance.
Identify the feature of the Sun labeled "E" in the image below.
Convection Zone
What type of tide would be created by the Earth-Moon-Sun arrangement shown in the image?
Spring Tide
What happens to a wave's frequency when its wavelength decreases? Use evidence from the diagram to support your answer.
Frequency INCREASES as Wavelength DECREASES.
They are inversely proportional (i.e. if one goes up, the other goes down).
Place the following objects in order of decreasing size: solar system, planet, galaxy, star
Galaxy > solar system > star > planet
2 students were looking up at the night sky. One of them says that the brightest stars in the night sky are the closest stars to Earth. Is this student correct? Why or why not?
No. Apparent brightness does not take distance into account... What factors affect a star's brightness?
Describe how the Sun’s core uses nuclear fusion to generate energy.
The Sun's core uses nuclear fusion to combine 2 atoms of hydrogen (H) into 1 atom of helium (He), a process that releases immense amounts of energy in the forms of heat and electromagnetic radiation.
What season would the northern hemisphere of Earth experience at position A in this diagram?
Summer
Which electromagnetic radiation wave shown below would you expect to carry the most energy?
A)

B)
This is a major difference between a constellation and a galaxy.
Answers will vary. Accept all reasonable/accurate answers related to size, appearance, organization, composition, and/or distance from Earth.
What info about stars cannot be determined from the H-R Diagram shown below?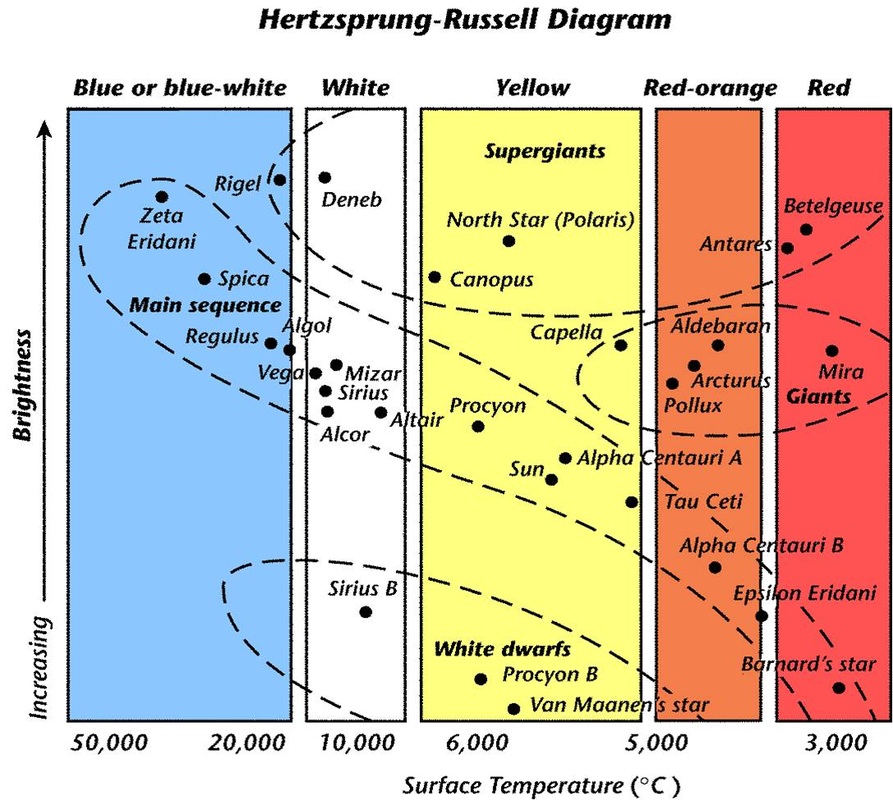
Answers will vary. Accept all reasonable/accurate answers such as distance from Earth and exact composition.
Predict how a change in activity (increased or decreased) for the Sun’s convection zone, sunspots or flares might impact space weather and Earth’s climate.
If the convection zone’s activity changed, it could alter the Sun’s magnetic field, affecting the solar cycle. More sunspots and flares could increase space weather effects, impacting satellites and power grids. Reduced solar activity might also contribute to cooler temperatures on Earth.
Write 1 equation that models the relationship between distance versus gravity AND for mass versus gravity. (ex. More/Less ____ = More/Less gravity)
More mass = More gravity
More distance = Less gravity
Explain how the electromagnetic spectrum is used to study stars.
Answers should be related to... taking pictures of deep space with telescopes, identifying elements of stars and galaxies, calculating the rate at which other galaxies are moving either away from or toward us.





