x-intercept
The point or points where the function touches the x-axis.
The point where the function touches the y-axis.
y-intercept
A relationship in which each input has exactly one output is called:
A Function

This formula helps describe where the parabola turns around.
f(x)=a(x-h)^2+k
A) Standard Form
B) Vertex Form
C) Factored Form
D) Quadratic Formula
f(x)=a(x-h)^2+k
B) Vertex Form
Roots of a quadratic are another name for what?
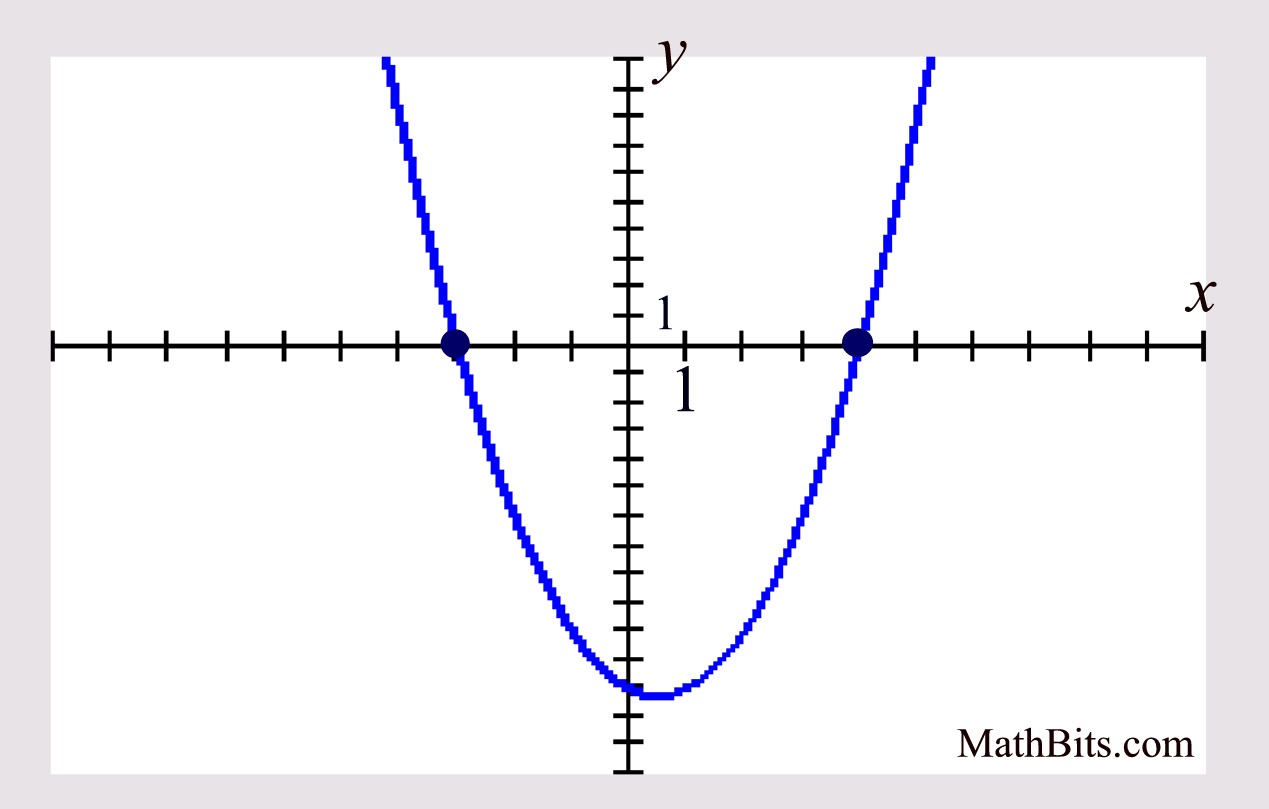
Roots are also known as x-intercepts.
Parabola
The u-shaped curve that's created by plotting a quadratic function on a graph.
A function that squares the input
(x^2)
in the process of finding the output. They always create a parabola on the graph.
Quadratic Function
An unknown number, or a symbol used in the place of a number that can change:
A variable.

This formula is sometimes called General Form.
f(x)=ax^2+bx+c
A) Standard Form
B) Vertex Form
C) Factored Form
D) Quadratic Formula
f(x)=ax^2+bx+c
A) Standard Form
Zeros of a quadratic are another name for what?

Zeros are also known as x-intercepts.
Axis of Symmetry or Line of Symmetry
The vertical line which separates the graph of a function into symmetrical halves.
The turning point of a parabola or other function lines.
Vertex
A function that measures distance:
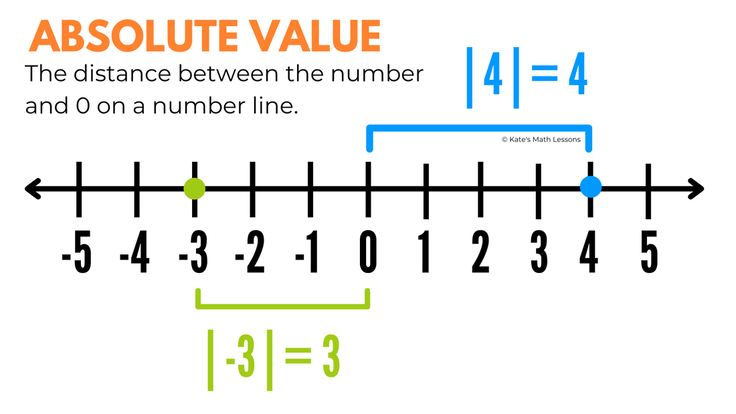
This formula is used to solve quadratic equations.
y=a(x-h)2+k
A) Standard Form
B) Vertex Form
C) Factored Form
D) Quadratic Formula
y=a(x-h)2+k
B) Vertex Form
Solutions to a quadratic are another name for what?

Solutions are also known as x-intercepts.