The name of the singlet ground state representing the lowest energy electronic state of an atom/molecule where all the electrons are paired.
What is S0?
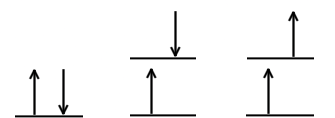
The states represented in this visual.
What is the singlet ground state, the singlet excited state, and the triplet excited state?
The process where a molecule in its ground state (S0) absorbs a photon and has an electron excited to a higher electronic state.
What is absorption?
The law found in the experiment recorded in 1852 in which one part consisted of moving a solution containing quinine through the visible spectrum resulting in nothing and the ultraviolet spectrum where the solution glowed a blue light, leading to the conclusion that the dispersed light was always of longer wavelength than the incident light?

What is Stokes law?
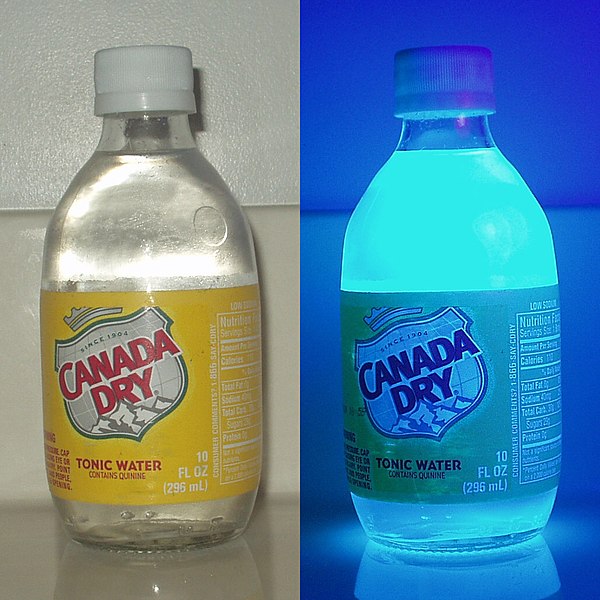

Type of luminescence depicted in this image.
What is fluorescence?
The name of the first singlet excited state where an electron becomes excited and moves to a higher energy orbital while remaining paired/anti-parallel with the other electron in the original orbital.
What is S1?
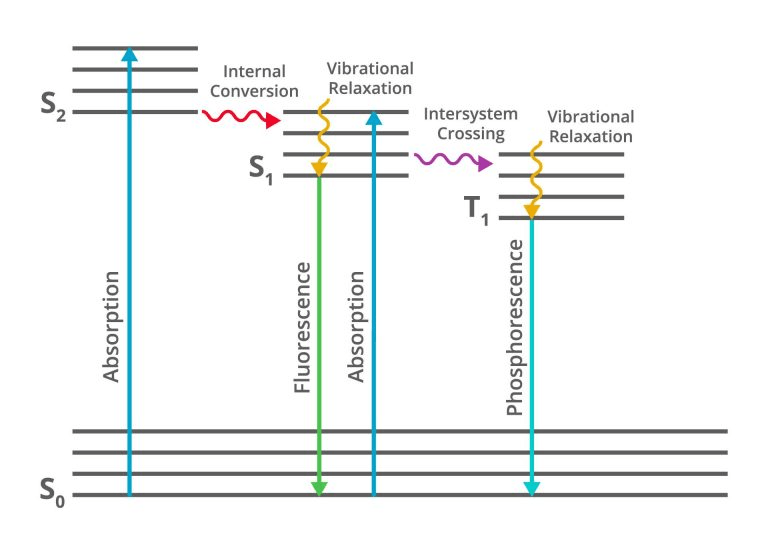
The name of this figure.
What is the Jablonski diagram?
The process where a molecule loses excess vibrational energy and moves down the vibrational levels of the electronic state until it reaches the lowest vibrational level of the electronic state.
What is vibrational relaxation?
Fluorescein, which was first synthesized in 1871 by Adolf von Baeyer through a condensation reaction between phthalic anhydride and resorciniol with a zinc chloride catalyst.
What is the first synthetic fluorescent dye?


Type of luminescence depicted in this image.
What is phosphorescence?
The name of the excited state where the spin of the electron as it is excited to a higher energy orbital is flipped so the electron in the original orbital and the electron in the higher energy orbital now have the same spin.
What is T0?
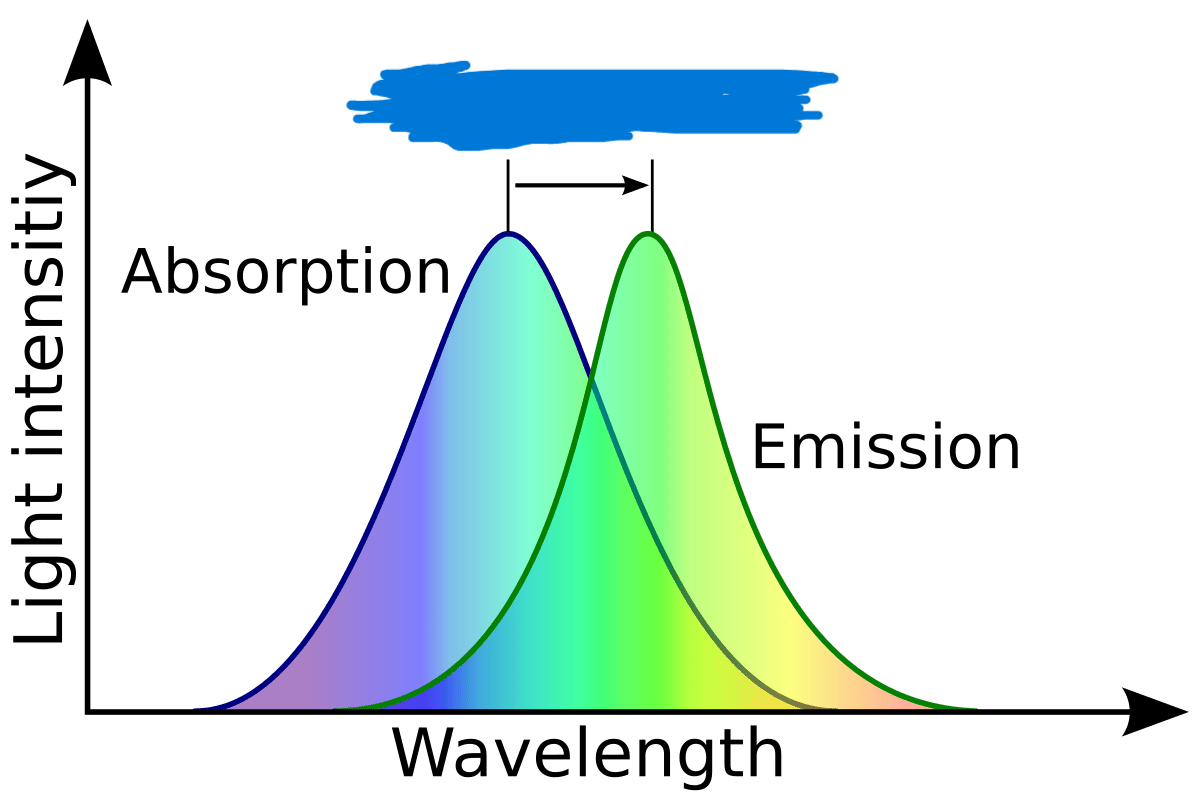
The phenomenon depicted in this graph.
What is the Stokes shift?
A non-radiative process where the vibrational energy levels of a higher electronic state overlap with the vibrational energy levels of a lower electronic state, causing the molecule to transition from the higher electronic state to the lower one, and converting electronic energy to vibrational energy during the process?
What is internal conversion?
Edmond Becquerel’s contributions to photoluminescence.
What is measuring the decay times of the phosphorescence of various compounds using his phosphoroscope built in 1858 up to lifetimes shorter than 0.1 ms?
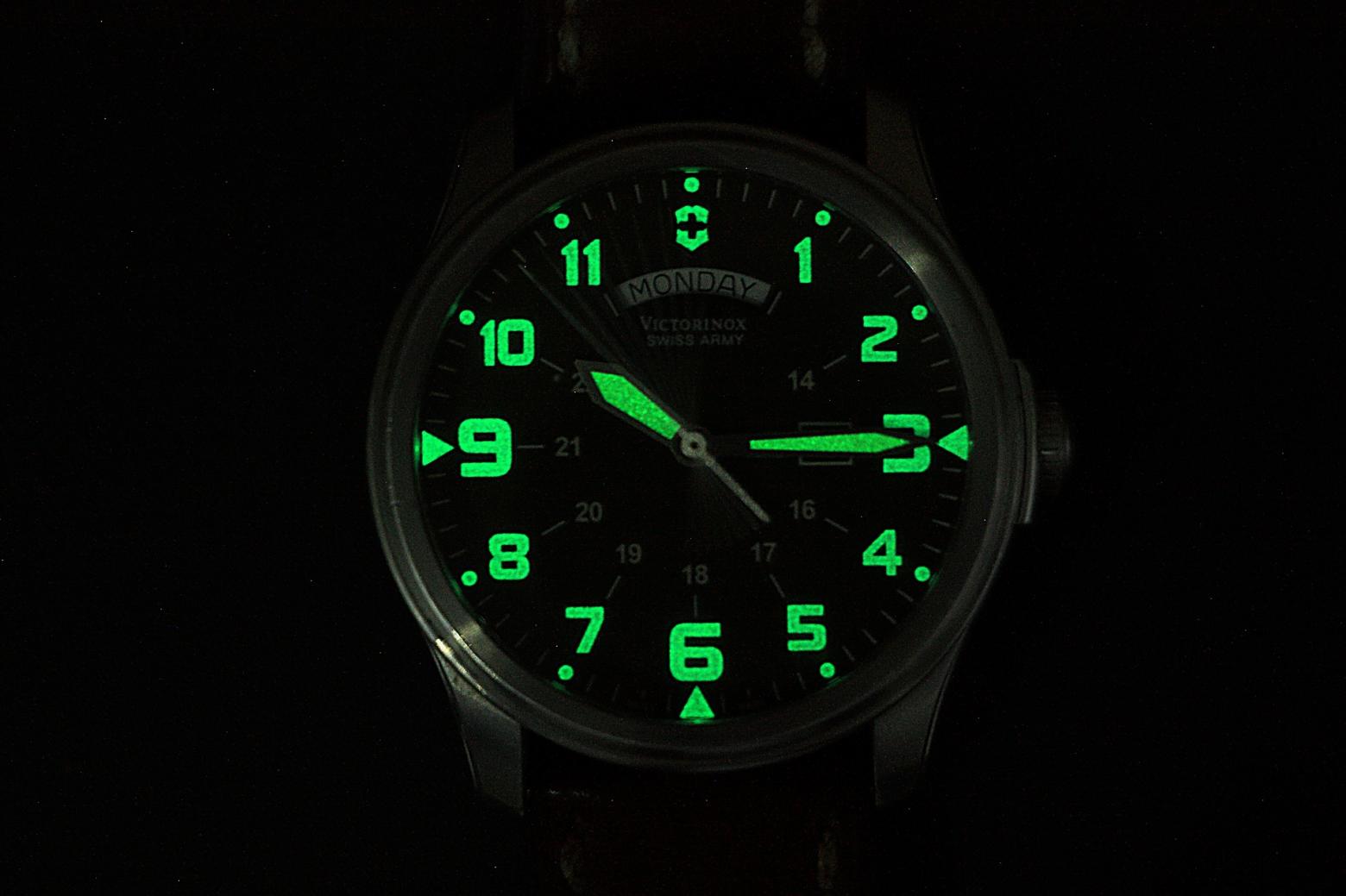


Type of luminescence depicted in this image.
What is phosphorescence?
The name of the excited state that is higher in energy than the first singlet excited state where an electron becomes excited and moves to a higher energy orbital while remaining paired/anti-parallel with the other electron in the original orbital.
What is S2?
Quencher.
What is a molecule/substance that facilitates the non-radiative pathways of a molecule going from the excited state to the ground state, and thus decreasing the intensity of light emitted during luminescence?
The non-radiative transition between (usually) the excited singlet state (S1) to the lower energy triplet state (T1) caused by spin-orbit coupling (interaction between the electron’s spin angular momentum and its orbital angular momentum)?
What is intersystem crossing?
The time when the GFP (green fluorescent protein) was first cloned.

When was 1992 where Prasher et al. cloned the gene encoding GFP, paving the way for GFPs to be used as markers for proteins?

Type of luminescence depicted in this image.
What is fluorescence?
FINAL CHEM-PARDY!
Explain fluorescence and phosphorescence including the difference between them.