What is the layer in the atmosphere that absorbs dangerous Ultraviolet (UV) - B Radiation called?
Ozone layer
Supply short term energy storage and provide structure to the cell
Carbohydrate
Changes light energy into chemical energy used by the cell through photosynthesis
Chloroplast
Identify the type of transport.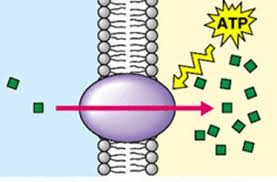
Active Transport
Water being released from the stomata in order to cool the plant down.
Transpiration
Identify and give function of structure D.

Stigma- collects pollen; STICKY!
___________ is the increase in concentration of a toxic substances in the tissue of an organism at higher trophic levels
Biomagnification
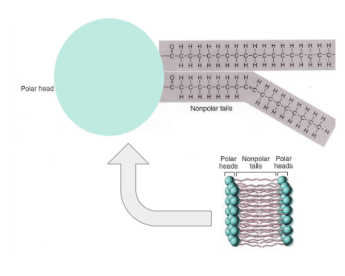
Lipid
Folds and transports proteins
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Where is the energy stored within ATP?
Phosphate bonds
Name ALL the reactants of cellular respiration.
Glucose and Oxygen
Which structure of the plant is not functioning correctly if leaves are yellowing and stem is drooping?
Roots
Name THREE non-renewable resources.
Crude Oil, Coal, Natural Gas, Nuclear energy
Monomer of proteins
Amino acid
Ribosomes make proteins. Where are ribosomes created?
Nucleolus
Name all THREE types of passive transport.
Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion, Osmosis.
All do not require energy and move from high concentration to low concentration.
Name ALL the reactants of photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight
________ transports water, _________ transports food and both are types of __________ tissue.
XYLEM transports water, PHLOEM transports food and both are types of VASCULAR tissue.
Name FOUR renewable resources.
Wind, Water, Solar, Geothermal, Biomass
________ are special kinds of proteins that are biological catalysts and ____________ reactions.
ENZYMES are special kinds of proteins that are biological catalysts and SPEED UP chemical reactions.
What are TWO DIFFERENCES between the plant and animal cell?
Plants have chloroplasts, large central vacuole and a cell wall.
Animal cells have lysosomes.
_________ uses vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing particles to the _______ of the cell
EXOCYTOSIS uses vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing particles to the OUTSIDE of the cell.
Which gas is produced by autotrophs and needed for heterotrophs?
Oxygen
What are the female and males structures of the flower that are responsible for plant reproduction.
Pistil (stigma, style, and ovary) and Stamen (anther and filament)
__________ is meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Sustainability
What elements make up Nucleic Acid macromolecules. Name ALL elements.
Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), Nitrogen (N), and Phosphorus (P)
List all THREE parts of the Cell Theory.
All living things are made of cells.
Cells are the building blocks of life.
Cells come from pre-existing cells.
Engulfing of solids is called _________ and engulfing of liquids is called ___________.
Engulfing of solids is called Phagocytosis and engulfing of liquids is called Pinocytosis.
What are ALL of the cellular processes that occur in the leaves?
Cellular Respiration, Photosynthesis and Transpiration.
Identify structures F, G, H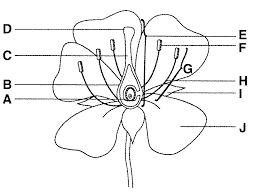
F= Anther- produces pollen
G= Stamen- male reproductive structure
H= Filament- supports the anther