It is naturally occurring.
What is a Mineral?
Alfred Wegener
Who is the person credited with developing the theory of continental drift?
A seismograph this wave first.
What is a P-Wave?
Earthquakes and volcanoes are most likely found in these locations.
Plate Boundaries
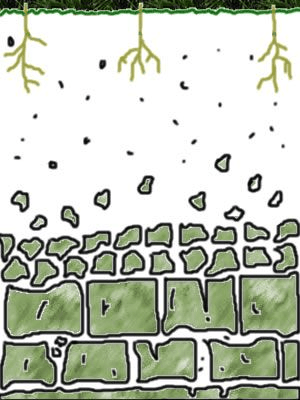 The process when rocks break into smaller pieces due to exposure to natural elements.
The process when rocks break into smaller pieces due to exposure to natural elements.
What is Weathering?
Name of rock identification strategy that examines how light reflects off of it.
What does a mineral's luster describe?
The area where two tectonic plates meet.
What is a Plate Boundary?
An instrument that measures and records details of earthquakes, such as force and duration.
What is a siesmograph?
Molten rock that has formed deep within the Earth.
What is Magma?
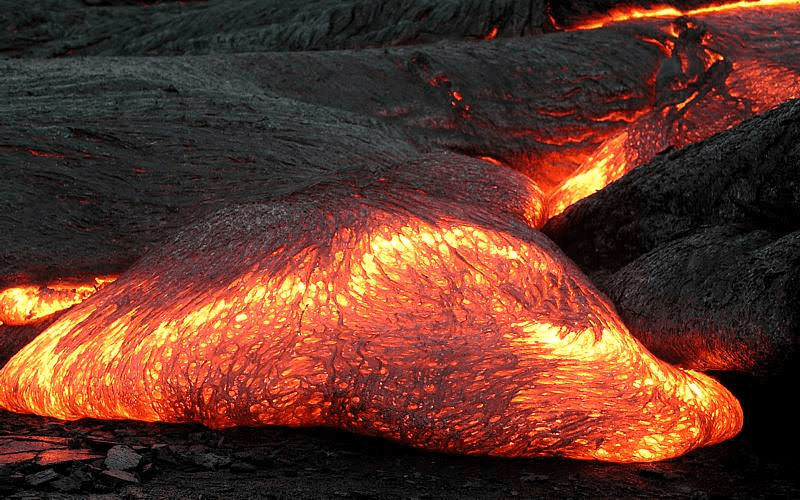

What is LAVA?
Made of minerals.
What are ROCKS?
Two tectonic plates collide at a _______ plate boundary.
What is CONVERGENT?
In order to pinpoint an earthquake's epicenter, scientists need data from at least _______ seismographic stations
What is THREE?
Where the oceanic plate slides under the continental plate.
What is a Subduction Zone?
These rocks often provide evidence of life.
What are sedimentary rocks?
Name of this type of rock and how you know. 
What is Igneous?
The land mass where all of the continents were once together in one large continent is called ________________.
What is Pangea?
Structures built on areas of wet soil are vulnerable to sinking or collapse during an earthquake. This is because the wet soils undergo _________________________ due to the shaking and vibration of an earthquake.
What is liquefaction?
One major belt of volcanoes that surrounds the Pacific Ocean
What is the Ring of Fire?
This type of rock and how you know.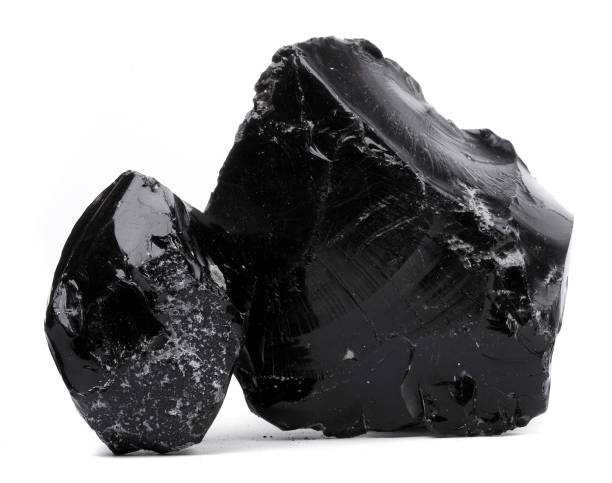 
What is Igneous? Glassy Texture.
This type of rock and how you know.

What is Sedimentary? Compacted/Cemented Layers
The land mass where all of the continents were once together in one large continent is called ________________.
What is Pangea?
The Richter scale is used to measure an earthquake's _____________________, or the amount of energy released by the earthquake.
What is MAGNITUDE?
Recent volcanic eruption in the Ring of Fire studied in class.
Type of rock and how you know. 
What is Sedimentary? Evidence of Life.
Name of this crazy creature.
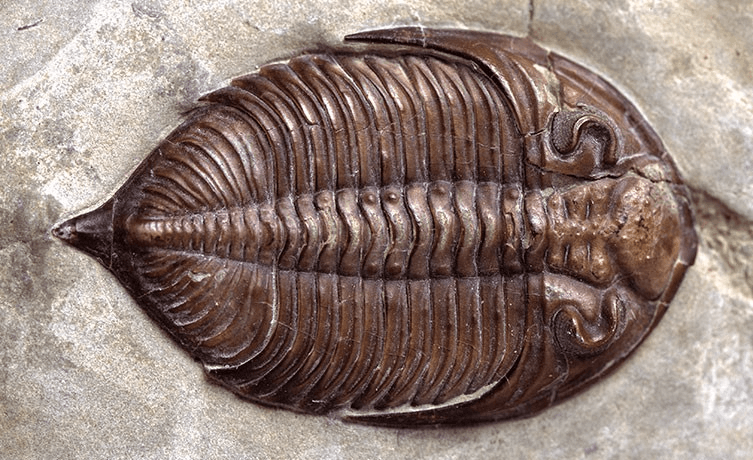

What is a Trilobite?
Three pieces of evidence that supports Alfred Wegner's hypothesis is...?
What is fossils of the same species are found on different continents.
Rocks on either side of this type of fault move past each other without much upward or downward movement.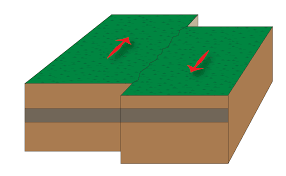
What is TRANSFORM?
Seventy-five percent of Earth’s volcanoes—more than 450 volcanoes—are located here.
What is the Ring of Fire?
Five ways scientists identify rocks.
What are Luster, Color, Hardness, Streak, Chemical Reactions, Magnetism, Other?
Type of new rock and how you know.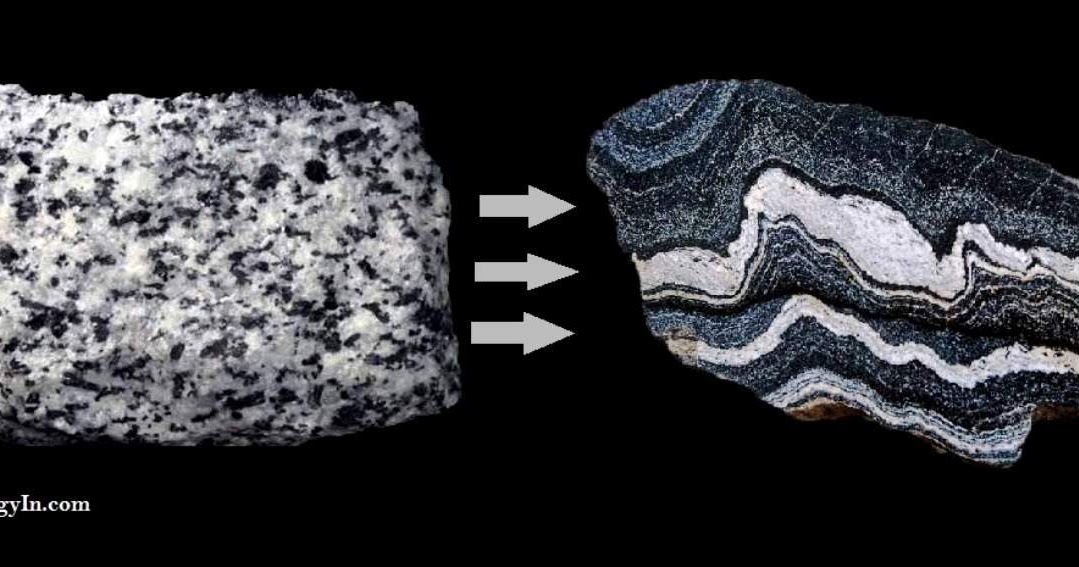 
What is Metamorphic rock? Banded Crystals.
Crust is destroyed at this type of plate boundary.
What is convergent?
Major fault from Northern CA to Baja Mexico.
What is the San Andreas?
Molten material that reaches the surface.
What is Lava?
Common MN Rock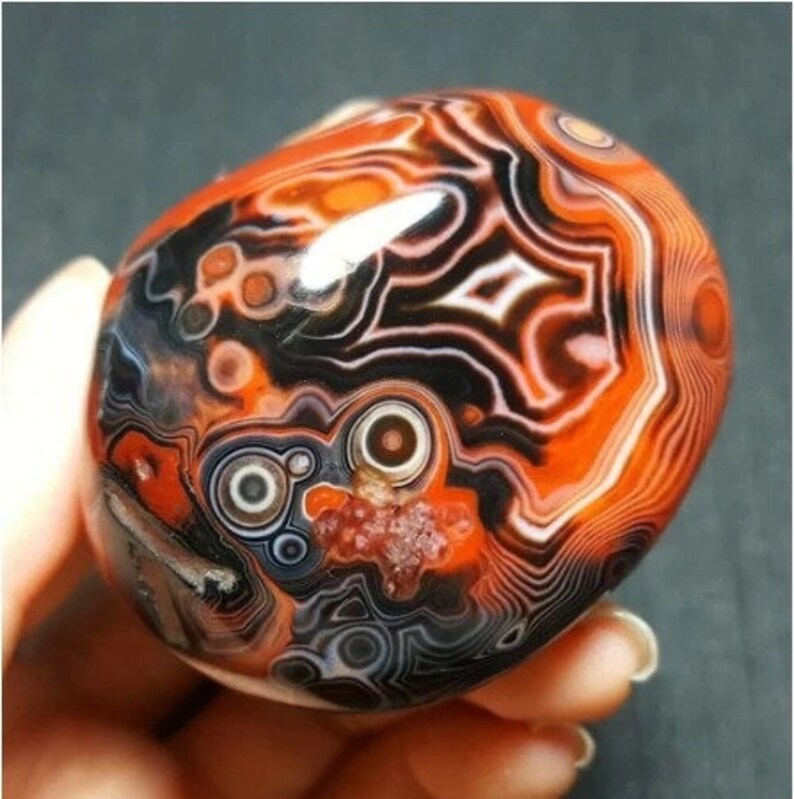
What is an Agate?
Intrusive igneous rock common to MN
What is Granite?
A plate boundary where the plates divide.
What is Divergent?
These waves cause particles of rock material to move at right angles to the direction in which the waves are traveling.
What are S-Waves?
Scientists that study volcanoes.
What are volcanologists?
Schist and quartzite are examples of metamorphic rocks. These processes are necessary for the formation of metamorphic rocks.
What are Heat and Pressure?