Describe all of the types of slopes that may be seen on the following graphs:
Position vs. Time:
Velocity vs. Time:
Acceleration vs. Time:
Position vs. Time: curved, diagonal or horizontal
Velocity vs. Time: diagonal or horizontal
Acceleration vs. Time: ONLY horizontal
A skier starting from rest skis straight down a slope 50. meters long in 5.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the skier?
WHICH EQUATION WOULD YOU USE TO SOLVE THIS?
d = vot + 1/2at2
Describe the motion in the x- and y- directions for both a horizontal and angled projectile.
Horizontal -->
x-direction: constant velocity
y-direction: free fall
Angled -->
x-direction: constant velocity
y-direction: throwing upwards
Describe the motion of an object when it is in equilibrium.
It is either at rest or moving at a constant velocity
Describe the difference between distance and displacement.
Distance is a scalar quantity that includes every step taken.
Displacement is a vector quantity that is the difference between the final position and the initial position.
What physical quantity does the slope represent on the following graphs:
position vs. time
velocity vs. time
position vs. time --> velocity
velocity vs. time --> acceleration
A skier starting from rest skis straight down a slope 50. meters long in 5.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the skier?
a = 4 m/s2
A golf ball is propelled with an initial velocity of 60. meter per second at 37º above the horizontal. Determine the horizontal and vertical components of the golf ball's initial velocity.
vox = 47.9 m/s
voy = 36.1 m/s
Write your own definition for the following forces:
Normal Force
Frictional Force
Tension Force
Normal Force- a supportive force acting on an object by the surface it's in contact with
Frictional Force- an opposing the motion of an object
Tension Force- an applied force used when there is string, rope, wire, etc. involved
Object A is 2 kg mass moving at 10 m/s. Object B is a 10 kg object moving at 2 m/s. Object C is a 7 kg mass moving at 3 m/s.
Which object has the greatest inertia?
Inertia = mass
Object B
What physical quantity does the area below the line represent on the following graphs:
velocity vs. time
acceleration vs. time
velocity vs. time --> distance or displacement
acceleration vs. time --> change in velocity
As a car is driven south in a straight line with
decreasing speed, the acceleration of the car must be
A) directed northward
B) directed southward
C) zero
D) constant, but not zero
A) directed northward
Speeding Up --> acceleration and velocity have the same sign (+a +v or -a -v)
Slowing down --> acceleration and velocity have opposite signs (+a -v or -a +v)
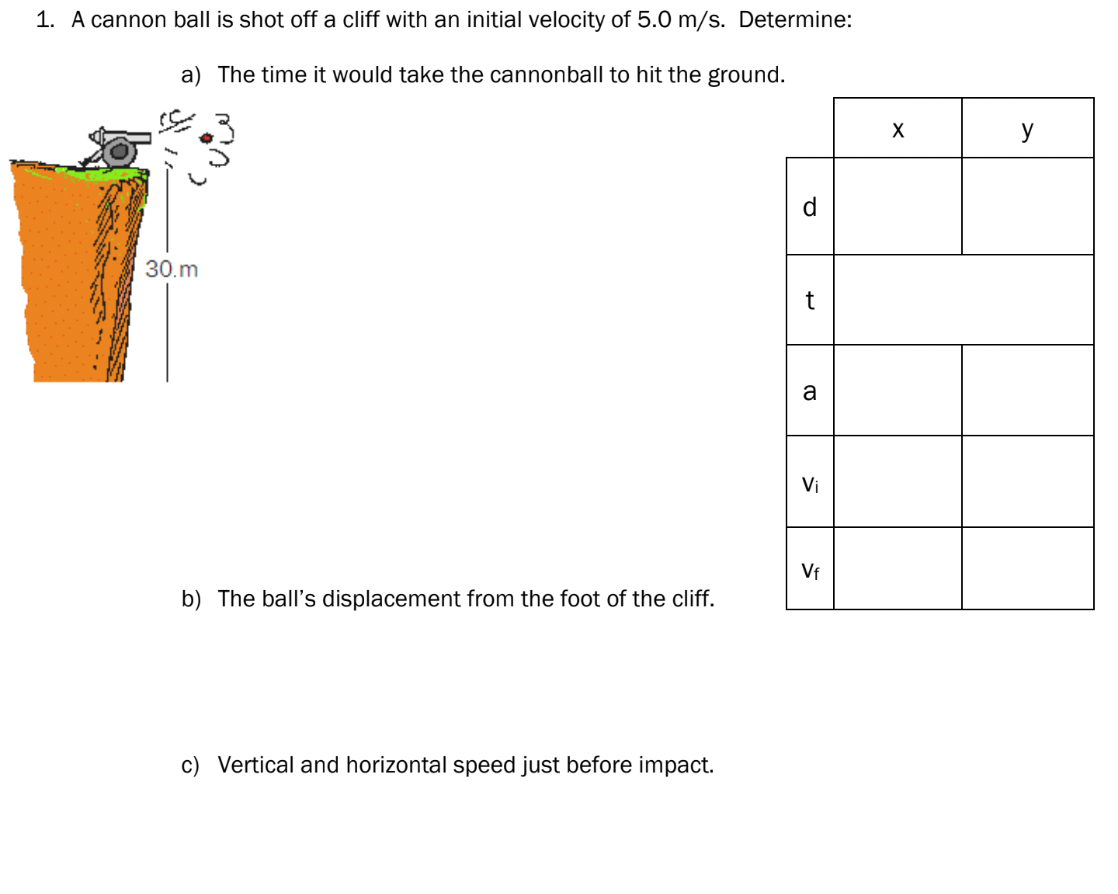
t = 2.45 s
d = 12.3 m
vfx = 5 m/s
vfy = -24.5 m/s
What force is needed to give an electron an acceleration of 1.00 x 1010 m/s2?
9.11 x 10-21 N
When an object is thrown vertically upwards, its speed ______________ as it moves upwards, and ______________ as it moves downwards.
decreases (as it moves upwards)
increases (as it moves downwards)
Draw the velocity vs. time graph for an object in free fall.
a graph with a positive, diagonal slope showing velocity starting from rest and increasing
A 3.00-kilogram mass is thrown vertically upward with an initial speed of 9.80 meters per second. What is the maximum height this object will reach? [Neglect friction.]
vf2 = vo2 +2ad
d = 4.8m
Object A is dropped from the top of a cliff. Object B is thrown horizontally from the same cliff at the same time that Object A is released. Compared to Object A, when will Object B hit the ground? Justify your answer.
They will hit the ground at the same time. Vertically, their motions are the exact same- they're traveling the same vertical distance, gravity is the acceleration for both, they both have vertical initial velocities of 0 m/s, so they will take the same amount of time to fall.
A 55-kilogram ice skater slides across a level ice surface and the force of friction acting on the skates has a magnitude of 11 newtons.
Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ice skater and the ice.
0.02
Daily Double!
The team that selected this automatically gets the points!
Draw the position vs. time graph for an object in free fall.
a graph showing a curved line slope where the slope is getting steeper
A ball is thrown horizontally at a speed of 24 meters per second from the top of a cliff. If the ball hits the ground 4.0 seconds later, approximately how high is the cliff?
d = vot + (1/2)at2
d = 78m

vox = 6.44 m/s
voy = 2.74 m/s
ttop = 0.27 s
ttotal = 0.54 s
dy = 0.38 m
dx = 3.48 m
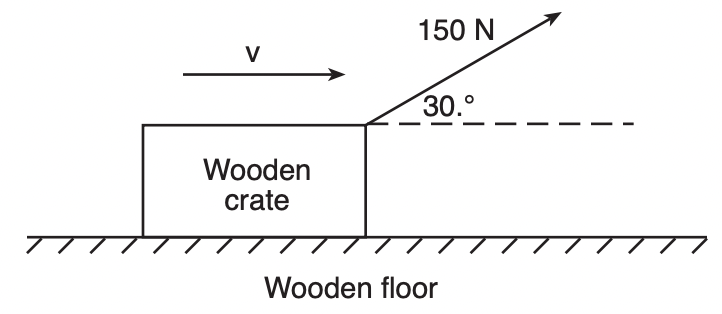 A 150-newton force, applied to a wooden crate at an angle of 30.° above the horizontal, causes
the crate to travel at constant velocity across a horizontal wooden floor, as represented above.
A 150-newton force, applied to a wooden crate at an angle of 30.° above the horizontal, causes
the crate to travel at constant velocity across a horizontal wooden floor, as represented above.
Calculate the magnitude of the force of gravity of the wooden crate.
Fg = 505 N
A 1.20 × 103 kilogram car is traveling east at 25 meters per second. The brakes are applied and the car is brought to rest in 5.00 seconds. State the direction of the acceleration of the car.
West