Recommended treatment of early localized Lyme disease in pregnancy
Amoxicillin or cefuroxime axetil (either)
Diagnosis associated with eyelid swelling, ophthalmoplegia, pain with eye movement, and proptosis
Orbital cellulitis
Primary biliary cholangitis
antimitochondrial antibodies
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis + IgA nephropathy, arthritis, GI bleed
Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP)
Most common drug reaction, usually presents with truncal rash with fever and pruritus
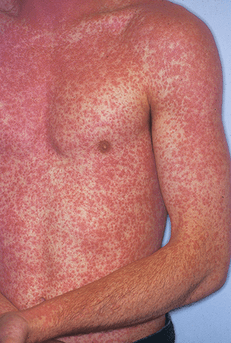
Morbilliform Rash
Most likely agent causing aphasia and weakness in patient with CD4 count < 100/µL and this MRI
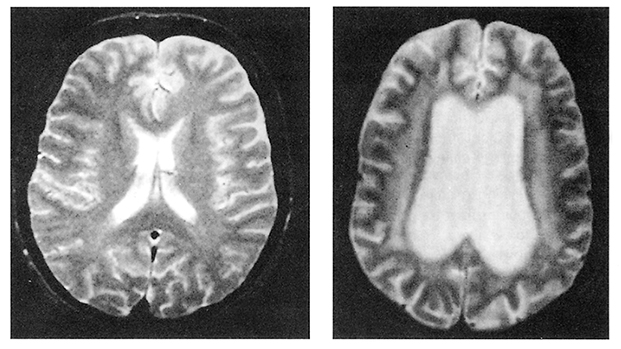
JC virus causing PML
Condition characterized by floaters, photopsias, and squiggly lines followed by a sudden peripheral visual field defect
Retinal detachment
Celiac disease
anti-tissue transglutaminase IgA
anti-endomysial IgA
Cause of elevated osmolar gap with normal acid-base
Isopropyl alcohol poisoning
Patchy skin lesions of varying pigmentation, increase in hot climates, KOH prep reveals “spaghetti and meatballs” appearance
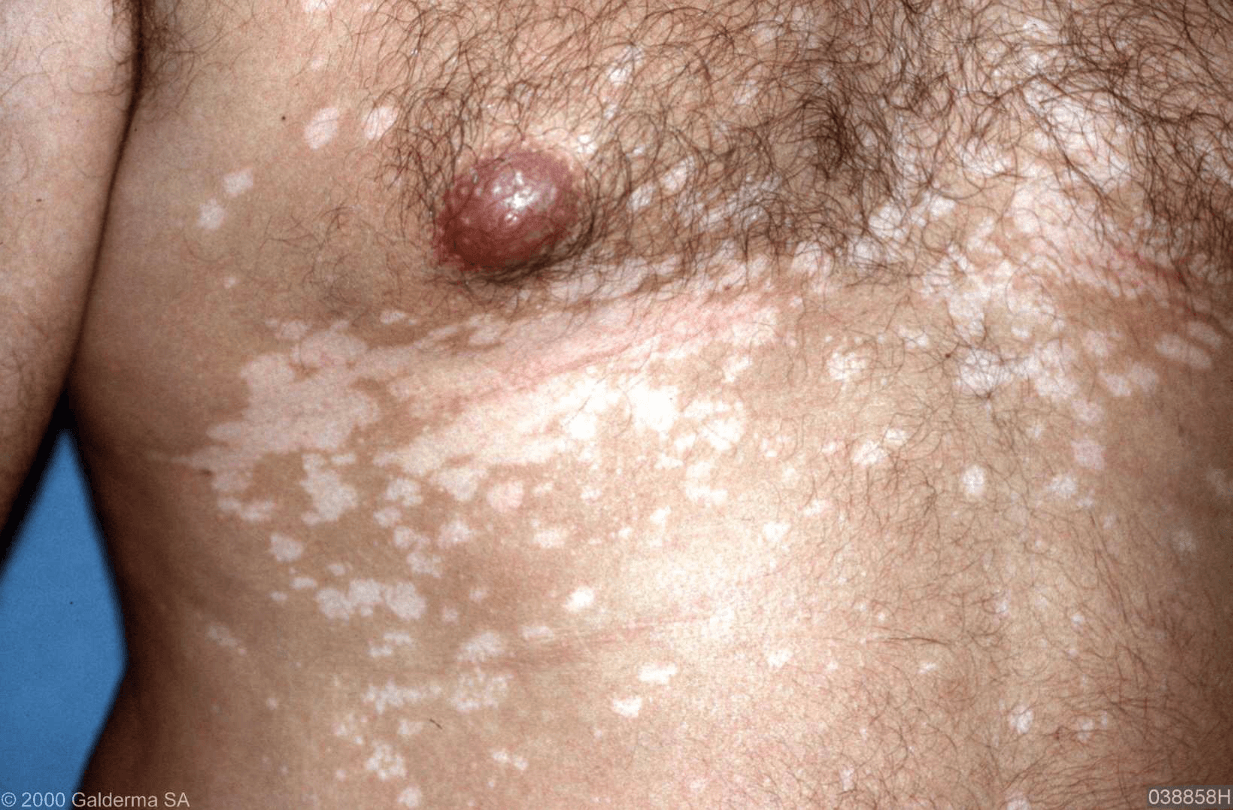
Tina Versicolor from Malassezia Furfur
Name 2 infectious conditions (zoonoses) associated with rats
Hanta virus
Lassa fever
Leptospira interrogans (leptospirosis)
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus
Spirillum minus (rat bite fever)
Streptobacillus moniliformis (rat bite fever)
Yersinia pestis (plague)
The most common cause of granulomatous uveitis
Sarcoidosis
Antisynthetase syndrome
anti-Jo 1 (histidyl-tRNA synthetase)
Cause of ATN/AKI following abdominal surgery, and diagnostic test
Abdominal compartment syndrome, diagnosed by measuring intravesicular pressure > 20mm Hg
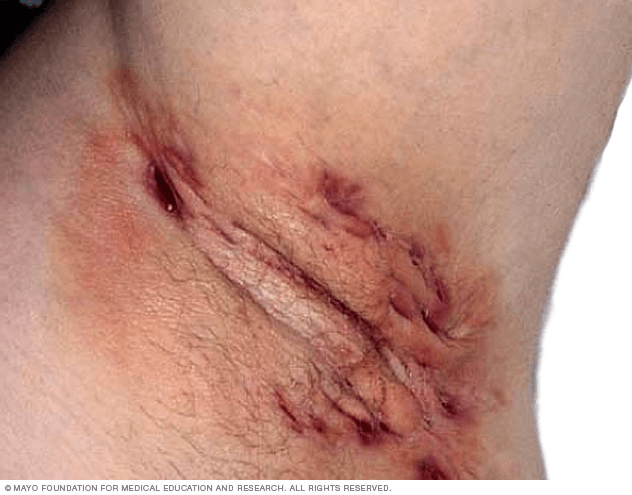
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Treatment of this organism seen in an immunocompromised patient
TMP/SMX (Nocardia)
A 52-year-old woman presented to the emergency department with a 24-hour history of severe pain and blurred vision in the left eye.
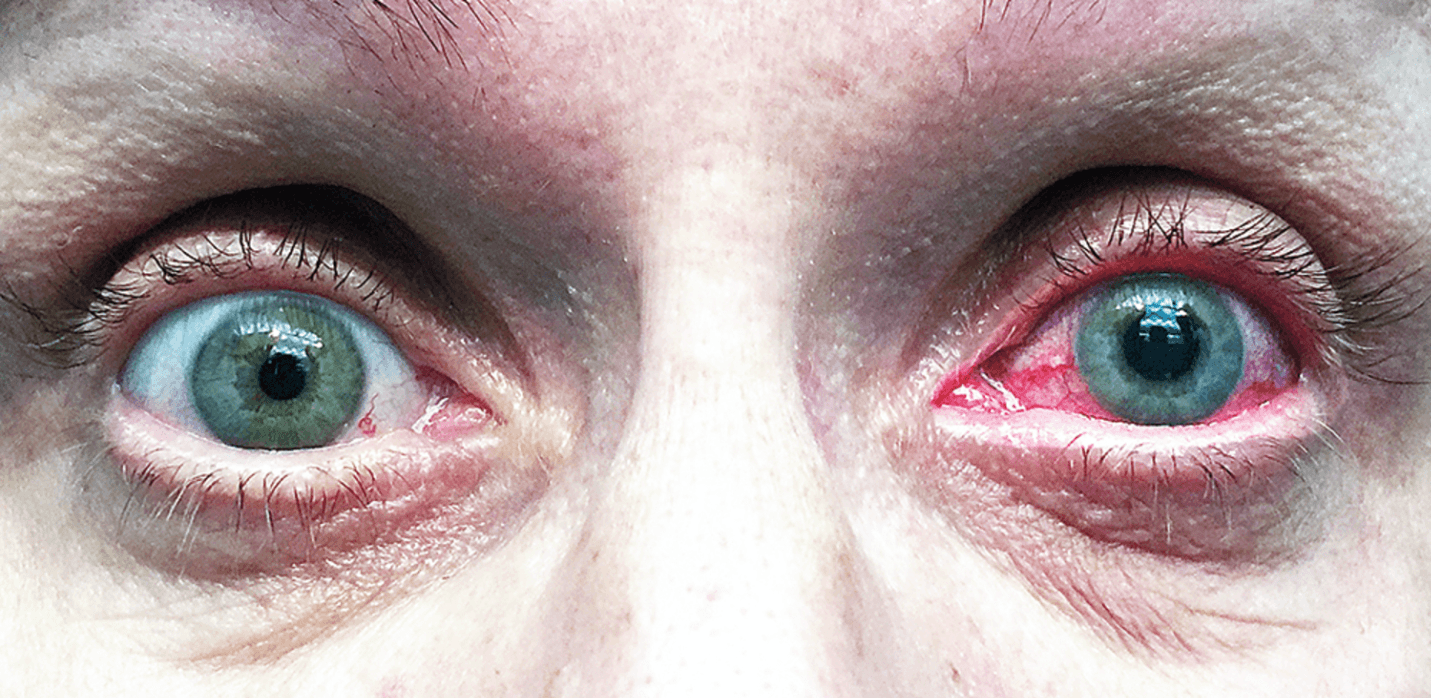
Acute angle-closure glaucoma
This is an ophthalmologic emergency characterized by a rapid increase in IOP due to impaired outflow of aqueous humor. Symptoms can be precipitated by dim light and anticholinergic and sympathomimetic medications.
Treatment - intravenous and topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, α2-adrenergic agonist, and laser iridotomy
Antibody predicting scleroderma renal crisis
anti-RNA polymerase III
Hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, NO hypertension, Decreased urinary Ca excretion
Bartter syndrome (mimics loop diuretics) --> Increased urinary Ca excretion
Liddle's syndrome --> Hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis WITH hypertension
Generalized skin erythema after stopping steroids
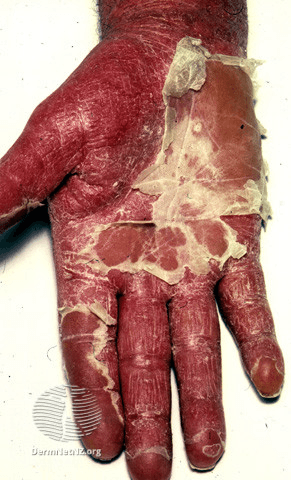
Erythrodermic psoriasis
Name the parasite
Trichuris trichiura (Whipworm)
Eggs are swallowed via soil-contaminated food or hands, hatch in intestine, and migrate to colon.
Adults reside in large intestine. They anchor themselves to colonic mucosa with one end embedded in the mucosa and the other end free within the lumen; they feed on fluids, digested tissue, and blood.
A man presented with difficulty walking and urinary incontinence. On examination, his pupils were nonreactive to bright light but constricted when focusing on a near object. What is the diagnosis?
Tabes dorsalis
Pupils that are nonreactive to bright light but briskly constrict when focusing on a near object are known as Argyll Robertson pupils, which are characteristic of tabes dorsalis.
Tabes dorsalis is a form of neurosyphilis that is characterized by degeneration of the nerves in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, which leads to ataxia and loss of proprioception, as well as this pupil finding.
CNS involvement of lupus
anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies
Name the condition with this urine crystal
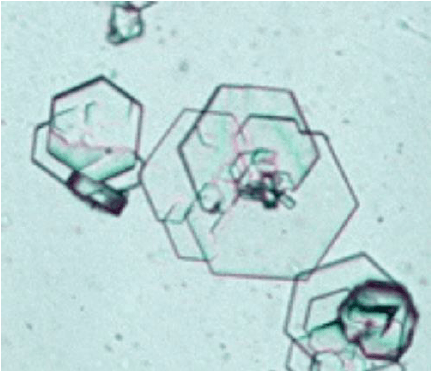
Cystinuria
Name of the rash and associated condition.
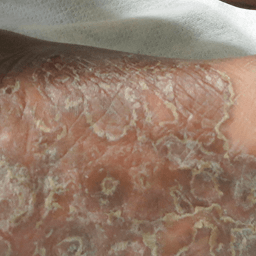
Keratoderma blenorrhagicum, seen in reactive arthritis