This force is attributed to random electron movements about an atom creating temporary dipole moments
London Dispersion Forces
This is the phase change of going from a gas to a solid
Deposition
_____ dissolves _____
Like dissolves like
Also acceptable:
polar dissolves polar
AND
nonpolar dissolves nonpolar
This is the electron and molecular geometry of Sulfur Tetrafluoride
Electron: trigonal bipyramidal
Molecular: Seesaw
A photon with a wavelength of 450 nm has this many joules of energy
h = 6.626e-34 j*s
c = 3e8 m/s
4.41e-19 Joules
E=(Planck's Constant)(Speed of Light)/(Wavelength)
Rank the forces from weakest to strongest:
Hydrogen Bonding
Ion-Dipole
London Disperson
Dipole-Dipole
London Dispersion
Dipole-Dipole
Hydrogen Bonding
Ion-Dipole
Pressure is held constant at 1. As temperature increases from 5 to 10, this phase change occurs

Sublimation
This is the bond enthalpy in 2 moles of carbon tetrachloride
2 moles * 4 (C-Cl)
2*4(328)
2*1312 kJ
2624 kJ
This is the electron geometry and molecular geometry of bromine pentafluoride
Electron: octahedral
Molecular: Square pyramidal
2C8H18 (l) + 25O2 (g) > 16CO2 (g) + 18H2O (g)
7.46 moles of C8H18 react with 8.28 moles of O2. How many moles of carbon dioxide form?
O2 is limiting, solve it to get 5.2992 moles of CO2
These are the intermolecular forces that exist in ammonia
London Dispersion
Hydrogen bonding (dipole-dipole)
If pressure is held at 3 and temperature is increased from 0 to 25, these are the 2 phase changes which will occur
Melting then vaporization
Rank the following from least to most soluble in water:
CH3(CH2)6Cl
CH3(CH2)6OH
HO(CH2)2OH
1) Least soluble 3) most soluble
1. CH3(CH2)6Cl
2. CH3(CH2)6OH
3. HO(CH2)2OH
-2, -1, 0, 1, 2
An electron has an n value of 4. These are the possible l values.
0, 1, 2, 3
Rank the following from least to greatest boiling point:
Cl2, CBr4, Ar
Ar < Cl2 < CBr4
This is the phase(s) that this substance exists in at a pressure of 2 and temperature of 10
Solid, liquid, gas
This value is the reaction enthalpy when 1 mole of propane reacts with 5 moles of oxygen gas to create 3 moles of carbon dioxide and 4 moles of water
ΔH = bonds broken (reagents) - bonds formed (products)
Reagents:
Propane: 2(C-C) + 8(C-H) = 2(348) + 8(413)
Oxygen Gas: 5(O=O) = 5(495)
Products:
Carbon Dioxide: 6(C=O) = 6(799)
Water: 8(O-H) + 8(463)
ΔH = (5x495 + 2x348 + 8x413) - (8x463 + 6x799)
ΔH = -2023 kJ
(remember charges and phase changes and balanced coefficients)
Al2(SO4)3 (aq) + 3Pb(NO3)2 (aq) -> 2Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3PbSO4 (s)
Pb2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) -> PbSO4 (s)
CNO- (arranged C-N-O where N is the central atom), has 3 resonance structures where octet rule is obeyed, although the 3 are not equally preferred. This is the number of pi bonds between the nitrogen and oxygen in the primary/preferred resonance structure
C≡N-O THIS IS PREFERRED, 0 pi bonds
C=N=O
C-N≡O
Rank the following from least to greatest vapor pressure:
Kr, CF4, H2, N2, CBr4, CBr2F2
CBr2F2 < CBr4 < CF4 < Kr < N2 < H2
Increasing temperature or pressure beyond point C creates this type of substance
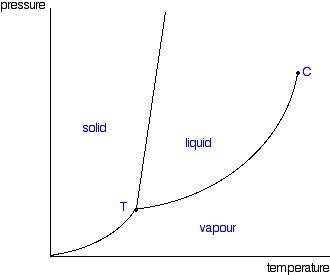
Supercritical fluid
Rank the following from least to most soluble in hexanes:
CH3(CH2)6OH
CH3(CH2)6CH3
HO(CH2)2OH
1) Most soluble 2) least soluble
1. CH3(CH2)6CH3
2. CH3(CH2)6OH
3. HO(CH2)2OH
Ammonia and oxygen gas react to form nitrogen monoxide and water. 1.01 g of ammonia and 1.72 g of oxygen gas react together. This is how many grams of water form from the reaction.
1.16 grams
(see slideshow for answer key)
This is the energy output of a light source that emits photons at a rate of 819 photons per second with wavelengths of 158 nm. (note units)
h = 6.626e-34 j*s
c = 3e8 m/s
Ephoton = hc/λ
Ephoton = (6.626e-34)(3e8)/(158e-9)
Ephoton = 1.2581e-18 J/photon
Output:
1.2581e-18 J/photon x 819 photons/sec =
1.03e-15 J/s