The transfer of thermal energy from a warmer to cooler object
If you have the Impulse and Force what can you find?
The transfer of heat through empty space by electromagnetic waves.
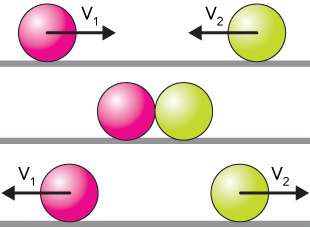
Two dodge balls are rolling toward each other and bounce off, is momentum conserved?
The type of heat transfer that occurs when you burn your hand when you touch the metal end of a curling iron.
The average heat or thermal energy of the particles in a substance.
If you decrease the velocity does the momentum increase or decrease?
The transfer of heat by direct contact between particles.
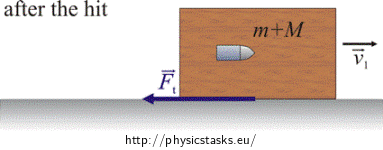
When fighting fires, a firefighter must use great caution to hold a hose that emits large amounts of water at high speeds. Why would such a task be difficult?
The hose is pushing lots of water (large mass) forward at a high speed. This means the water has a large forward momentum. In turn, the hose must have an equally large backwards momentum, making it difficult for the firefighters to manage.
Is Momentum and Impulse a scalor or a vector?
Heat always moves from _________ to __________.
warmer; cooler
If you increase the momentum does the mass or velocity increase?
Trick Question. It could be either.
T or F: The temperature of a substance depends on how much of the substance you have.
If the change in momentum is 10Ns, then what is the Impulse?
Faster moving particles will have _______ kinetic energy and therefore a _______ temperature than slower moving particles.
more; higher
A .25kg marble is rolling on the floor at 2m/s, what is the momentum?
0.5 Ns or 0.5 kg*m/s.
In which phases of matter do the particles have kinetic energy?

What do you have when you divide the Impulse by the Time?
Force.
3 scales for measuring temperature.
What is Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin?
If you have force, time, and mass what can you find?
Explain how convection works.
Fluids close to the heat source warm up, the particles spread out, becoming less dense, fluid rises; cooler fluid is less dense so it sinks.
The total momentum of all the objects in a system before a collision is equal to the total momentum all the objects in a system after the collision.
What are insulators used for?
To prevent or slow down the transfer of thermal energy.