This radiograph has rotation.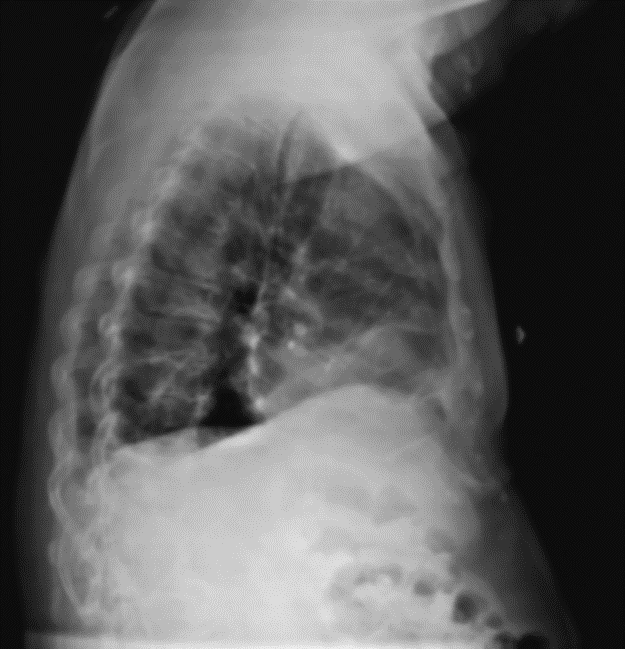
What is: True
What does K.U.B. stand for?
What is: Kidneys, Ureters, Bladder
What is the correct way to view a forearm on a monitor?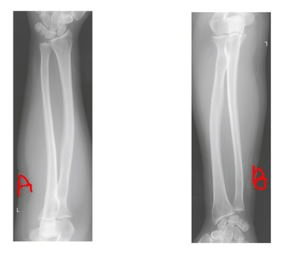
What is: A
How much kVp would you use most likely for a shoulder?
What is: 75
Requires a patient rotation of 45-60, medial & lateral borders of scapula are superimposed
What is: Y view
This image was taken on a typical patient.
The primary marker was used on the wrong side in this radiograph.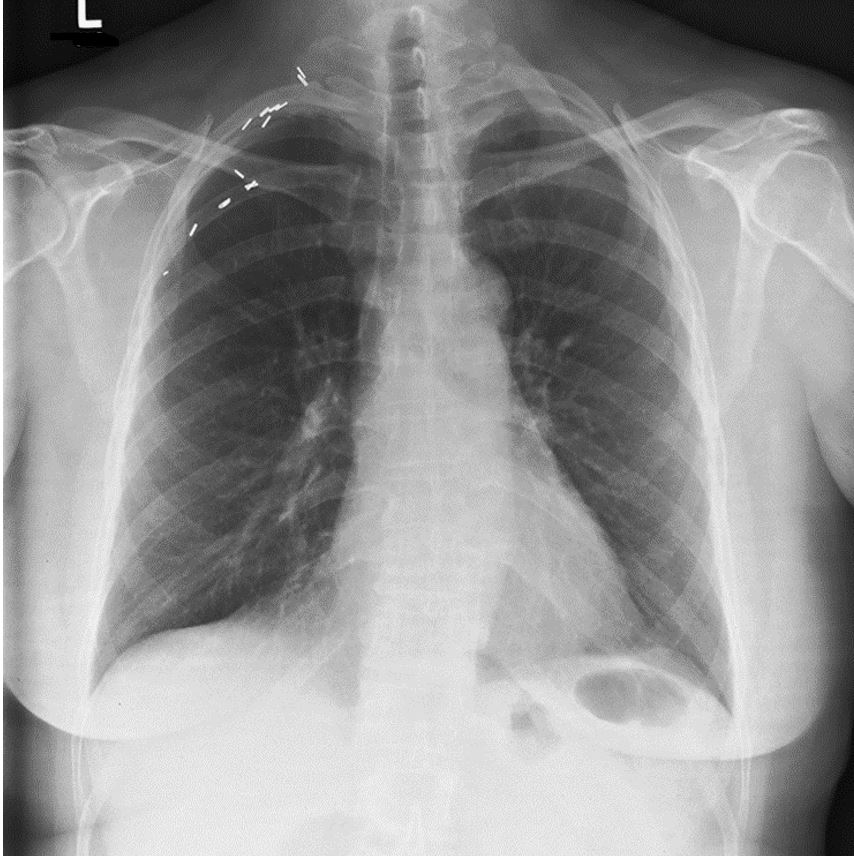
What is: True
Why is the right kidney usually lower in the abdomen than the left kidney?
What is: The presence of the liver
What positioning consideration is crucial when imaging a lateral forearm or lateral elbow?
-The elbow and shoulder should be in the same plane
-The elbow is bent at a 90 degree angle
-The epicondyles are perpendicular to the IR
-All of these are correct
What is: All of these are correct
You have an asthenic patent for a clavicle exam. How many degrees would angle the tube for the axial projection?
Which view best visualizes glenoid cavity with patient in a posterior oblique position with 45° rotation toward IR
What is: Grashey (AP Oblique projection)
Why is the routine for a lateral CXR performed with the left side up against the IR versus the right?
What is: The heart will be magnified/larger if performed as a right lateral.
In which of the four major quadrants of the abdomen would the appendix be found?
What is: Right lower quadrant
What special wrist projection would best demonstrate the posterior (or dorsal) aspect of the carpal bones?
What is: Carpal Bridge (Tangential projection)
Why is the arm abducted for an AP Scapula projection?
What is: to move the scapula away from thoracic structures
Best visualizes bicipital/intertubercular groove?
What is: Fisk (Tangential projection)
What is a reason to why a CXR should be taken erect?
-The diaphragm can move further down
-Prevent engorgement of vessels
-Visualize air and fluid levels
-All of the answers are correct
What is: All of the answers are correct
What vertebral level is the iliac crest?
What is: L4
What position is the hand when the radial tuberosity (tubercle) is seen posteriorly, adjacent to the ulna?
What is: Thumb up/hand with maximal external rotation
In a lateral Scapula projection, what structure of the scapula is best demonstrated when the affected arm is reaching across the chest?
What is: Body
The patient is supine with affected arm abducted 90 degrees and externally rotated with CR directed at axilla
What is: Lawrence (inferiorsuperior axial projection)
Which of the following is a clinical indication of a CXR?
Intussusception
Kidney stones
Fibroids
Pneumothorax
What is: Pneumothorax
What region is the bladder located?
What is: hypogastric
What is the name of the two small depressions found on the anterior aspect of the distal humerus?
What is: Radial and coronoid fossa
Which term describes the medial end of the clavicle?
What is: Sternal extremity
Visualizes the glenoid cavity but with an additional 45 degree caudad angle directed towards the scapulohumeral joint
What is: Garth (AP Apical Oblique Axial)