This subatomic particle carries a positive charge.
What is a proton?
X-rays are produced when high-speed electrons strike this material in the X-ray tube.
What is the anode (or target)?
This interaction occurs when an X-ray photon is completely absorbed by an inner-shell electron.
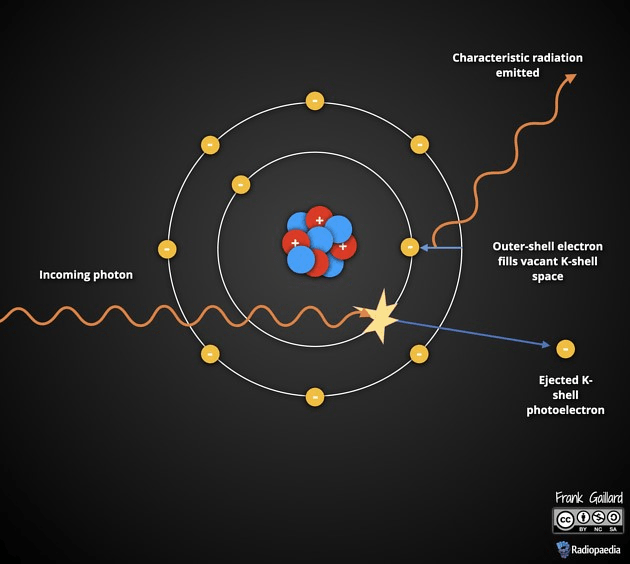
What is the photoelectric effect?
The negatively charged component of the X-ray tube that emits electrons.
What is the cathode?
X-rays are part of this spectrum of energy waves.
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The central part of an atom, where protons and neutrons are located.
What is the nucleus?
This type of X-ray is produced when an incoming electron interacts with the nucleus of a target atom.
What is Bremsstrahlung radiation?
This type of interaction results in scattered radiation and occurs with outer-shell electrons.
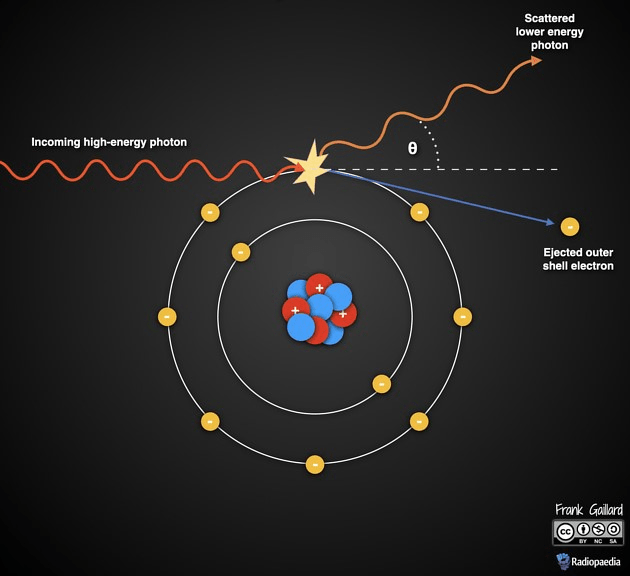
What is Compton scattering?
This material, used in the anode, has a high atomic number and high melting point.
What is tungsten?
This property of electromagnetic radiation determines the energy of an X-ray photon.
What is frequency (or wavelength)?
The number of protons in an atom determines this property, which is unique to each element.
What is the atomic number?
The process in which an incoming electron ejects a K-shell electron, creating this type of radiation.
What is characteristic radiation?
This is the predominant type of interaction in soft tissue with low-energy X-rays.
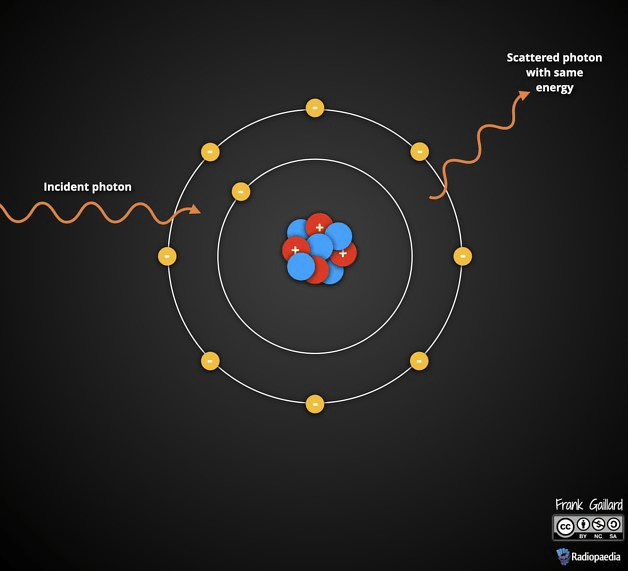
What is coherent (or Rayleigh) scattering?
This part of the X-ray tube helps direct electrons from the cathode toward the anode.
What is the focusing cup?
The speed at which all electromagnetic waves travel in a vacuum.
What is the speed of light?
This term describes atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What are isotopes?
The energy of X-rays in the beam is controlled by this setting on the X-ray machine.
What is kilovoltage peak (kVp)?
As X-ray energy increases, this interaction becomes less likely in dense materials.
What is the photoelectric effect?
Excessive heat in the X-ray tube can cause this type of damage to the anode.
What is pitting (or cracking)?
X-rays and gamma rays differ in their origin. Gamma rays come from this source.
What is the nucleus of an atom?
The binding energy of an electron is strongest in this shell of the atom.
What is the K-shell?
The majority of X-rays produced in the X-ray tube fall under this type of radiation.
What is Bremsstrahlung radiation?
Scatter radiation produced during Compton interactions has this impact on image quality.
What is reduced contrast?
This component of the X-ray tube prevents leakage radiation by enclosing the tube.
What is the lead housing (or tube housing)?
This is the equation that relates the energy of a photon to its frequency.
What is E = hf (Planck's equation)?