What is the difference between particulate radiation & electromagnetic radiation?
Particulate - travels in a straight line at high speeds
Electromagnetic - movement of wave like energy through space
What are the 2 main causes of a blank film?
1. Film not exposed to radiation
2. Film went through fixer before developer
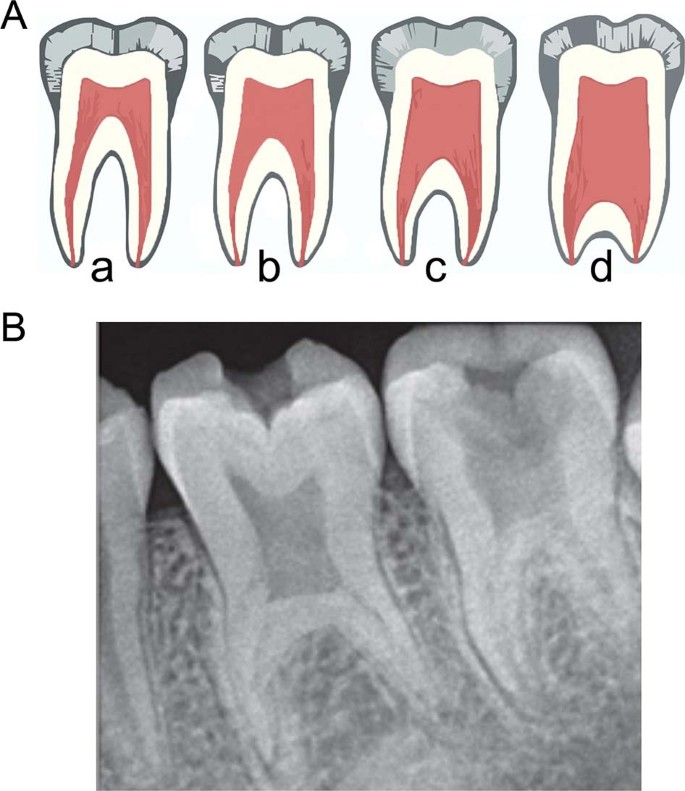
What anomaly is pictured?
Taurodontism
List 4 anatomical parts of the tooth seen in x-rays
•Enamel
•Dentin
•Cementum
•Pulp cavity
What is most of the energy converted to as electrons pass from the cathode to the anode?
Heat
99% converts to heat; 1% converts to x-rays
kV determines ____ of X-rays whereas mA determines ____ of X-rays
Quality;Quantity
What is the main cause of a film that is completely black?
Film was exposed to white light prior to processing
What anomaly is seen in this image? 
Hypercementosis
What condition is defined as: "the condition of having supernumerary teeth, or teeth that appear in addition to the regular number of teeth"?
Hyperdontia
What does the SLOB rule stand for?
Same Lingual Opposite Buccal
Describe the difference between wavelength, frequency, & velocity?
wavelength - distance between wave crest
Frequency - number of waves that pass
Velocity - speed of wave
What appearance will the film have if processed with dirty rollers and/or dirty solution?
Dark rolled lines
What landmark is this?
Superior Foramina of Incisive Canal
What anomaly is seen in this image?
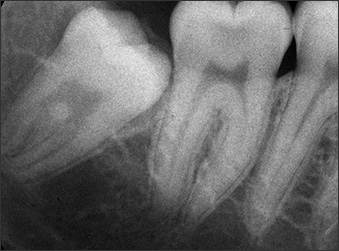
Enamel Pearl
List in order the steps for film processing
1. development
2. rinsing
3. fixing
4. washing
5. drying
What is the intensity of the X-ray beam if the distance is doubled? What about when it is halved?
Doubled - beam is a quarter as intense
Halved - beam is 4 times as intense
What causes static electricity artifacts on film?
Rapid removal of film from packet
Humidity is too low
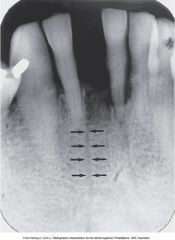
What landmark is this?
Nutrient Canal
What anomaly is seen in this image?
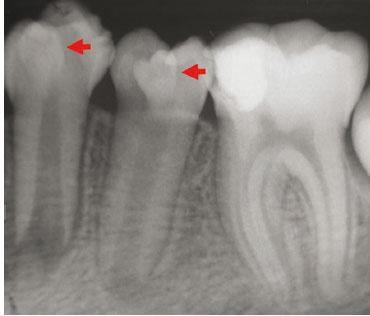
Dens in dente
Which of the following could NOT have caused a black film?
a. light leak
b. unexposed film
c. irradiating an edentulous area
d. using white light in the developing room
B - unexposed film
1. Low kVp produces a ____ contrast image with a ____ scale contrast
2. High kVp produces a ____ contrast image with a ____ scale contrast
1 - high;short
2 - low; long
What will film look like if the developer is too COLD?
What feature is highlighted in pink?

Zygomatic Process
Where is the hamulus located?
The pterygoid hamulus is a hook-shaped bony process located bilaterally on each medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone, posterior and medial to each maxillary tuberosity.
A round radiolucency is seen on a radiograph located apical to the second mandibular premolar or between the apices of the premolars. What is the most likely reason for this radiolucency?
a. Abscess
b. Genial tubercles
c. Lingual foramen
d. Mental foramen
D - mental foramen