What view is this?
Oblique
What view is this and is most useful when?
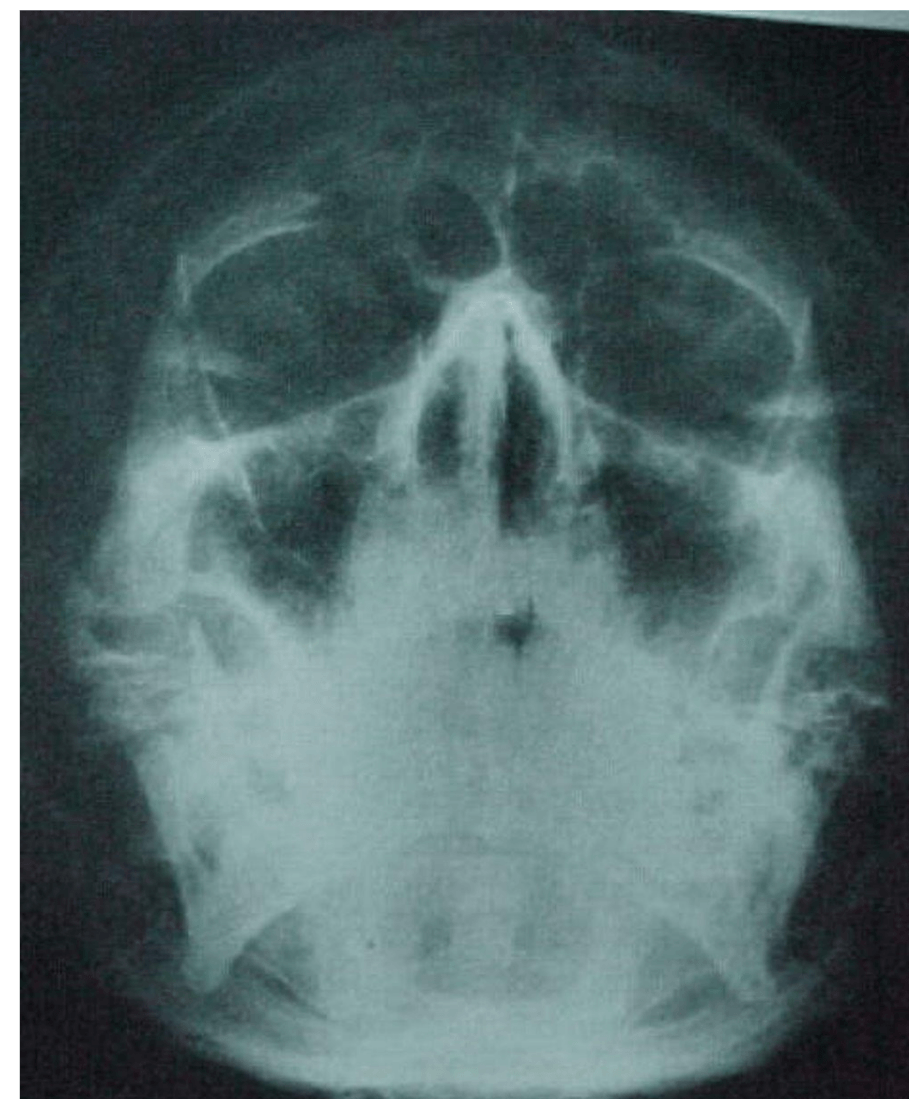
Waters view aka Dens, used when a patient can't open their mouth or is unconscious/ has cervical collar
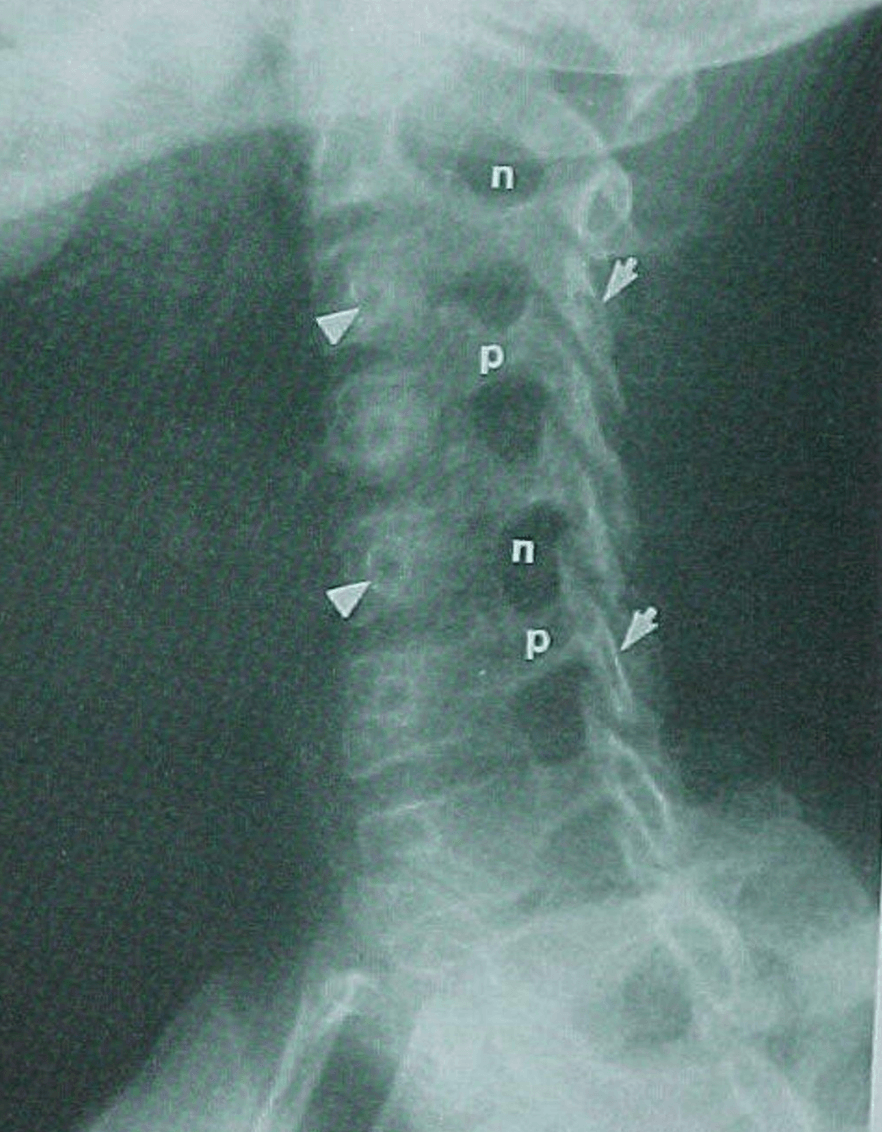
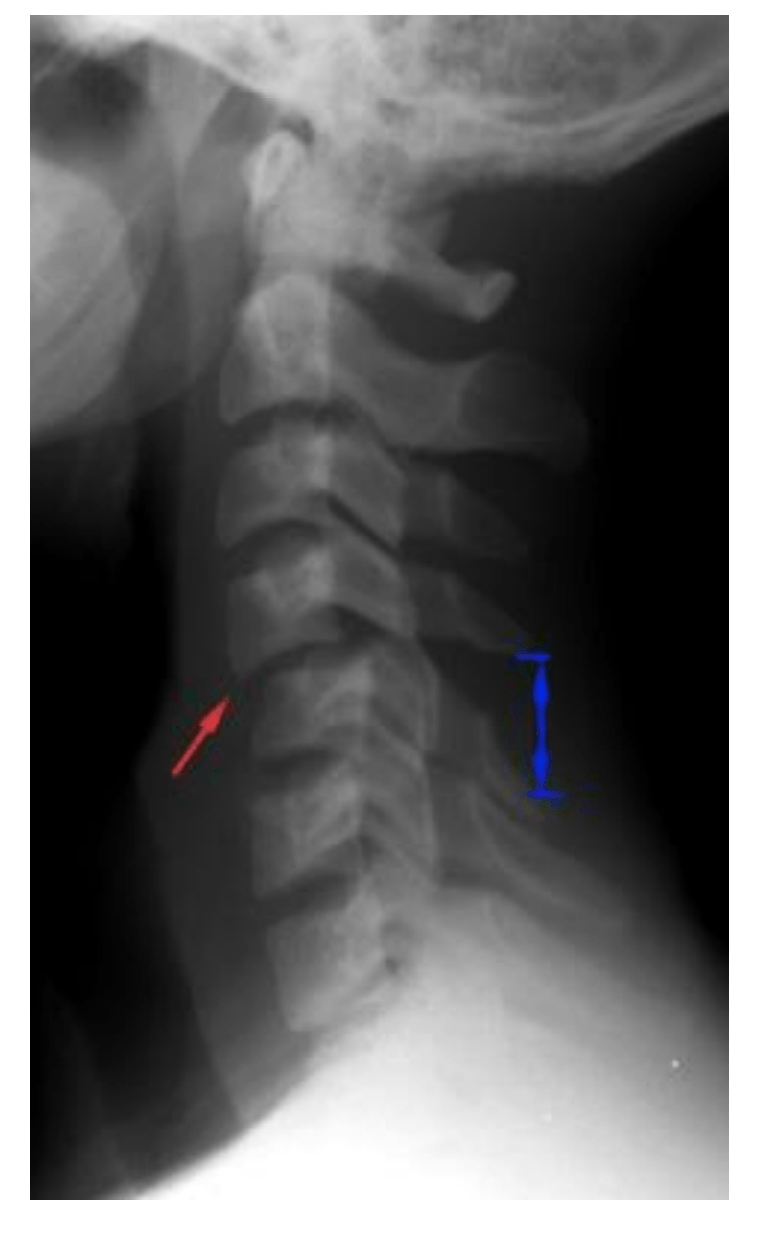
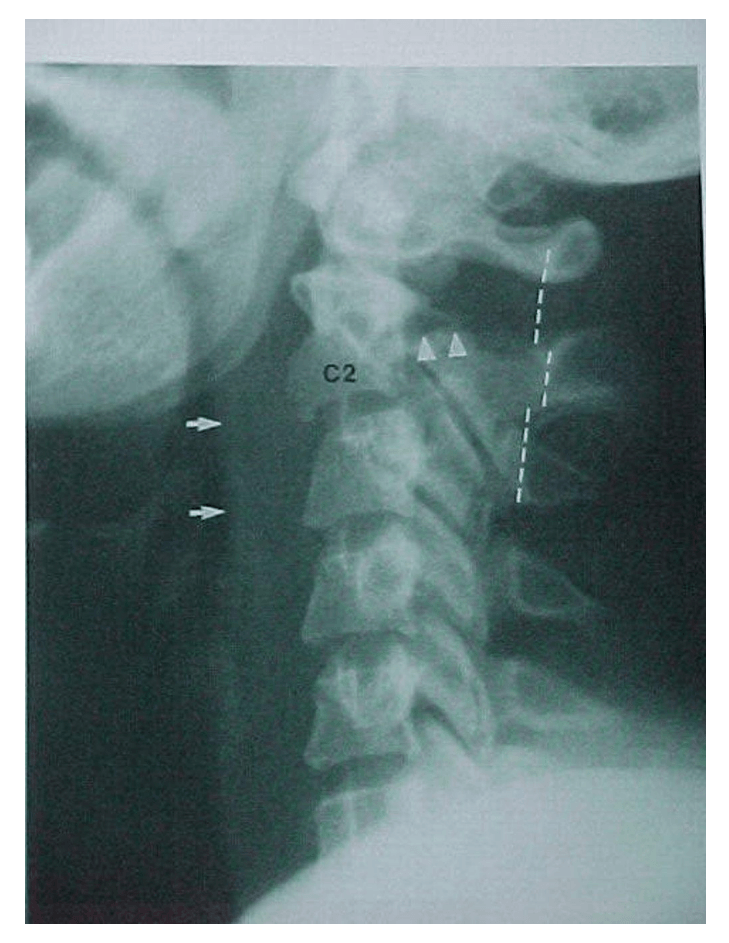
Pt was involved in an MVA and complained of severe neck pain shortly after. Lateral film was obtained. What is your assessment?
Can't make an assessment because a full film is not available. Can't see C7 or T1
What is considered a normal c-spine soft tissue measurement in an adult vs a child for this location?
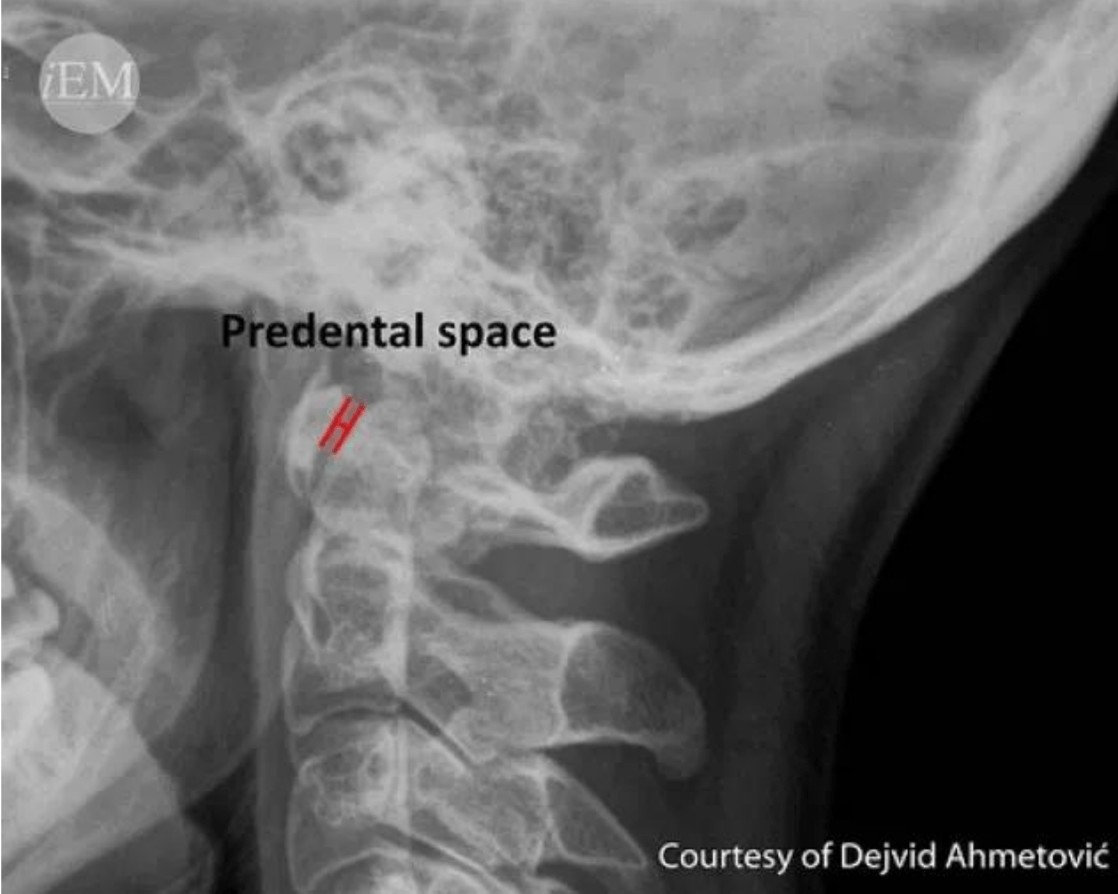
Adult </= 3mm
Child </= 5mm
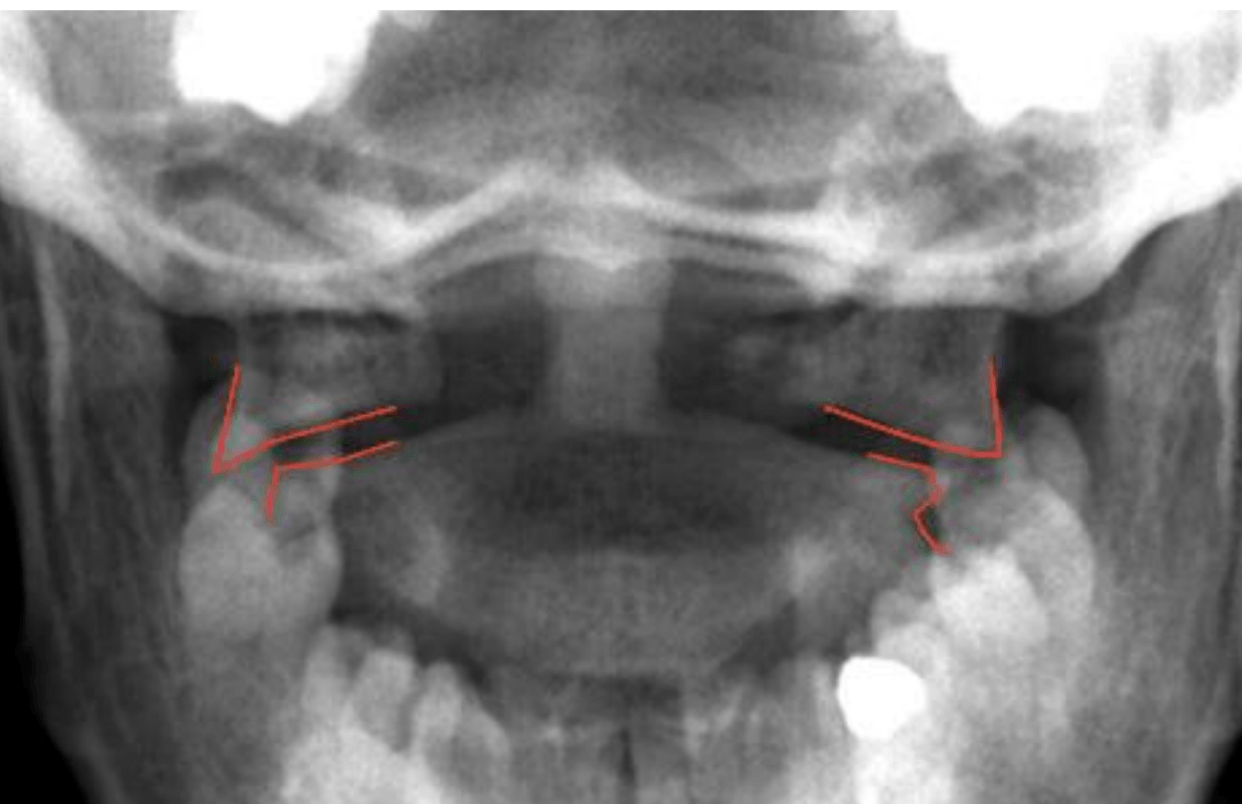
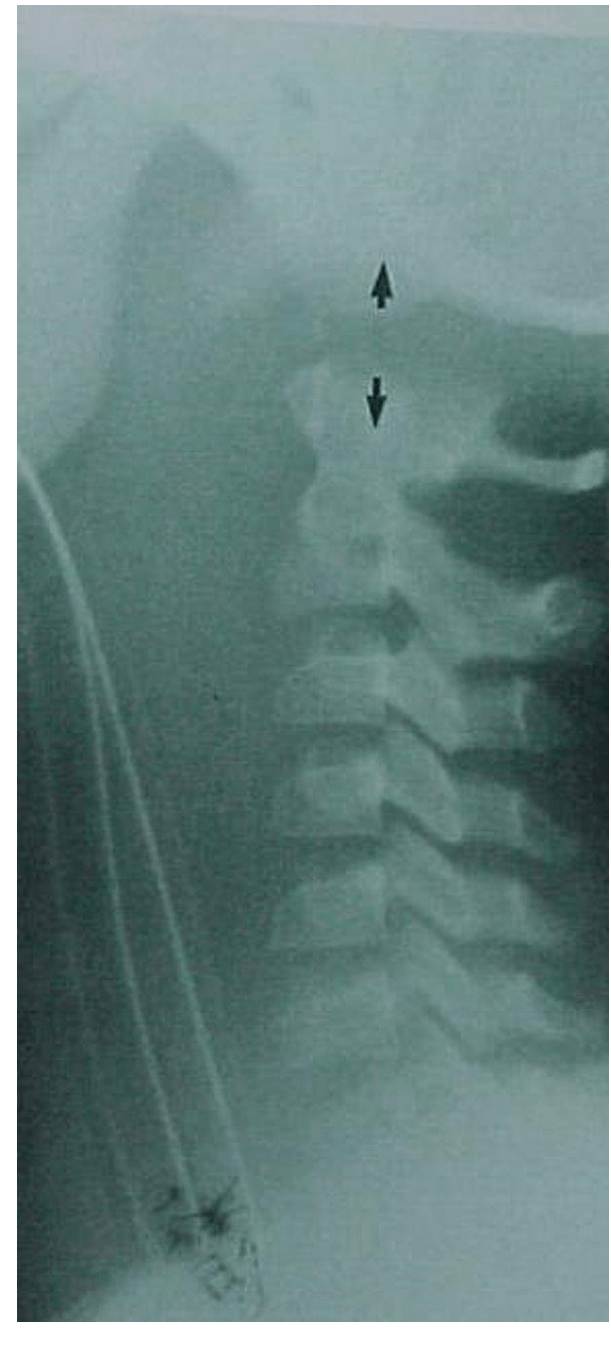
What does this image show? Specifically !
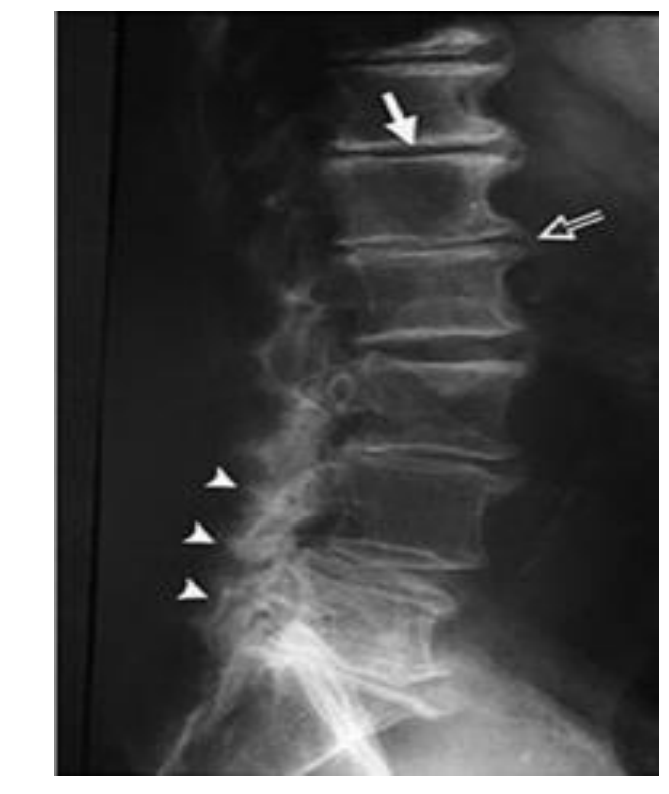
Degenerative joint disease
irregular decreased jt space
osteophyte formation
sclerosis
What type of fx is this and what's the likely cause?
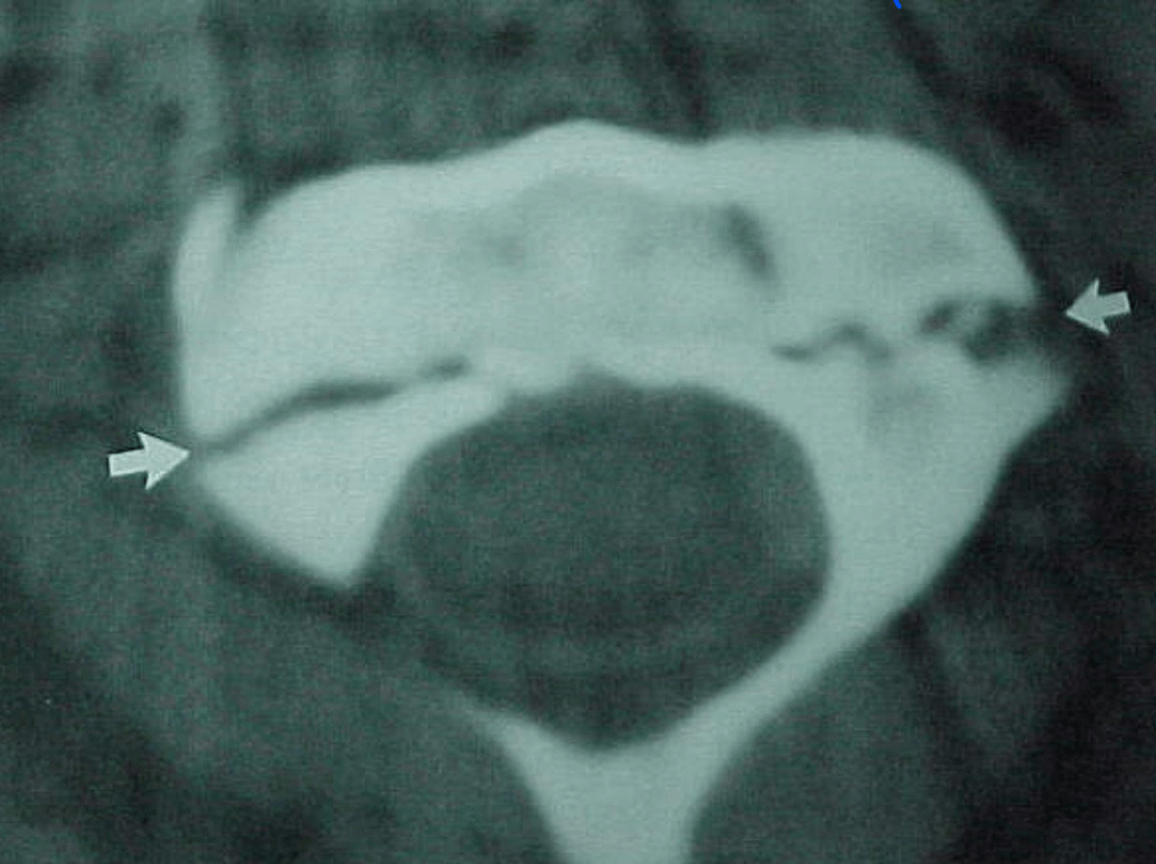
Jefferson's (C1) Fx, Unstable Cervical Spine Fx
Usually caused by vertical force that compresses the lateral masses between the occipital condyles and the axis driving them apart.
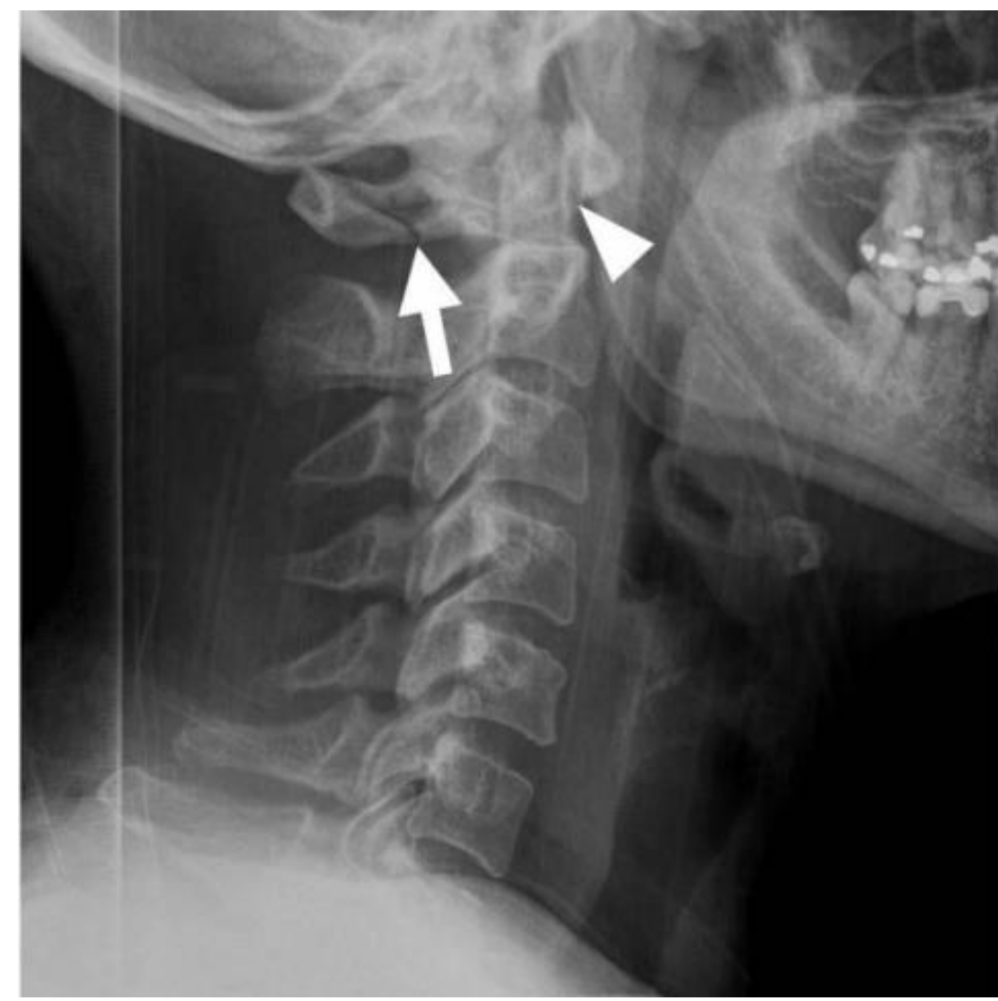
What fx do you see and the likely cause might be what?
Hangman's Fx caused by hyperextension
What type of imaging is this?
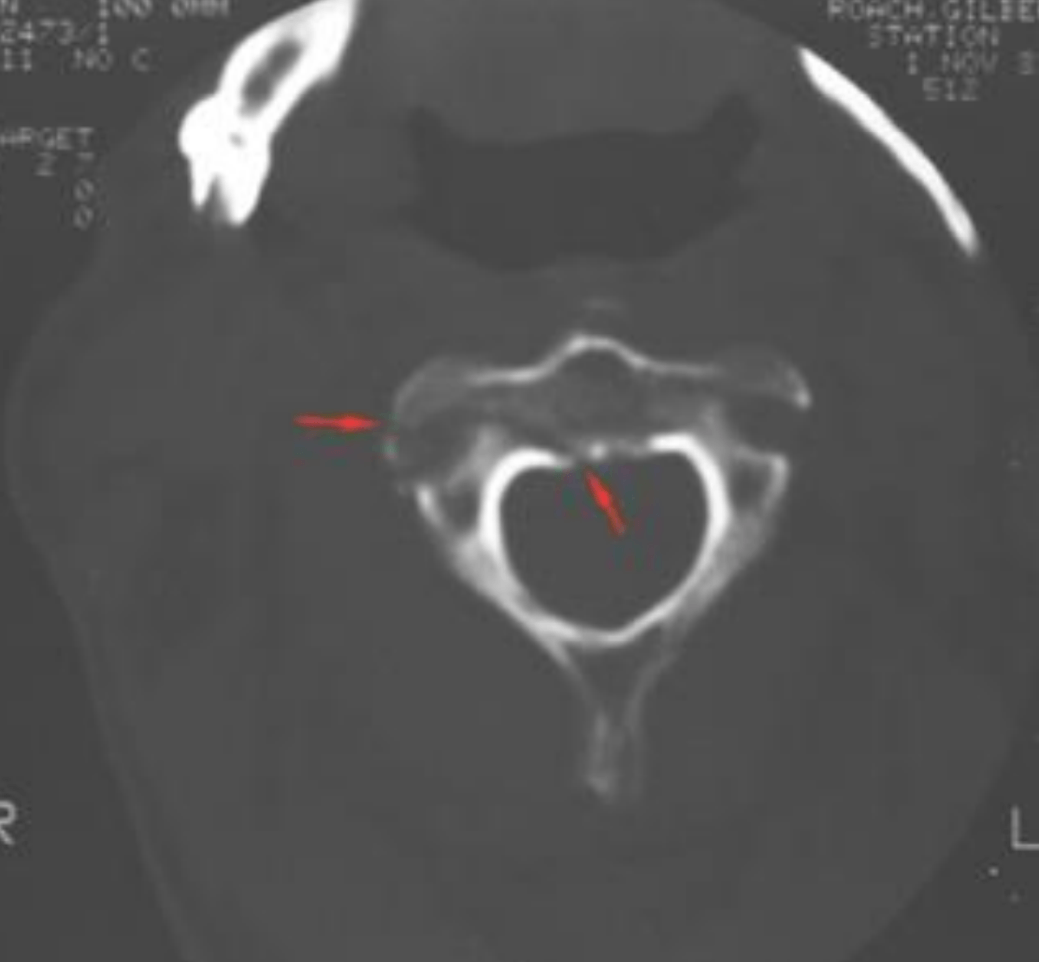
CT imaging, preferred for all C-spine fx
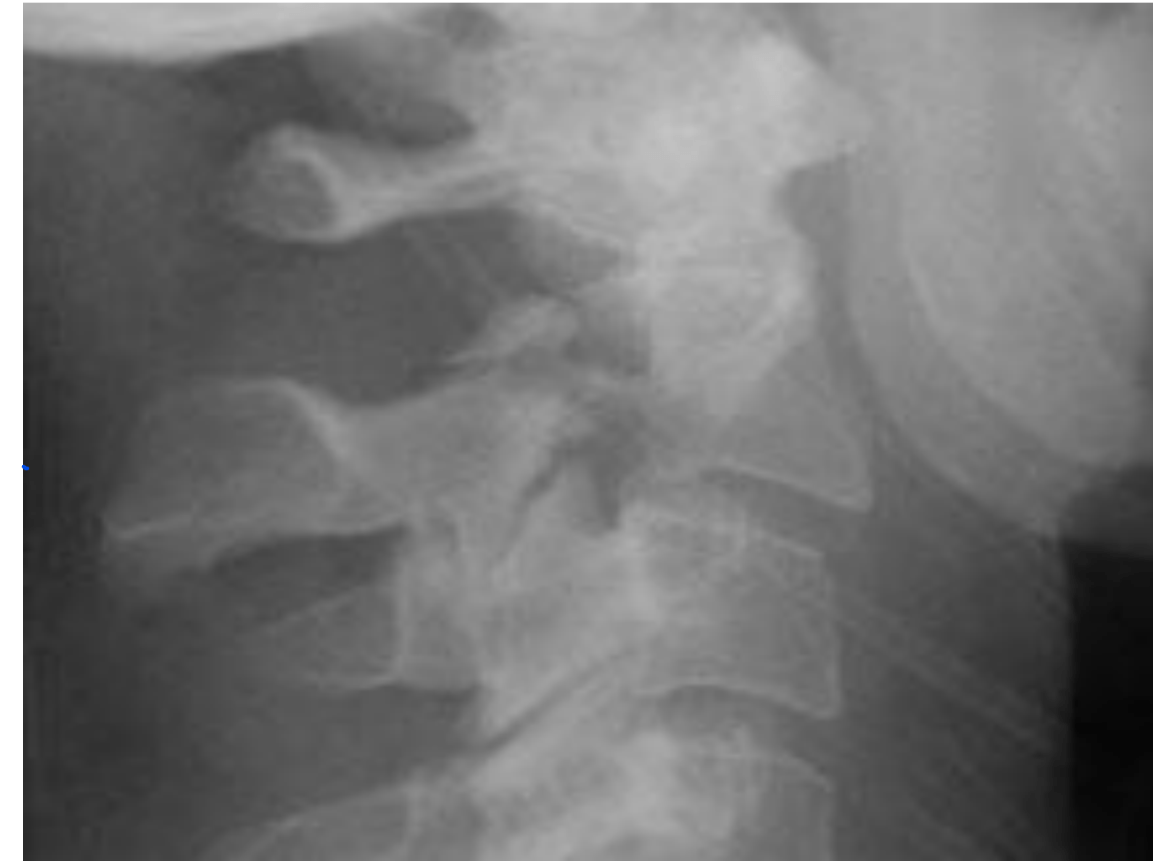
T/F This is a normal finding.
F, This is unilateral facet D/L resulting from rotatory injury of the cervical vertebrae: simultaneous flexion & rotation
What do you see in this image? what bones are damaged?
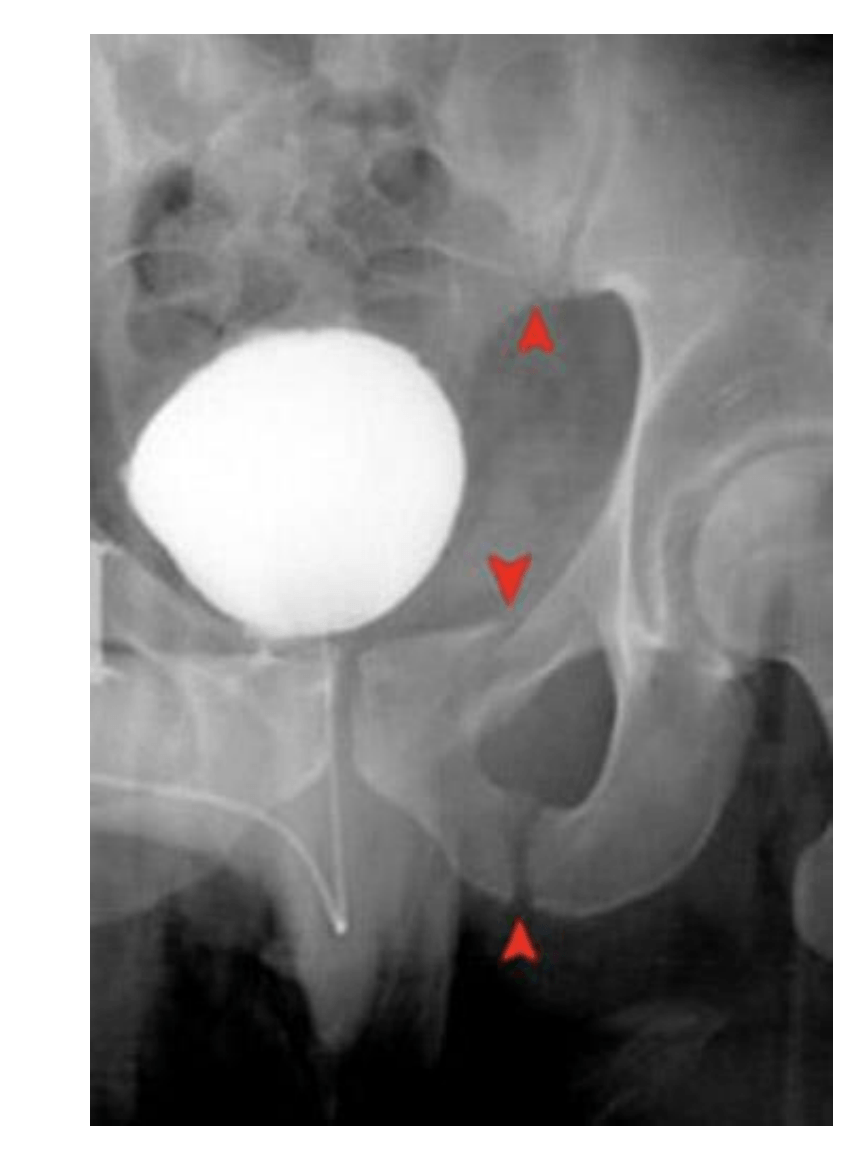
Malgaigne Fx
SI jt and ipsilateral ischiopubic rami
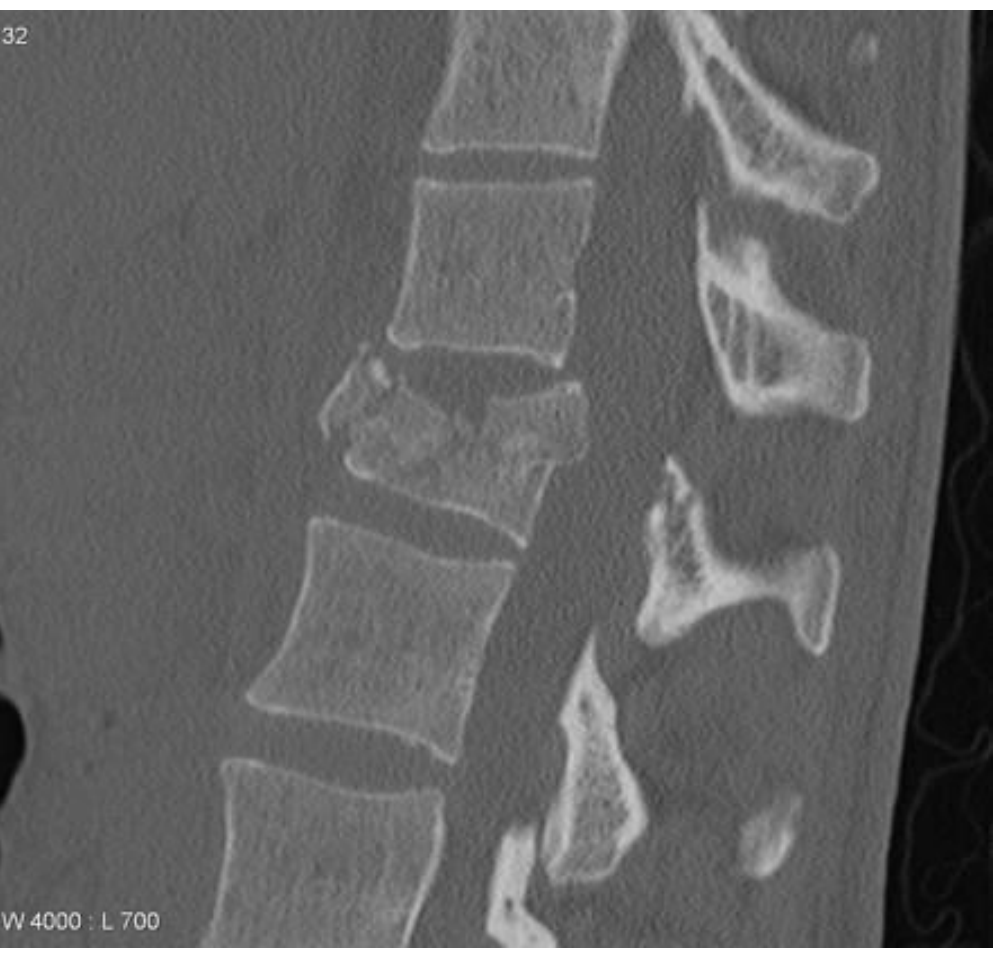
Is what you see normal?
No, it is a Jefferson's (C1) unstable cervical spine Fx
What Fx do you see and what are we most concerned with in these cases?
Burst Fx aka axial compression Fx causes injury to the spinal cord, secondary to displacement of posterior fragments commonly.
Immobilize Quick!
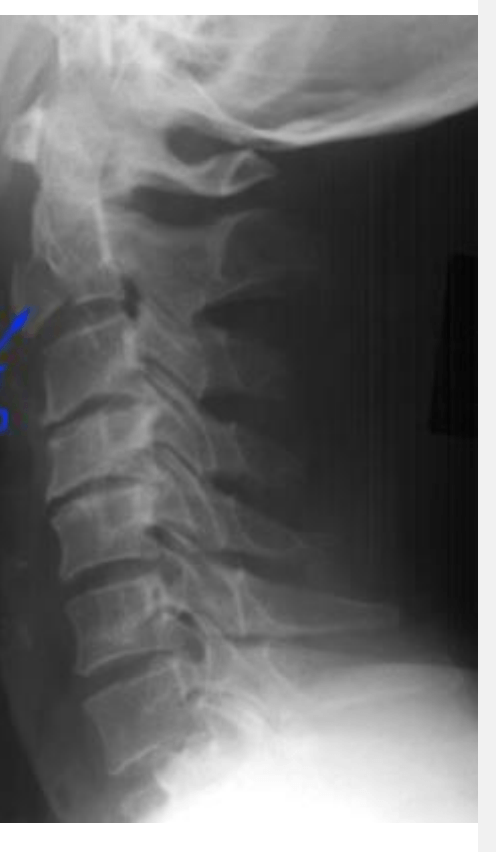
What is the likely fx you see here?
Hangman's Fx
What do you see and the likely cause?
Teardrop Fx
caused by forced extension of the neck with resulting avulsion of anteroinferior corner of the vertebral body .
flexion teardrop is more severe. (MRI will help distinguish the type)
What do you see in this image? and what age group will you see this finding in?
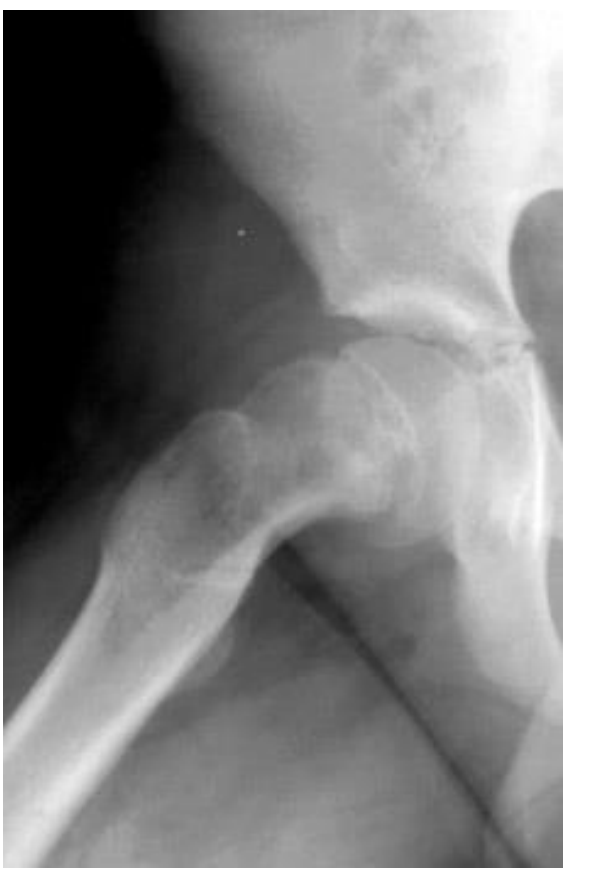
slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
occurs in children
When would you most likely see this time of Fx?
Shaken baby syndrome
Fx at base of skull, C1
could be pathological but should be concerned about abuse
This is an atypical presentation of what type of fx?
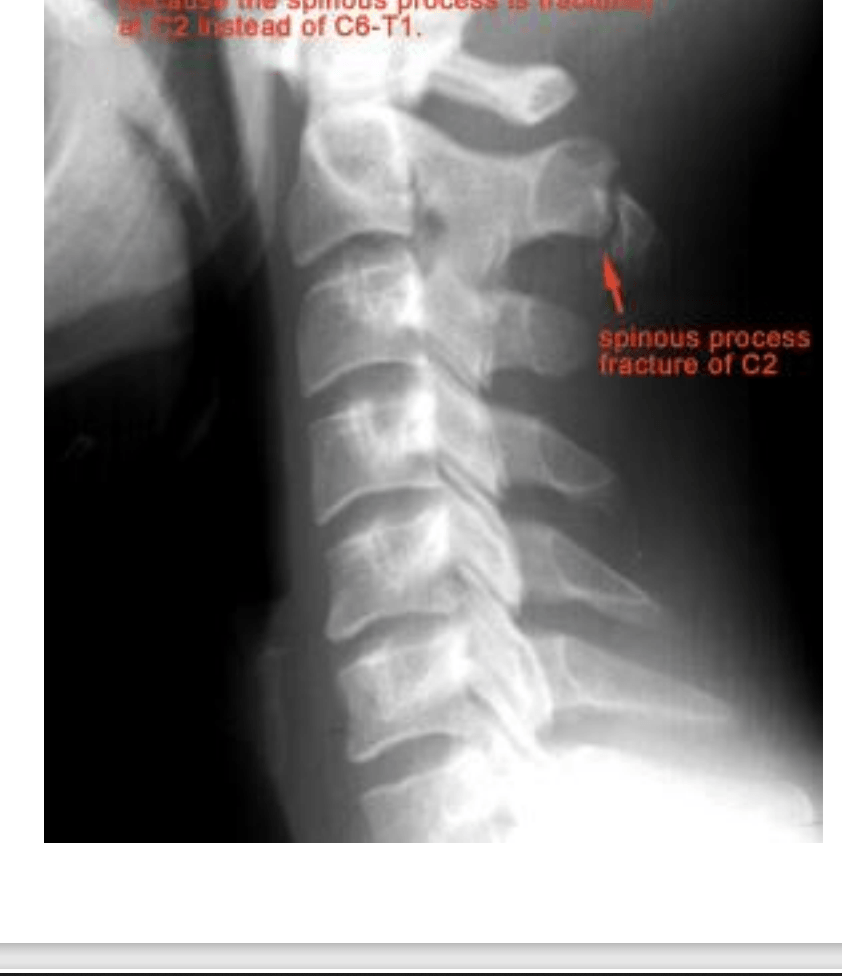
What do you see and the likely cause?
Hangmans (C2) Fx likely caused by hyperextension
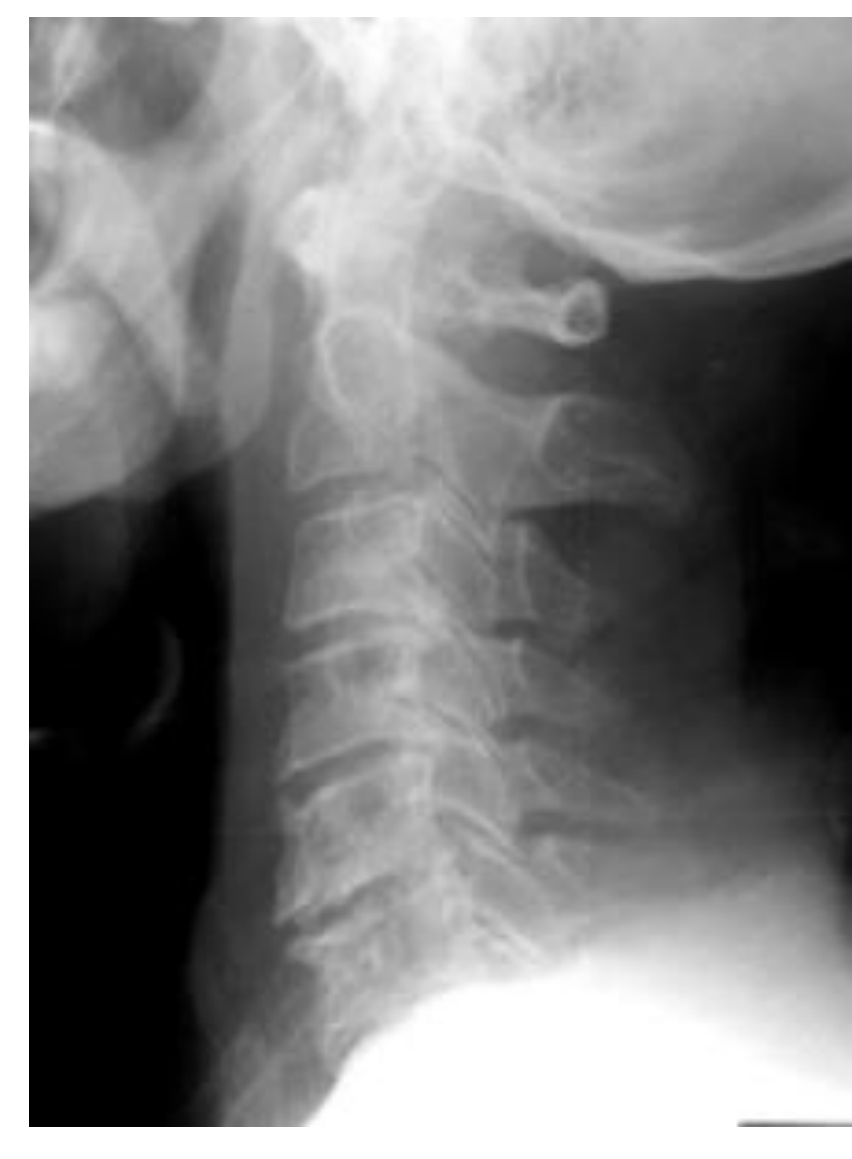
 What view is this and when is it beneficial?
What view is this and when is it beneficial?
Swimmer's view, helpful on heavier individuals . It enhances C7 and T1
Can you make a dx based on this image? why or why not?
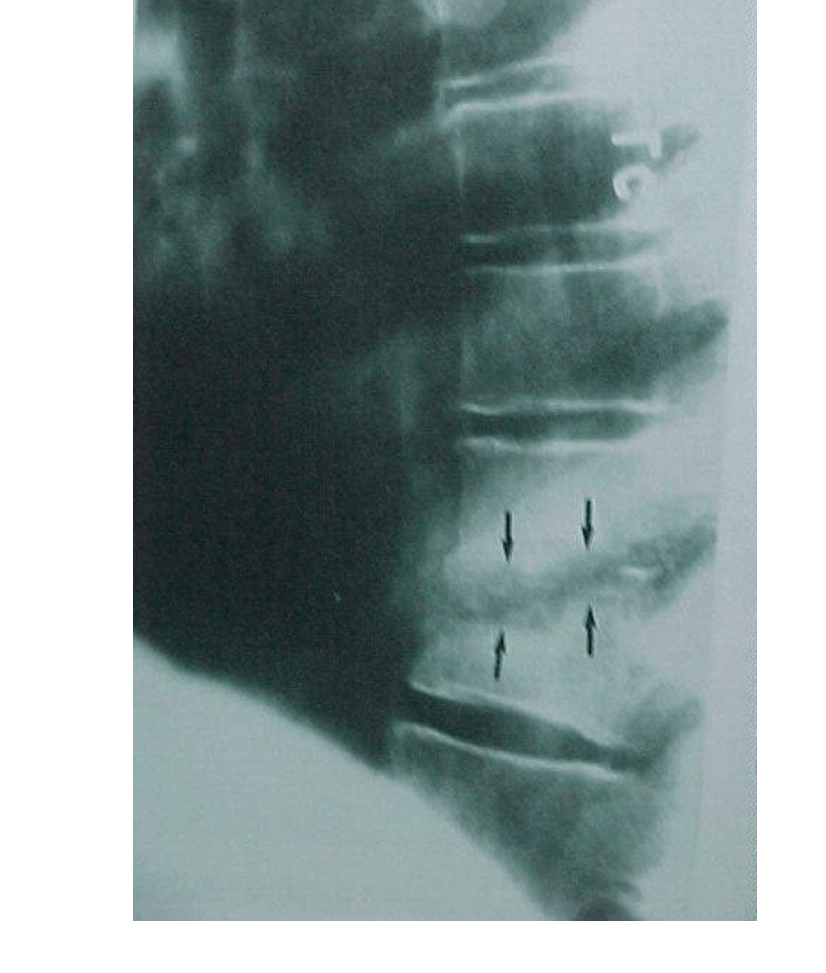
Yes, it is likely osteomyelitis due to the bone erosions.
Consider a Diff dx in someone with back pain and IV drug use
Who needs C-spine imaging? (5)
1. mental status less than alert or intox.
2. reports neck pain
3. midline neck tenderness (not muscle tenderness)
4. neurologic signs and symptoms
5. distracting injury (like extremity fx)
all pts get all 3 views : odontoid, posterior, lateral
T/F This is a normal finding.
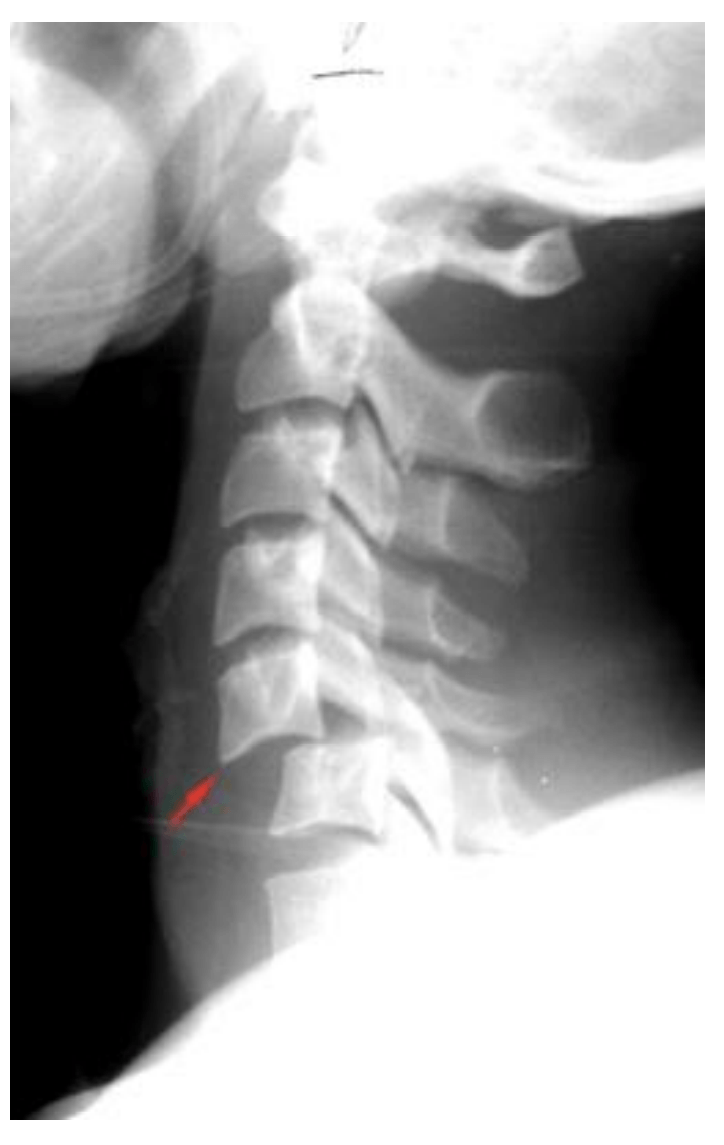
F
Bilateral facet d/l
High risk of cord damage
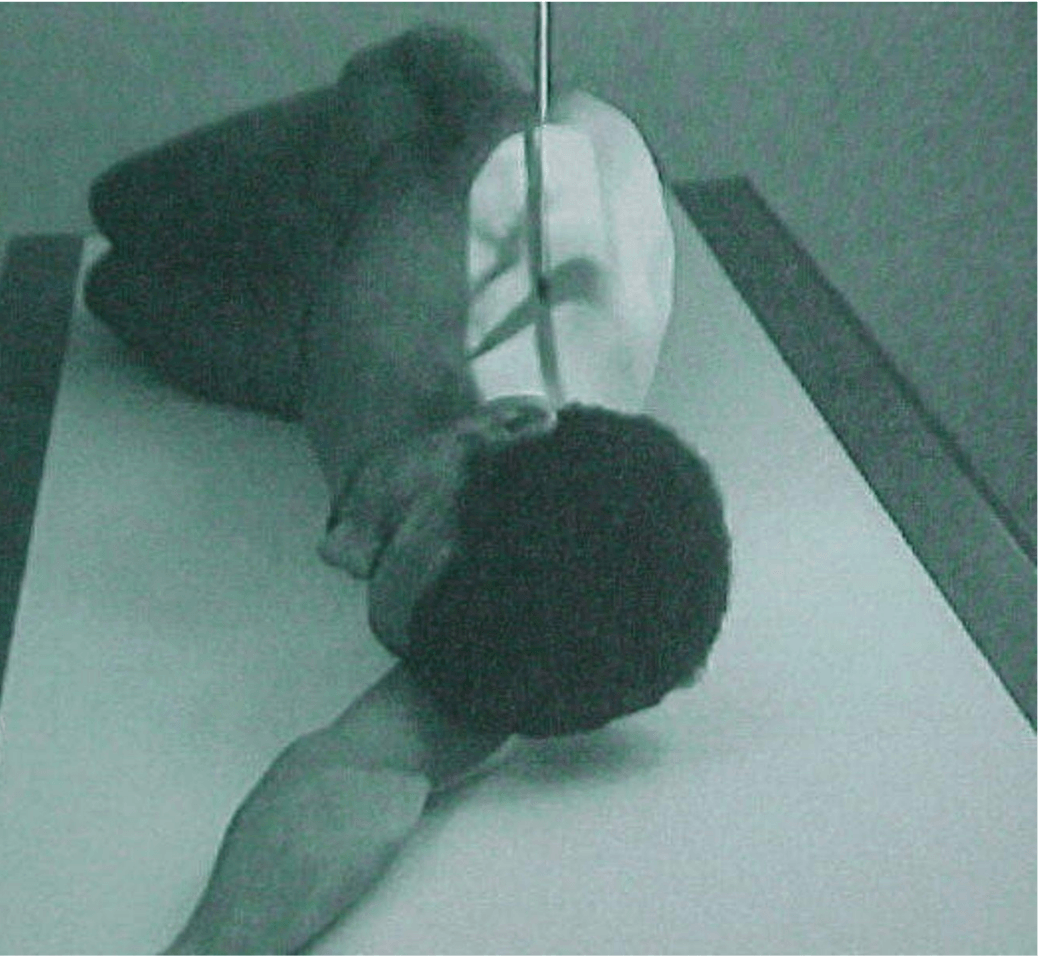
What view is required to get this image as a result?
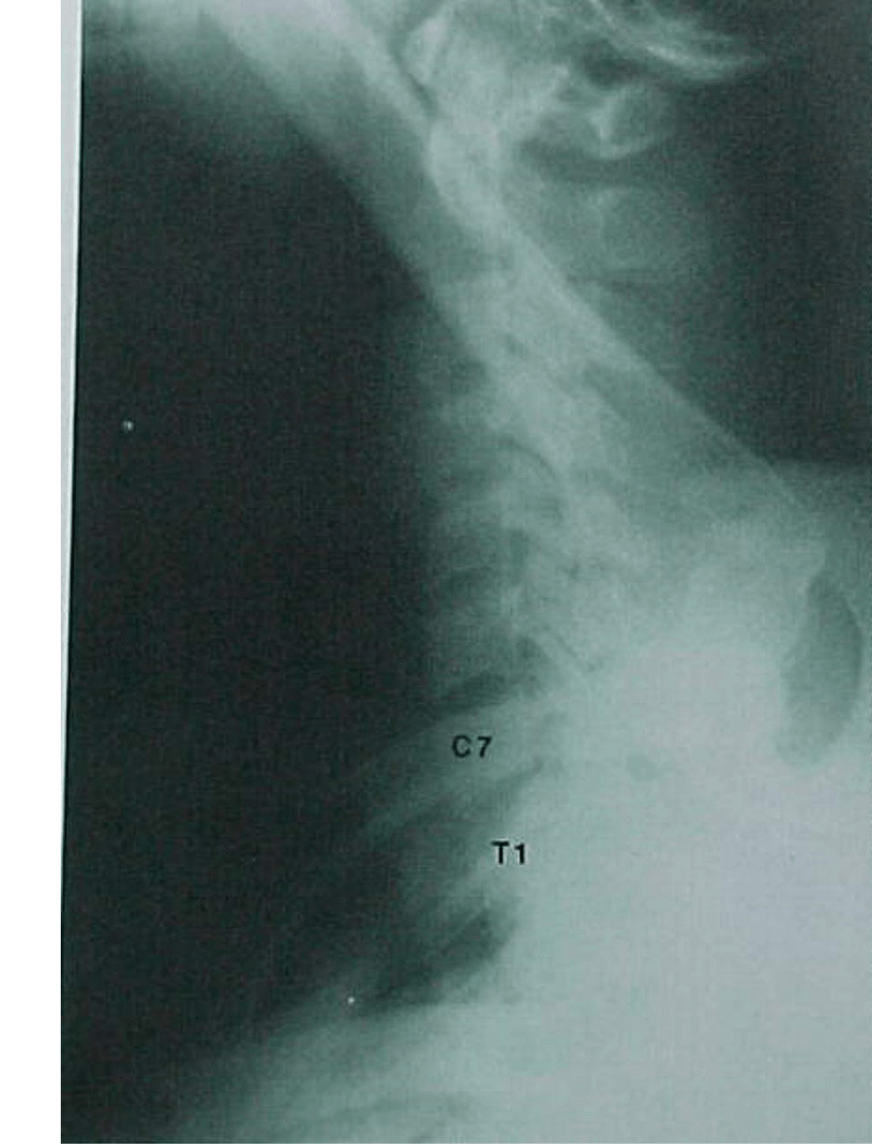
Swimmer's view because it enhances C7 and T1
Normal C-spine soft tissue measurements for adult and child for each of the following:
Predental space:
Retropharyngeal space:
Retrotracheal space:
predental: adults </= 3mm, child </= 5mm
retropharyngeal (ant to C3): </= 7 mm both
retrotracheal (ant to C6): </=22mm, child </= 14mm
what is the leading cause of death in patients with severe pelvic trauma?
hemorrhage .
be cautious when someone c/o pelvic pain after a fall