This lesion histologically can look identical to an osteoid osteoma
What is an osteoblastoma?

A fracture to a posterior element at C2 due to hyperextension.
What is a Hangman's fracture?

A likely cause for low back pain requiring an urgent medical referral and ultrasound follow up.
What is an abdominal aortic aneurysm?
This marble bone that can be a cause for a pathological fracture.
What is osteopetrosis?
The x-ray view that that would best evaluate for lateral patellar tracking.
What is the SUNRISE view?

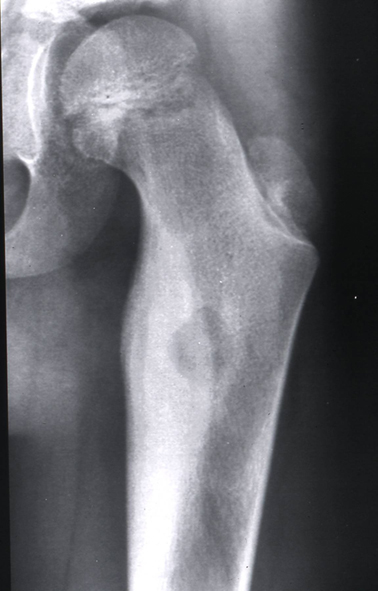
The typical age range for this painful lesion involving the metaphysis and epiphysis.
What is 20-40?
The condition that can result in vertebrae resembling the letter H.
What is sickle cell anemia?

Ossification of the medial collateral ligament secondary to trauma.
What is the Pellegrini Stieda?
Spinal wear and tear that can result in balance disturbances and bilateral arm weakness.
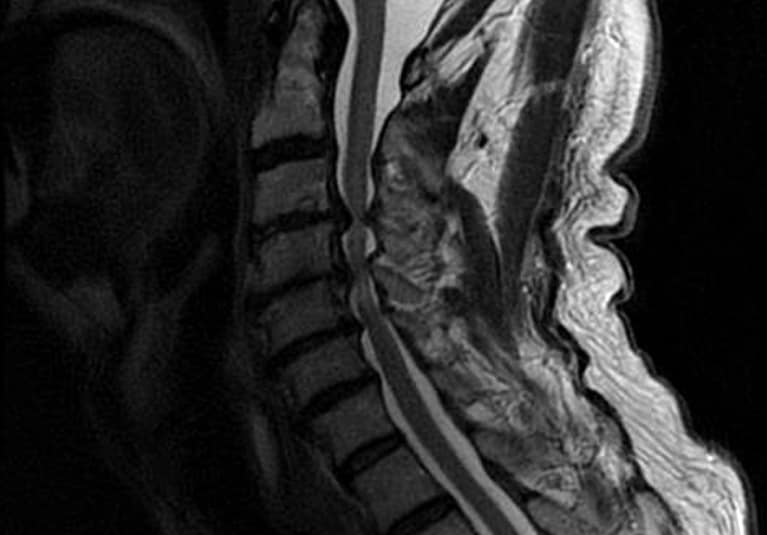
What is cervical spondylotic myelopathy?
The x-ray view that best shows the talofibular joint.
What is the MEDIAL OBLIQUE ANKLE?

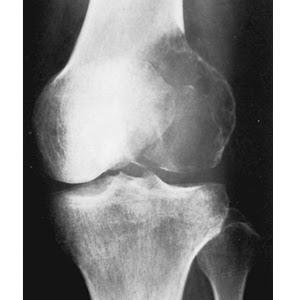
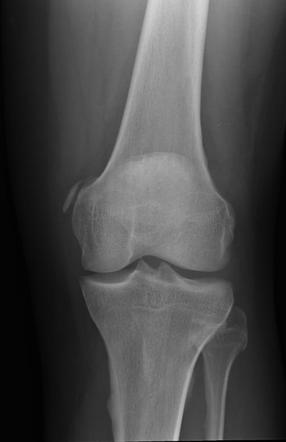
This benign lesion has a predilection for the epiphyses and apophyses.
What is a chondroblastoma?
The fracture most common to the elbow in adolescent baseball pitchers.
What is a medial epicondyle avulsion fracture?

This condition typically prefers a subligamentous spread in the spine in adults.
What is Pott's disease?
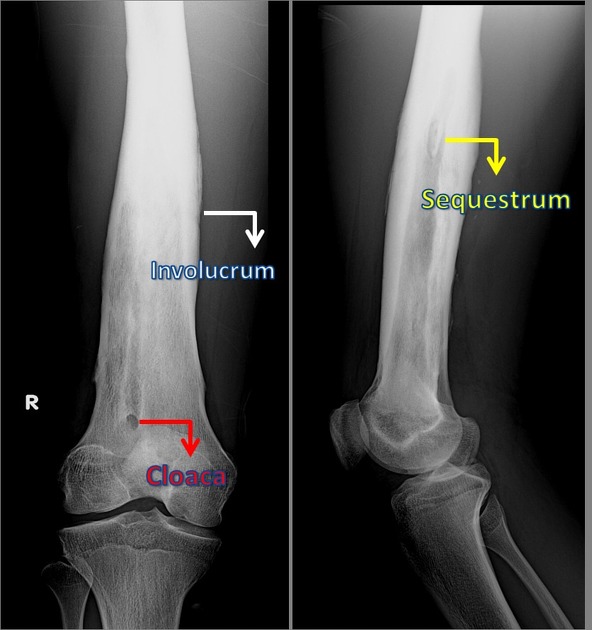
An osteonecrosed separated fragment that no longer responds to antibiotics.
What is a sequestrum?
The x-ray view that best shows the radial tuberosity.
What is the LATERAL OBLIQUE ELBOW?
This self-limiting lesion is typical to be eccentric in location.
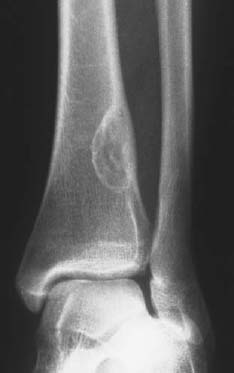
What is a non-ossifying fibroma?
An accessory ossicle along the dorsum of the wrist at the base of the 2nd and 3rd metacarpal.
What is an os styloideum?


The secondary ligament injury associated with a reverse Segond fracture.
What is the PCL?
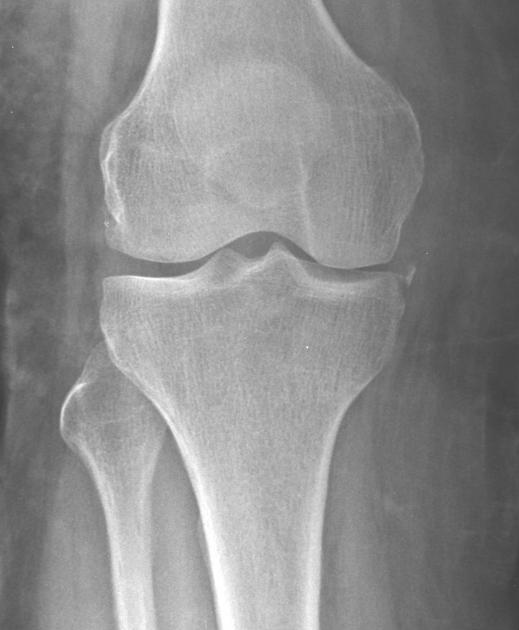
This arthritide is not a direct risk factor for avascular necrosis but it’s treatment medication can result in multiple infarctions.
What is SLE?
An alternative view to ulnar deviation to evaluate for widening of the scapholunate interval.
What is the CLENCHED FIST view?

This condition can present with a soap, bubbly lesion from overactive osteoclastic activity and is also called osteoclastoma.
What is hyperparathyroidism's brown tumour?

The most common fracture/dislocation injury of the foot, involving the tarsal-metatarsal joints.
What is a Lisfranc injury?
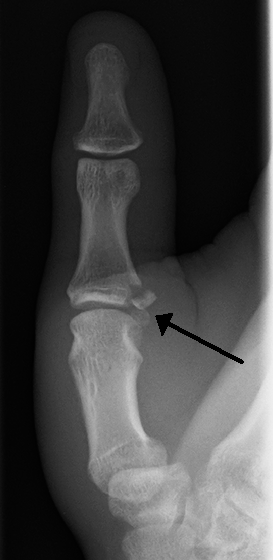
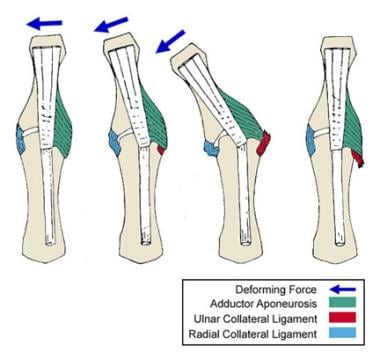
The ligament torn that can result in a Stener lesion.
What is the UCL?
The presence of this soft tissue finding typically suggests what underlying systemic condition?
What is diabetes?
The best view to request should you be concerned about a fibular head/neck fracture.
What are the MEDIAL OBLIQUE KNEE?
