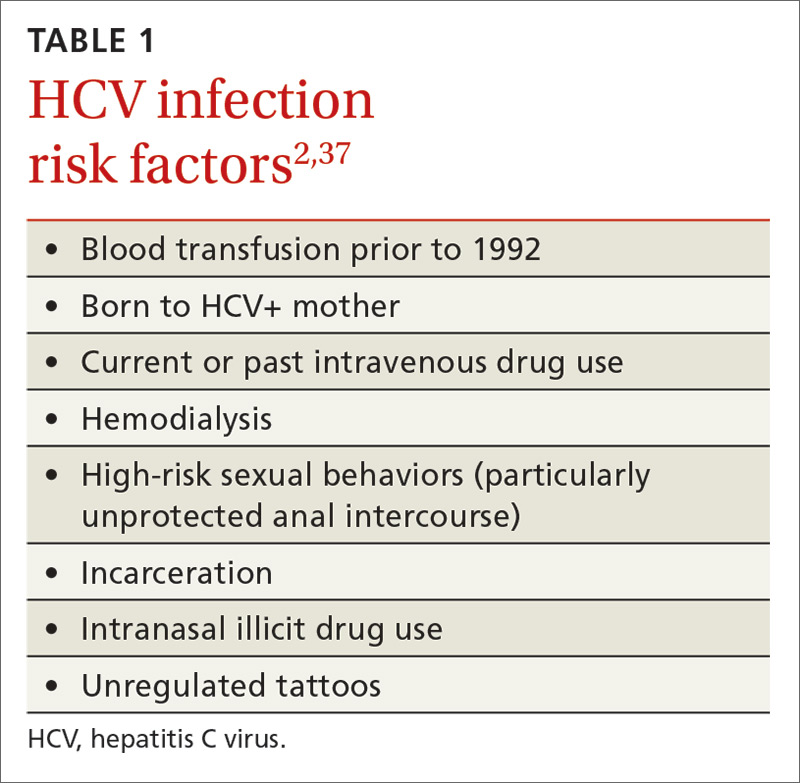
All adults aged 18-79yo should be screened at least once for this viral infection, and periodically for those at high risk.
What is Hepatitis C virus?

This pulmonary disorder, particularly in higher risk individuals such as an older male with a neck circumference >16 inches, should be screened for in all perioperative scenarios as it is associated with increased risk for cardiac events, pulmonary complications, and ICU admissions.
What is obstructive sleep apnea? Can utilize the STOP-BANG score.
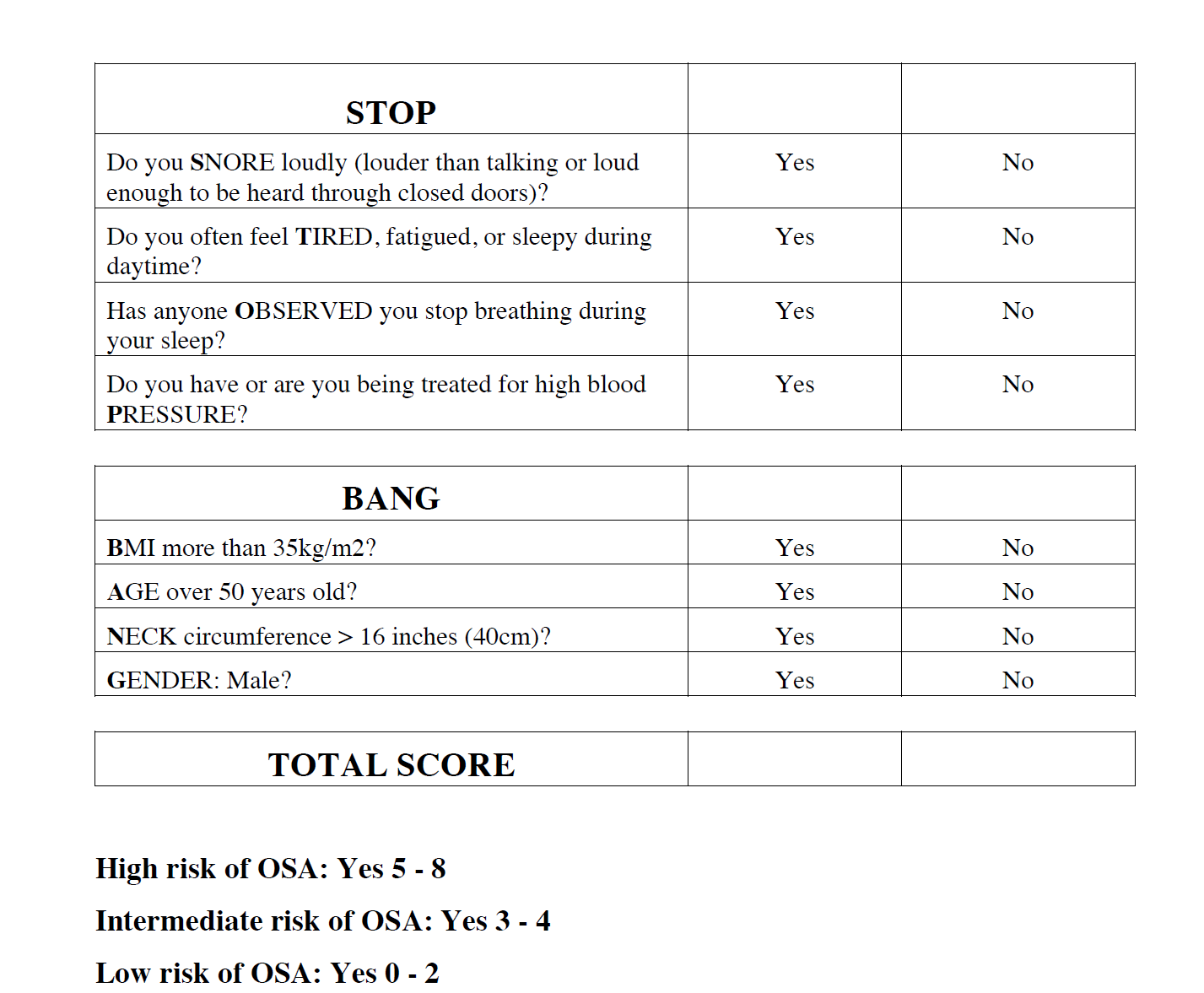
This autoantibody is the most specific biomarker for primary membranous nephropathy and is used both for diagnosis and monitoring disease activity.
What is PLA2R (phospholipase A2 receptor) antibody?
The combination of ICS-LABA for both daily maintenance and as-needed symptom relief is the cornerstone of this asthma therapy.
What is SMART (Single Maintenance and Reliever Therapy) therapy?
The triad of hematuria, hemoptysis, and strong linear IgG deposition along the GBM.
What is Goodpasture/Anti-GBM disease?
These infections should be screened for in all sexually active women less than 25 years old and all sexually active women >25yo who are at increased risk of infection.
What are chlamydia and gonorrhea?
This validated index uses six predictors — including high-risk surgery, ischemic heart disease, heart failure, cerebrovascular disease, insulin therapy, and creatinine >2 mg/dL — to estimate the risk of major cardiac complications after noncardiac surgery.
What is the Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI)?

This constellation of findings (syndrome) can be seen in a patient who presents with hematuria, HTN, and RBC casts. 24-hour urine with 2.2g proteinuria. Urine observed under microscope demonstrates the following:
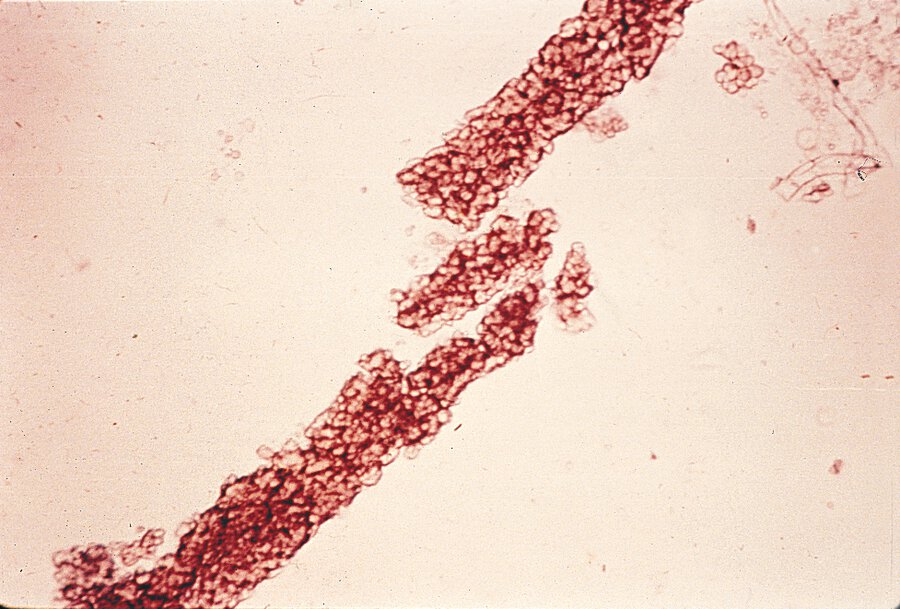
What is nephritic syndrome?
Common features of nephritis syndrome: hematuria (with dysmorphic erythrocytes or erythrocyte casts) and proteinuria (<3.5g/24hours or UPCR <3500 mg/g); hypertension, edema, and kidney dysfunction may also occur.
This is when the USPSTF recommends screening for gestational diabetes in asymptomatic pregnant persons.
What is at 24 weeks of gestation, grade B recommendation?
This is the most likely etiology, as a form of extra-renal manifestation, for a subarachnoid hemorrhage found in someone with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
What is a ruptured berry aneurysm?
Low-dose CT scan for lung cancer screening is indicated for adults of these ages who have this specific smoking history.
What are adults aged 50-80 years with a 20-pack year smoking history who currently smoke or quit in the past 15 years?
This is the recommendation for medication management in perioperative setting for a noncardiac surgery for a patient on beta blocker and ARB (ie, hold vs continue) for chronic HTN management.
What is to continue BB therapy and to hold ARB in perioperative setting.
2024 ACC/AHA guidelines
Recommendations for perioperative medical management
Beta-blockers. Continue them if the patient is already taking them. If there is a new indication to start a beta-blocker (eg, ischemia on a stress test), start it at least 8 days before surgery to assess tolerability and dose titration, but do not start it on the day of surgery.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers. If the patient has been taking these drugs chronically for hypertension and their blood pressure is controlled, withholding them 24 hours before surgery may limit intraoperative hypotension. If the patient takes them for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, it is reasonable to continue them perioperatively.
This non-steroidal mineralocorticoid antagonist (MRA) was approved by the FDA in those patients with T2DM and CKD who have persistent albuminuria despite maximal renin-angiotensin system inhibition and normal serum K levels.
What is finerenone?
Elderly patient with PMHx of anxiety and fibromyalgia gets admitted and request a medication to relieve her itching. Overnight she develops hyperthermia, tachycardia, decreased bowel movement, urinary retention, and delirium. This (syndrome) likely caused the patient clinical status change.
What is anticholinergic toxicity?

Tumor lysis syndrome causes these four primary electrolyte disturbances.
What is hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, and hyperuricemia?

For women aged 30-65yo, cervical cancer screening can be performed by any of these three strategies. Name at least two.
What is: 1) Pap (cytology alone) every 3 years, 2) high-risk HPV testing alone every 5 years, or 3) co-testing (Pap + HPV) every 5 years?

This is the pre-operative management of anticoagulation in a patient with Afib without high thrombotic risk for elective hip repair (describe management for someone on warfarin and for someone on DOAC).
What is to:
- Warfarin: stop 5 days before surgery
- DOAC (ie, apixaban, rivaroxaban, dabigatran): stop 2-3 days before surgery (if eGFR >50, otherwise stop earlier if eGFR is lower)
This is the most likely diagnosis in a 23yo M who presents with microscopic hematuria, progressive renal failure, sensorineural hearing loss, and ocular abnormalities. His biopsy shows a "basket-weave" appearance of the glomerular basement membrane.
What is Alport syndrome?
X-linked hereditary nephritis caused by mutations in type IV collagen -- characterized by progressive renal failure, sensorineural hearing loss, and ocular abnormalities.
This disorder often presents with skin fragility and bullae or erosions on sun-exposed areas (most frequently dorsal hands), with chronic hepatitis C being most common cause followed by alcohol-induced liver damage and hemochromatosis.
(Bonus 100 pts: how might you confirm diagnosis?)
What is porphyria cutanea tarda?
(Bonus Answer: increased plasma or urine porphyrin levels)
A patient with diabetes presents with mild hyperkalemia and a non-anion gap metabolic acidosis. Labs reveal urine pH <5.5. This type of RTA, caused by aldosterone deficiency or resistance, is most likely.
What is Type 4 RTA (hyperkalemic distal RTA)?
These are the time intervals for USPSTF Colon CA screening for average-risk individuals by each method below:
1) Stool DNA with FIT (fecal immunochemical test)
2) Guaiac fecal occult blood test (FOBT)
3) Flex Sig
4) Colonoscopy
5) CT Colonography
What is:
1) Stool DNA with FIT (fecal immunochemical test): Every 1-3 years
2) Guaiac fecal occult blood test (FOBT): Annually
3) Flex Sig: Every 5 years
4) Colonoscopy: Every 10 years
5) CT Colonography: Every 5 years
In a patient with known diabetes, these are the cutoffs for perioperative Hgb A1c and blood glucose concentration within 1-4 hours before surgery that are targeted for elective surgeries to avoid post-operative complications such as infection, CV events, and mortality.
What is a Hgb A1c <8% and/or a blood glucose concentration of 100-180 mg/dL within 1-4 hours before surgery?
This treatment modality should be considered for patients with ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis and serum creatinine >3.4 mg/dL (301 µmol/L), rapidly increasing serum creatinine or requiring dialysis, or for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and hypoxemia.
What is plasmapheresis?
These are the recommended minimum durations for dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) based on the following conditions:
1) Bare-metal stent (BMS) for stable CAD
2) Drug-eluting stent (DES) for stable CAD
3) DES for acute-coronary syndrome (ACS)
What are:
1) Bare-metal stent (BMS) for stable CAD: 14-30 days
2) Drug-eluting stent (DES) for stable CAD: 3-6 months
3) DES for acute-coronary syndrome (ACS): 1 year

A patient presents with Na 121. You think they are euvolemic, without hyperglycemia nor any other extra solutes of concern (HLD, protein). You order these labs, with their expected values/cutoffs, in order to diagnose SIADH. (provide >/</=, and provide the numerical cutoff)
What is:
Serum Osm: (Low) <280 mOsm/kg
Urine Osm: (High) >100 mOsm/kg
Urine Na: (High) >40 mEq/L