Associated with flu-like symptoms.
What is Lyme Disease?
petechial or purpuric rash that can progress to hemorrhagic lesions, often associated with fever, sepsis, and meningitis.
What is Meningococcemia?
A rash starting on the neck and spreading to the trunk, this condition can be associated with a red, "strawberry" tongue.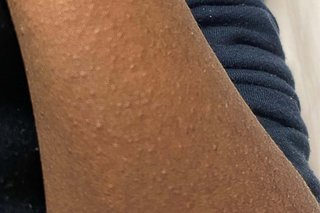
What is Scarlet Fever?
This highly contagious viral infection presents with a characteristic rash that starts as macules, progresses to papules, vesicles, and eventually crusts, often in different stages at once, typically starting on the trunk.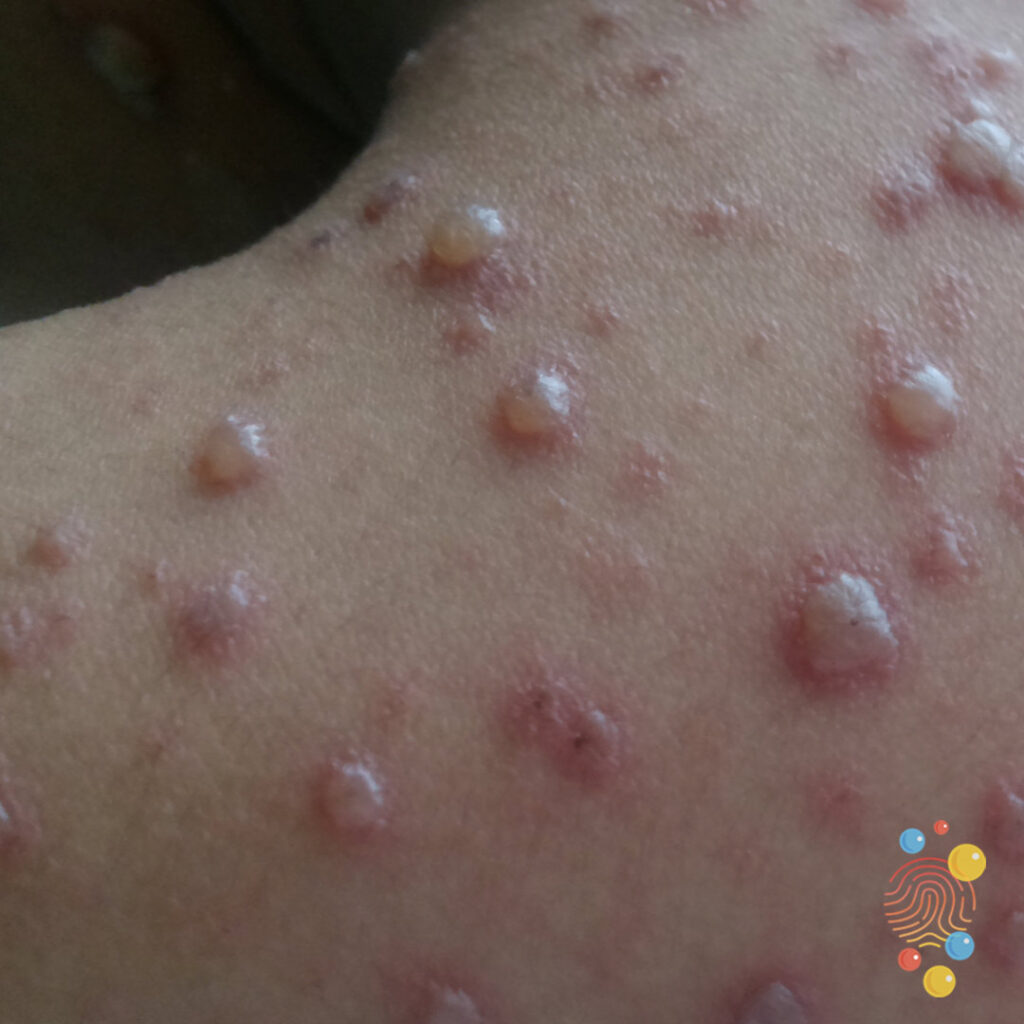
What is Varicella (Chickenpox)?
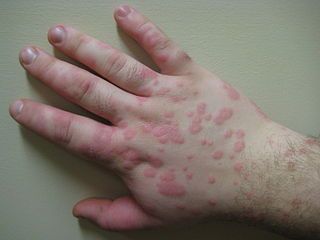
This condition, often a drug-induced hypersensitivity reaction, presents with mucosal involvement and blisters on less than 10% of the body surface area.
What is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)?
Intense pruritus, especially at night, and a characteristic burrow rash seen between the fingers, wrists, and other flexural areas.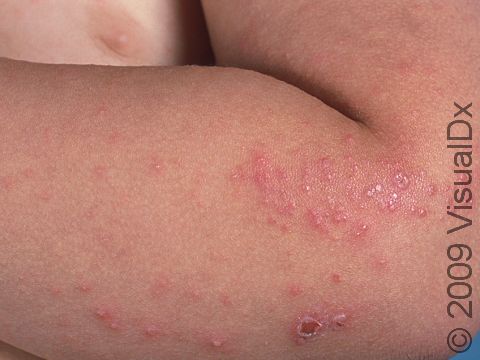
What is Scabies?
This condition, often seen in sepsis or trauma, presents with widespread purpura or ecchymosis due to the consumption of clotting factors, and can lead to multi-organ failure.
What is Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)?
target lesions on the palms and soles, often involving mucosal membranes.
What is Erythema Multiforme?
This eradicated viral infection, which presents with a distinctive rash that starts on the face and hands and spreads to the trunk, features deep pustules that scab over, leaving scars.
What is Smallpox?
This skin condition, most commonly affecting neonates and young children, presents with widespread erythema, flaccid bullae, and positive Nikolsky sign, caused by exotoxins from Staphylococcus aureus.
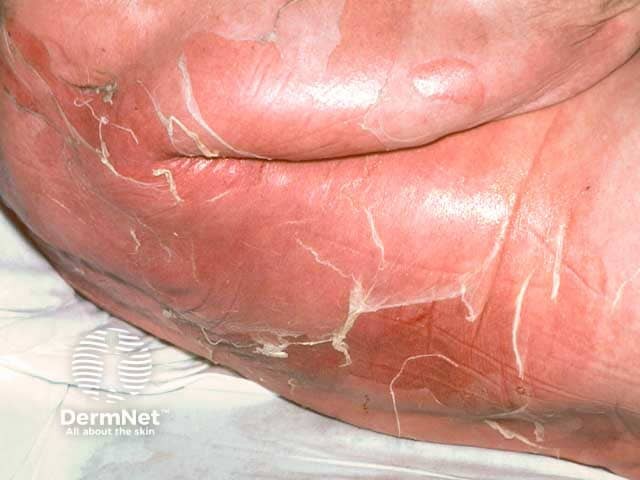
What is Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS)?
This self-limited viral rash often starts with a "herald patch" followed by a characteristic pattern on the trunk, and is more common in young adults.
What is Pityriasis Rosea?
Small, painless, erythematous lesions and tender nodules on the fingers or toes.

What is Infective Endocarditis?
Urticaria, hives, vomiting/diarrhea/SOB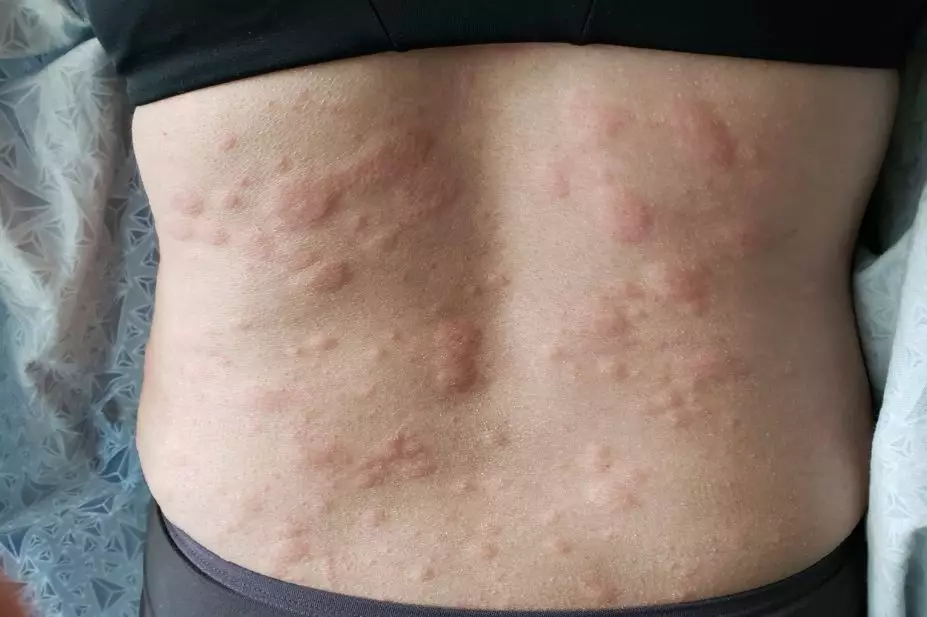
What is Anaphylaxis?
This rapidly progressing soft tissue infection involves extensive necrosis and can cause a purple or blue discoloration of the skin, often accompanied by severe pain and fever
What is Necrotizing Fasciitis?
This severe skin reaction involves widespread sloughing of the epidermis and is often triggered by drugs, with a positive Nikolsky sign.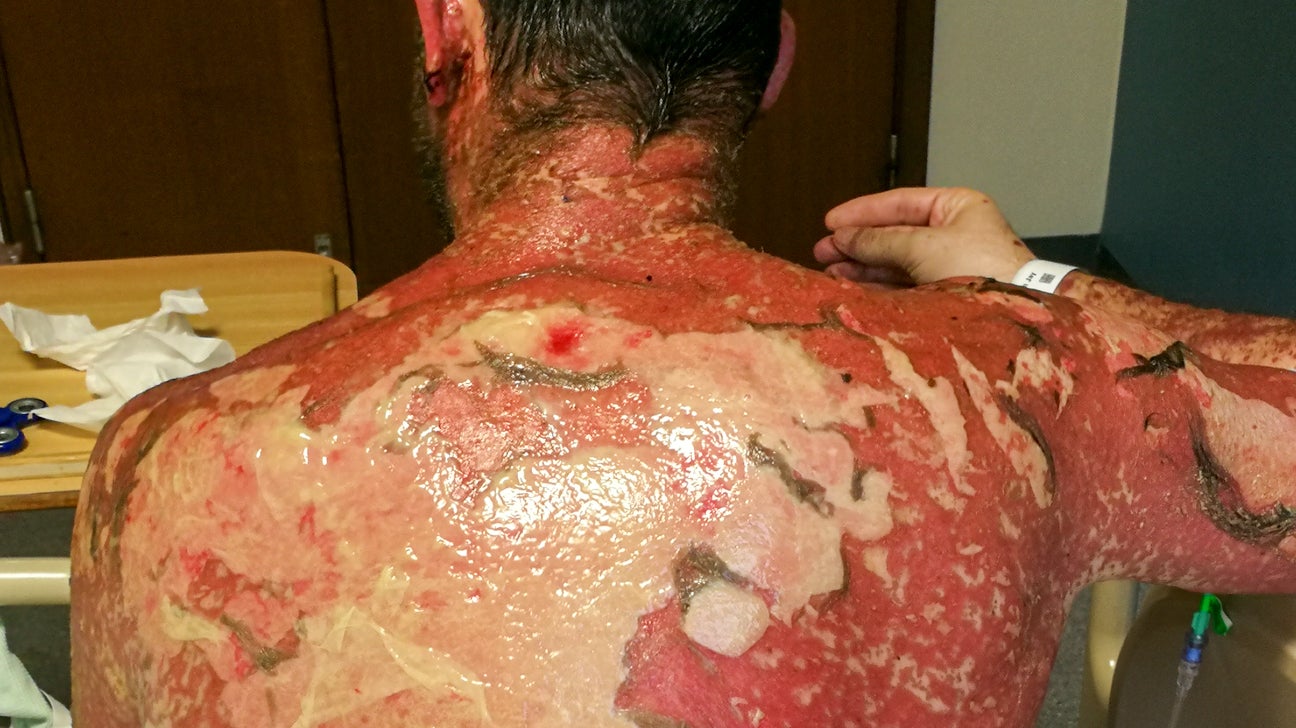
What is Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)?
Well-demarcated, silvery, scaly plaques, most commonly on the elbows, knees, and scalp, and is often associated with nail changes and joint pain.
What is Psoriasis?
Petechiae or purpura, often accompanied by joint pain (septic arthritis)
30930-0/asset/3f00fc8f-8998-44a0-a8d9-3997a9e878c0/main.assets/gr1_lrg.jpg)
What is Gonococcal Infection (Disseminated Gonococcal Infection)?
maculopapular rash that often involves the palms and soles, occurs 2-12 weeks after an initial painless sore (_ _ _ _ _ _ _)

What is secondary syphilis?
Tense, fluid-filled blisters on an erythematous base, often in flexural areas and without mucosal involvement.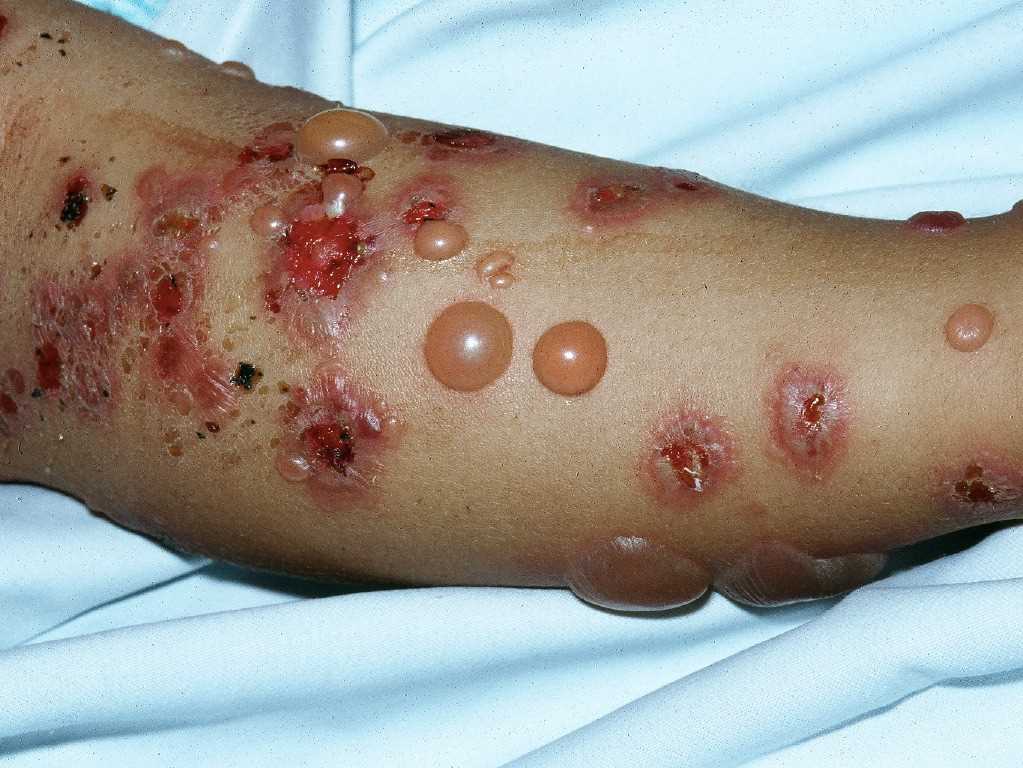
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
This systemic vasculitis in children under 5 years old presents with a classic rash, strawberry tongue, conjunctivitis, and fever lasting more than five days, along with swelling of the hands and feet.
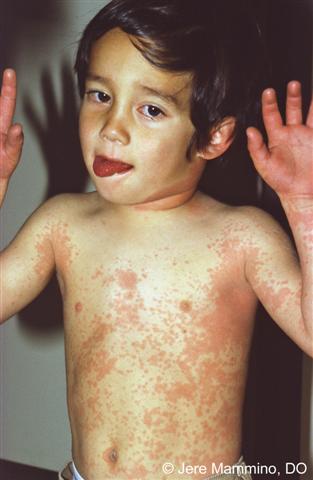
What is Kawasaki Disease?
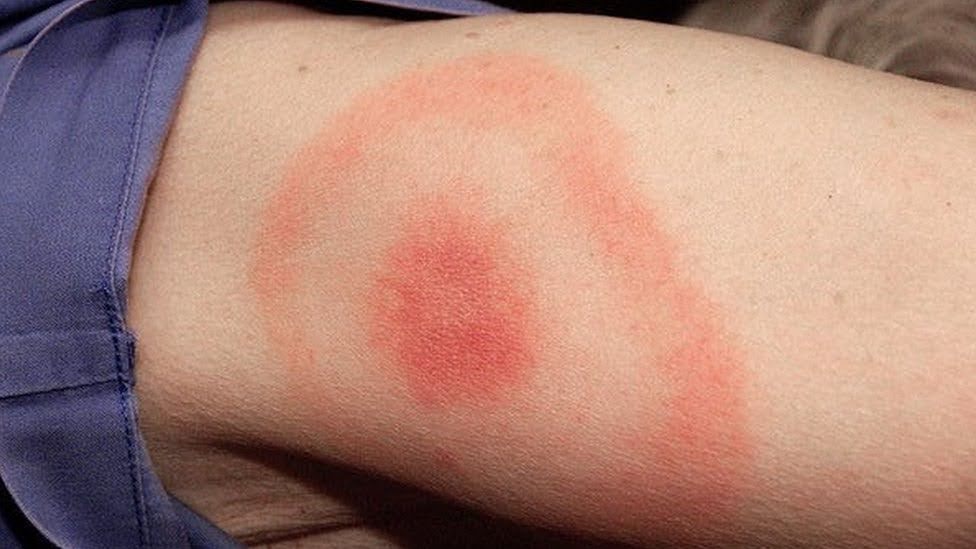
Presents with a petechial rash that starts on the wrists and ankles, often associated with fever, headache. Recent camping trip.

What is Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)?
Commonly affects children, presents with palpable purpura primarily on the lower extremities and buttocks (pressure-dependent areas), along with abdominal pain and joint swelling.
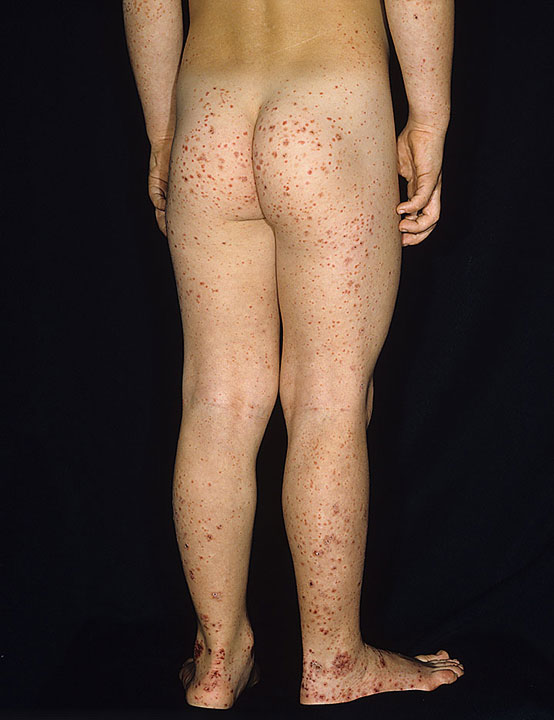
What is IgA Vasculitis?
This rash has a Dermatologic triad –
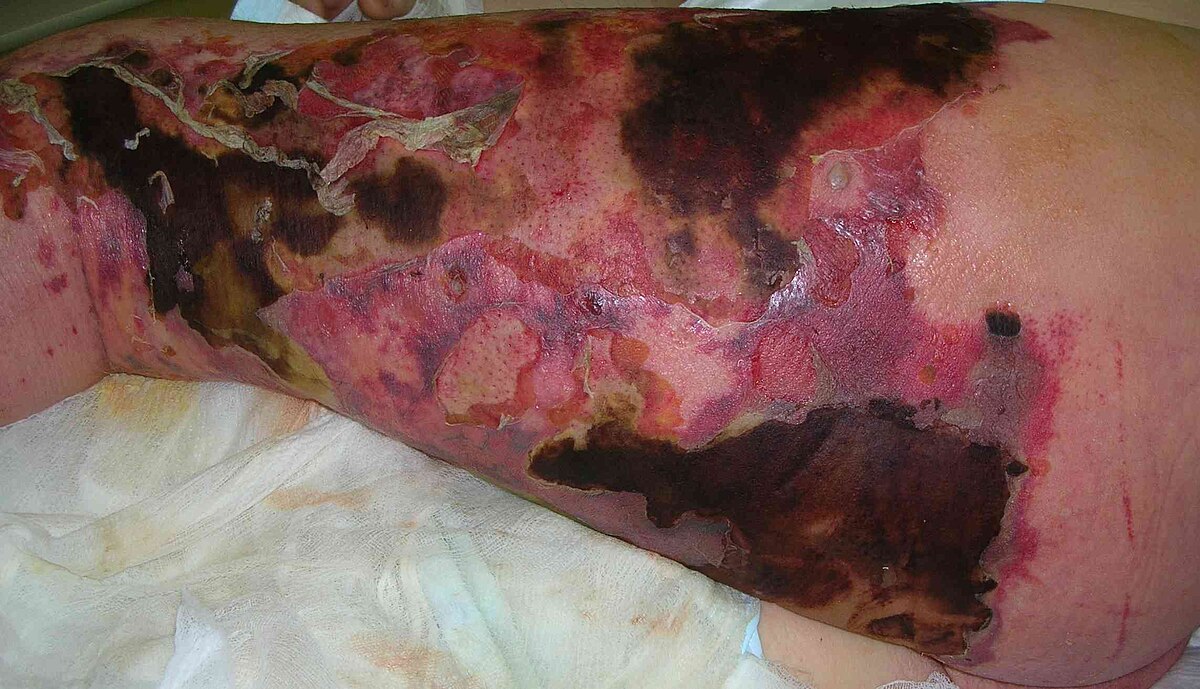
1.Widespread ecchymoses
2.Hemorrhagic bullae
3.Epidermal necrosis
What is purpura fulminans?
Flaccid, easily rupturing blisters and erosions, often starting in the oral mucosa, due to disruption of desmosomal adhesion between epidermal cells.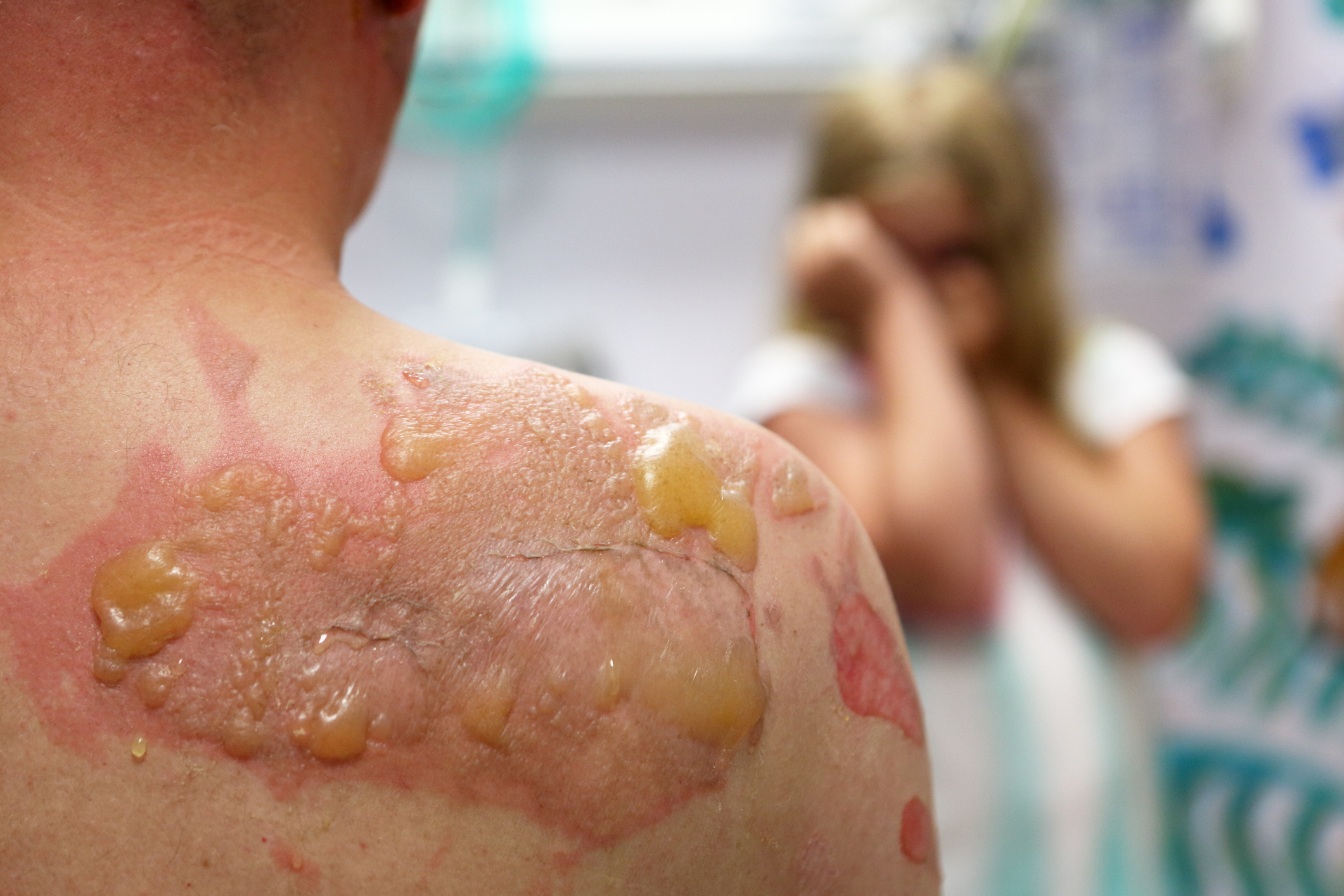
What is Pemphigus Vulgaris?
This rash, often associated with eating spoiled fish, presents as a flushed appearance, urticaria, and warmth due to the histamine release after ingestion.
What is Scombroid Poisoning?