What happens to the reaction rate as you decrease the temperature of the reaction?
Rate decreases
What's the molarity equation?
M = mol solute/L solution
What is the molarity of a 3.0 L solution made with 2.0 moles of K2MnO4?
0.67 M
I want my food to digest faster, so I am sure to chew it up thoroughly.
Does chewing food increase its surface area or decrease its surface area?
Does increasing the molarity make a solution more concentrated or more dilute?
What is the molarity of a solution with 0.32 moles of solute and 560 mL of solution?
0.57 M
Which solution would lead to the fastest reaction rate? Assume all of the compounds are the same.
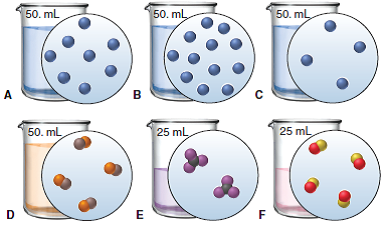
Solution B
Which of these has a higher molarity?

Left beaker (the darker one)
How many grams of CuCl2 are in 200. mL of 2 M solution?
50 g CuCl2
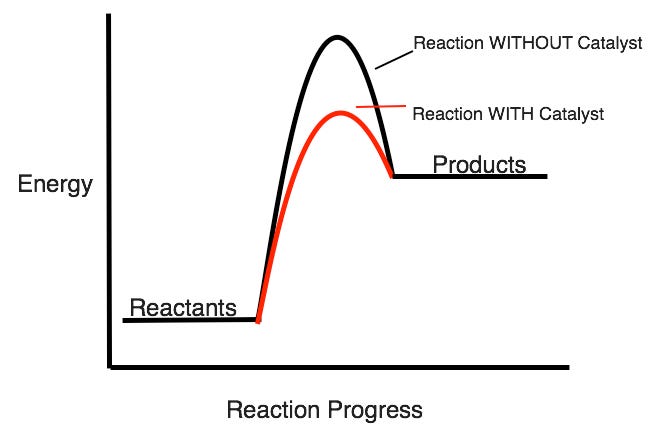
How does adding a catalyst affect the activation energy of a reaction? (raise it or lower it?)
Lowers activation energy
In carbonated water, what's the solute and what's the solvent?
CO2 = solute
water = solvent
A 0.75 M solution is made using 11 g of NaCl. How many mL of solution were made?
250 mL