What is the major muscle of ventilation?
What is the Diaphragm
What are the three types of triggers?
What is
- Time
- Pressure
- Flow
How high over the PIP should we set our high pressure alarm?
What is 10cmH2O above PIP
What temperature should you set your heater to for a patient on NIV?
What is 32
An inspiratory hold gives us what measurement?
What is a plateau pressure?
What is normal cuff pressure when measured in mmHg?
What is 20-25mmHg
What is normal range for V/Q?
What is 0.8-1.2
The force required to move gas through a tube (airway) is referred to as __________
What is Driving Pressure
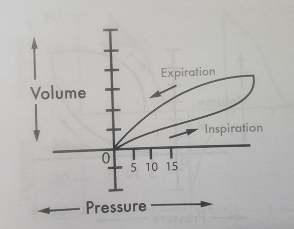
What is an advantage of the following inspiratory flow pattern?
What is...
- Increased I-Time
- More Comfortable for patients
When weaning a patient from an inverse ratio mode, changes should ideally be _______ hours apart
What is 6 hours?
During which part of a breath should an MDI be delivered?
What is inspiration
What is one of the hazards of AutoPEEP?
What is...
- Increase WOB
- Hemodynamic compromise
- Miscalculation of cL
- Barotrauma
- Volutrauma
Classify the following patients Mallampati?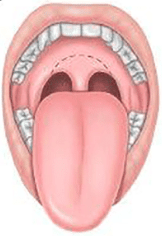
What is Class 2 ?
When there is ventilation in excess of (without) perfusion there is...
Deadspace
List 3 goals for mechanical ventilation
What is...
⚬ Provide pulmonary system with support
⚬ Maintain adequate ventilation
⚬ Decrease WOB
⚬ Restore acid/base balance
⚬ Improve oxygenation
⚬ Improve bronchial hygiene
What are the 5 types of cycles?
What is ...
Volume, Time, Pressure, Flow, High Pressure Limit
According to the NBRC what is the maximum PIP we should have for a patient...
What is <35cmH2O
Based on the following ventilator graphics, what is occurring with this patients lungs?
What is Decreased Compliance?
How do you fix auto-PEEP?
What is...
- Find a way to increase E-time (best option!)
- Changing Mode
- Consider sedation/paralytics
What are the signs of pulmonary complications
I. Decreasing PIP
II. Absent breath sounds
III. Pain and anxiety
IV. Increased HR, RR
What is II, III and IV
True/False
True shunts do not respond to oxygen
What is true
List the 4 factors that affect airway resistance
What is...
1. Viscosity of Gas
2. Velocity of Gas
3. Length of Airway
4. Radius of Airway
A patient in the ICU is intubated and being mechanically ventilated. They are getting a breath delivered every 6 seconds and are not attempting to initiate any spontaneous breaths.
Based on this information, what kind of trigger does this patient have?
What is Time-Trigger
In patients where we are concerned for elevated ICP's, we can prevent elevated ICPs by maintaining our PaCO2 range between....
What is...
25-30mmHg
Based on the following pressure volume loop what can you conclude is occurring?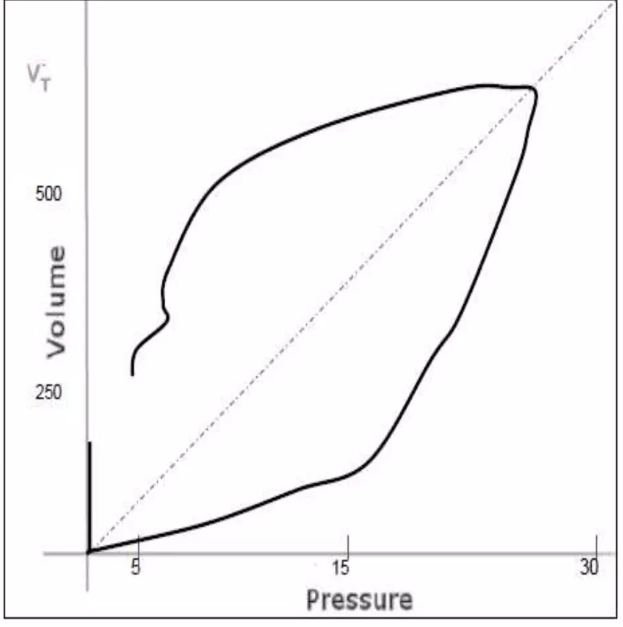
What is a leak?
A sudden zero reading on capnography indicates...
What is...
- Rapid QT drop
- Massive PE
- Leak
- Disconnect
- ETT obstruction
- Apnea
- Cardiac Arrest
True or False
An asthmatic patient would benefit most from a long weaning process?
What is False
Why is A-V Difference useful information for cardiopulmonary status...
What is...
O2 changes occur earlier in the venous system than arterial
True or False
Shunt and AaDO2 are inversely related. Therefore the greater the shunt the smaller the Aa gradient
What is False
- They are directly related. The greater the shunt the larger the Aa gradient
What are the three indications for PS or that more support is needed for a patient...
What is...
- Decreased Spontaneous Vt
- Increased Respiratory Rate
- Increased WOB
You have a patient who has high peak inspiratory pressures and is at risk for overdistention. This patient is not breathing spontaneously and is completely sedated and paralyzed.
Based on this information, what mode would be best for this patient?
What is ...
PC-CMV
The following ventilator graphics tells us that the patient is taking what kind of breath?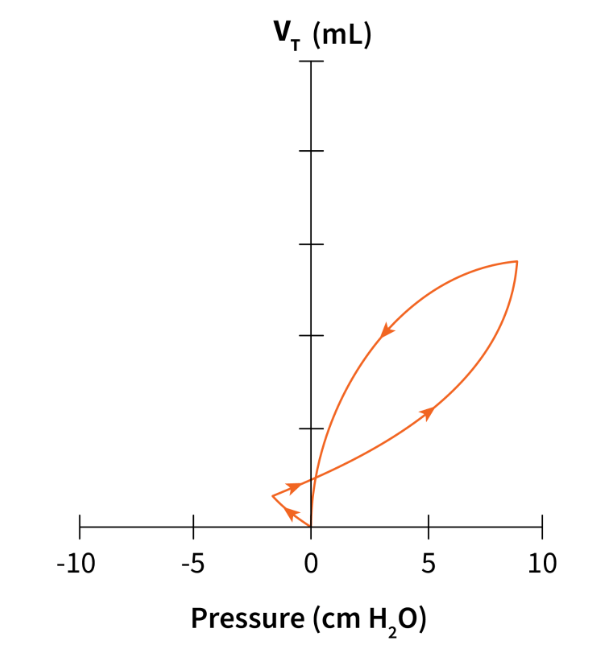
What is an assisted breath?
A-aDO2 is a useful measurement of efficiency of ____
What is gas exchange
You are working in the intensive care unit with your newly trached patient. Upon assessment you notice that the patients trach is pulsating with the patients heart rate. Their respiratory rate is 12, heart rate is 86 and SpO2 is 94% on a trach collar.
At this time what is the best course of action for this patient?
What is ...
- Call the physician this is an emergency, they are at risk for a brachiocephalic rupture
What are the shunt severity levels and what do they indicate?
What is
<10% we are okay with
10-19% there is an intrapulmonary abnormality
20-30% there is significant intrapulmonary disease
>30% it is life threatening
What are the three types of deadspace?
Anatomic
Alveolar
Physiologic
Based on the following characteristics...
- The patient is receiving Machine and Assisted Breaths
- The patient can initiate breaths in between set breaths
- The pressure is variable
- The patient has a set...
- RR
- VT
- FiO2
- PEEP
What mode is this patient in?
What is Volume Control - Assist Control (VC-AC)
What are the 4 kinds of Hypoxia, what happens in each of them?
What is ...
- Anemic Hypoxia: Availability Problem
- Hypoxic Hypoxia: Oxygenation Problem
- Histotoxic Hypoxia: Utilization Problem
- Circulatory Hypoxia: Pump Problem
You have begun caring for a patient in the ICU, they have the following ventilator readings. Based on these readings what can you determine about the patients lungs
Time PIP Vte Pplat RR
7:45am 23 354mL 18 16
11:37am 25 350mL 20 18
3:54pm 30 348mL 27 22
What is Decreased Lung Compliance
You are working with a patient in the ICU and they are intubated and being mechanically ventilated. Shortly after your shift starts you get an ABG and it is as follows...
7.30/40/80/18
Based on the information you have been provided what ventilators should you make on the ventilator to normalize their ABG?
What is no changes, administer bicarbonate!
You are working with a patient admitted to the intensive care unit. This patient had a drug overdose and was intubated for airway protection. Since then the patient has been spontaneously breathing and placed on PC-SIMV. The physician wants to work on getting this patient ready for extubation and has placed a patient on CPAP. This patient is decreased spontaneous tidal volumes but otherwise has normal vitals and work of breathing.
Based on this information, what is the most appropriate thing to do for this patient moving forward?
What is add pressure support?
What is one of the causes of decreased A-V difference...
What is ...
- increased cardiac output
- hypothermia
- cyanide poisoning
- skeletal muscle relaxation
- decreased o2 consumption