Full range of wave frequencies that characterize solar radiation
Electromagnetic spectrum
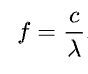 What does this formula calculate? And what is each variable? (specify the units)
What does this formula calculate? And what is each variable? (specify the units)
Frequency of a wave
c = speed of light
lambda = wavelength
Reason geostationary satellites appear "stationary"
Satellites in geostationary orbit (GEO) fly above Earth’s equator, moving from west to east, exactly matching Earth’s rotation:
This instrument shoots laser pulses into the sky and measures how the light bounces back off tiny particles in the air to figure out wind speed and direction.
Doppler LIDAR ( Light Detection and Ranging)
Doppler lidar is defined as a remote sensing technology that utilizes the Doppler effect to measure atmospheric winds by analyzing the frequency change of laser-produced radiation scattered from moving atmospheric particles. It is particularly effective in clear air and can provide detailed observations of wind and turbulence in confined three-dimensional spaces.
Collects data on external stimuli and reflects sunlight
Relationship between wavelength and frequency
The longer the wavelength the lower the frequency.
E = hf says what?
where h = Plank's constant
E = energy of a quantum
Energy is directly proportional to the frequency
Revisit period is related to this type of resolution in remote sensing image
Temporal resolution
Length of time it takes for a satellite to return to acquire another image of the same location
Scientists may choose this type of orbit to compare like-for-like images over time to investigate how weather patterns emerge, help predict extreme weather events, and to accumulate data on long-term problems like deforestation or rising sea levels.
Sun-synchronous orbit (SSO)
2 potential sources of atmospheric interference that energy can en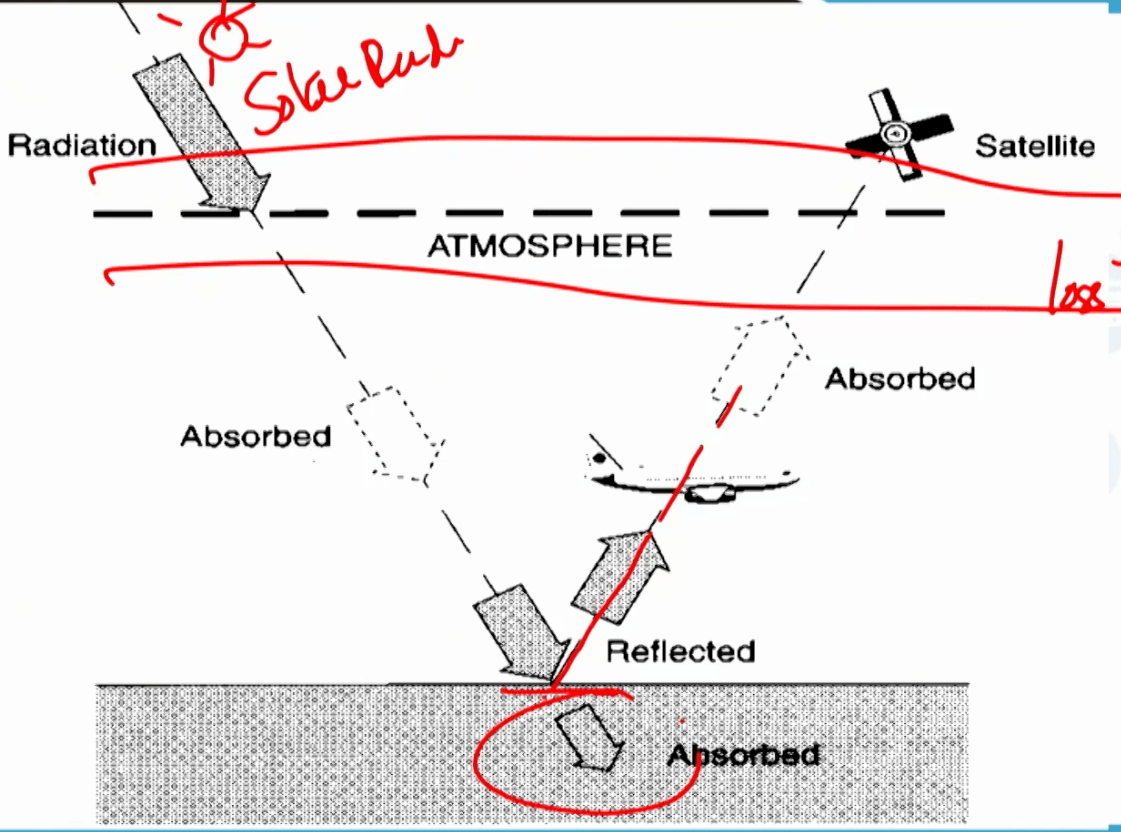 counter
counter
- Scattering (redirection) and or Absorption (conversion of energy into other forms of energy)
List the electromagnetic waves from longest wavelength to shortest wavelength. (clue: the waves are: x-rays, visible light, gamma, microwave, infrared, ultraviolet, microwave)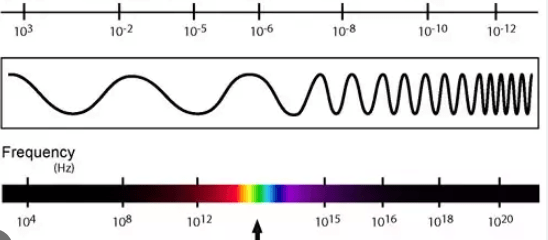 t
t
Radio, Microwaves, Infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, and gamma rays
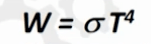
In this formula for total radiant emittance (Watts per meter square)
What is T in this formula? This is the Stephen-Boltzmann law
T is the temperature of the emitting material
Put simply, higher the temperature higher the emittance
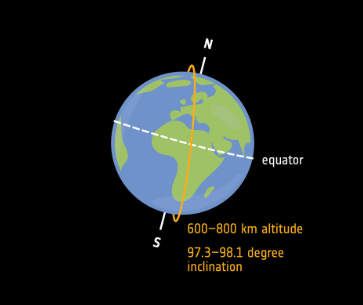
Type of orbit pictured here (in orange)
Sun-synchronous orbit
Type of polar orbit
Matching Earth’s rotation around the Sun
They pass over the same spot on Earth at the same local time every day
Geostationary orbits
what is this showing?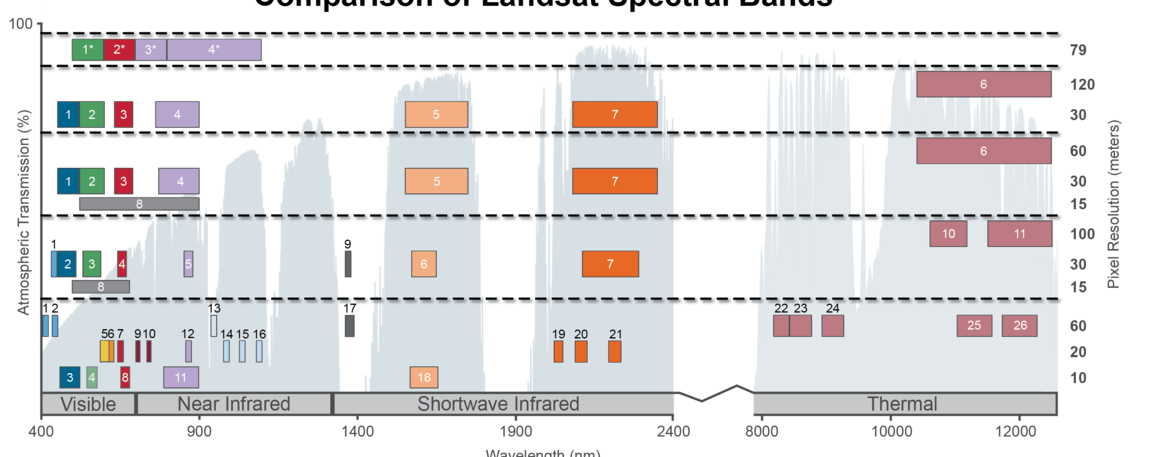
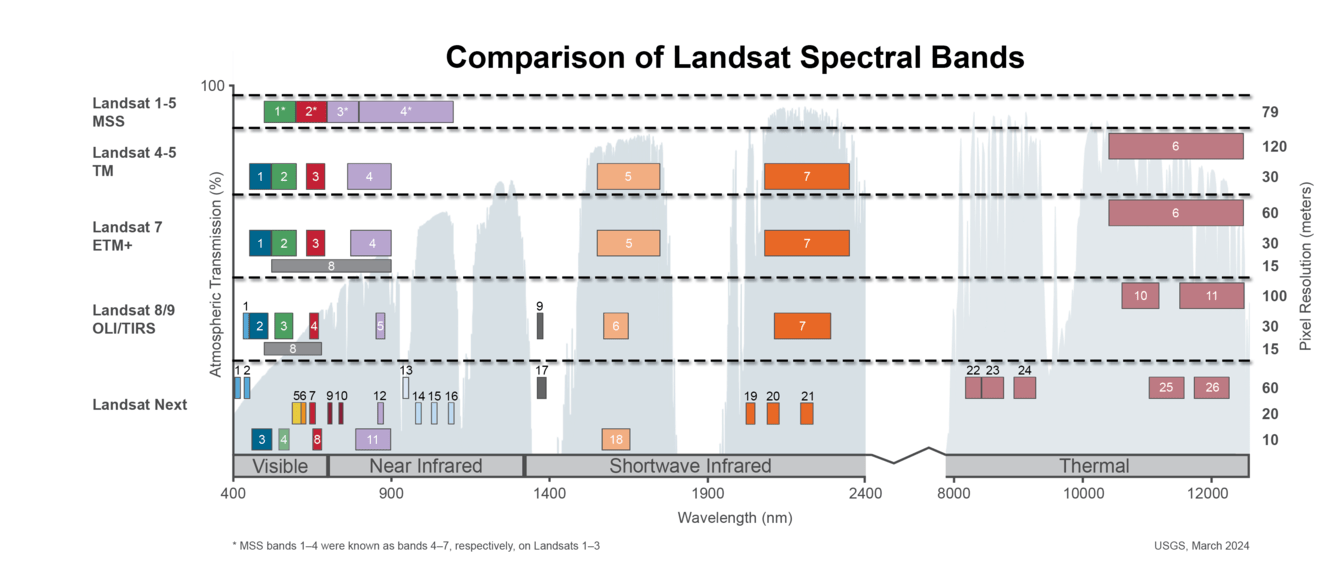
Spectral Bandpasses for all Landsat Sensors - Spectral bands are specific ranges or intervals of wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum that sensors are designed to detect and measure.
What is the frequency of the visible spectrum in order (specify the units)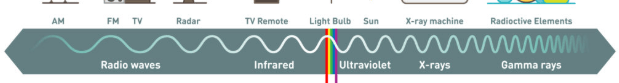
0.4 to 0.7 micrometers
or 400 nm to 700 nm
blue 450-485 nm
green 500-565 nm
red 625-750 nm
Wien's displacement has this to say about temperature and wavelength
As the amount of energy increases with temperature, the wavelength of maximum (peak) emission become shorter.
ISS is a LEO - am I talking about the star sign of the International Space Station?
No - the International Space Station is a lower earth orbit
Not the mythological nymph from the Odyssey, this satellite uses LIDAR to "see" through thin clouids, detect aersols and provide vertical slices of the atmosphere
CALIPSO - Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation used laser pulses to create detailed vertical profiles of Earth's atmosphere
This reflectance curve says this about the reflectance of vegetation
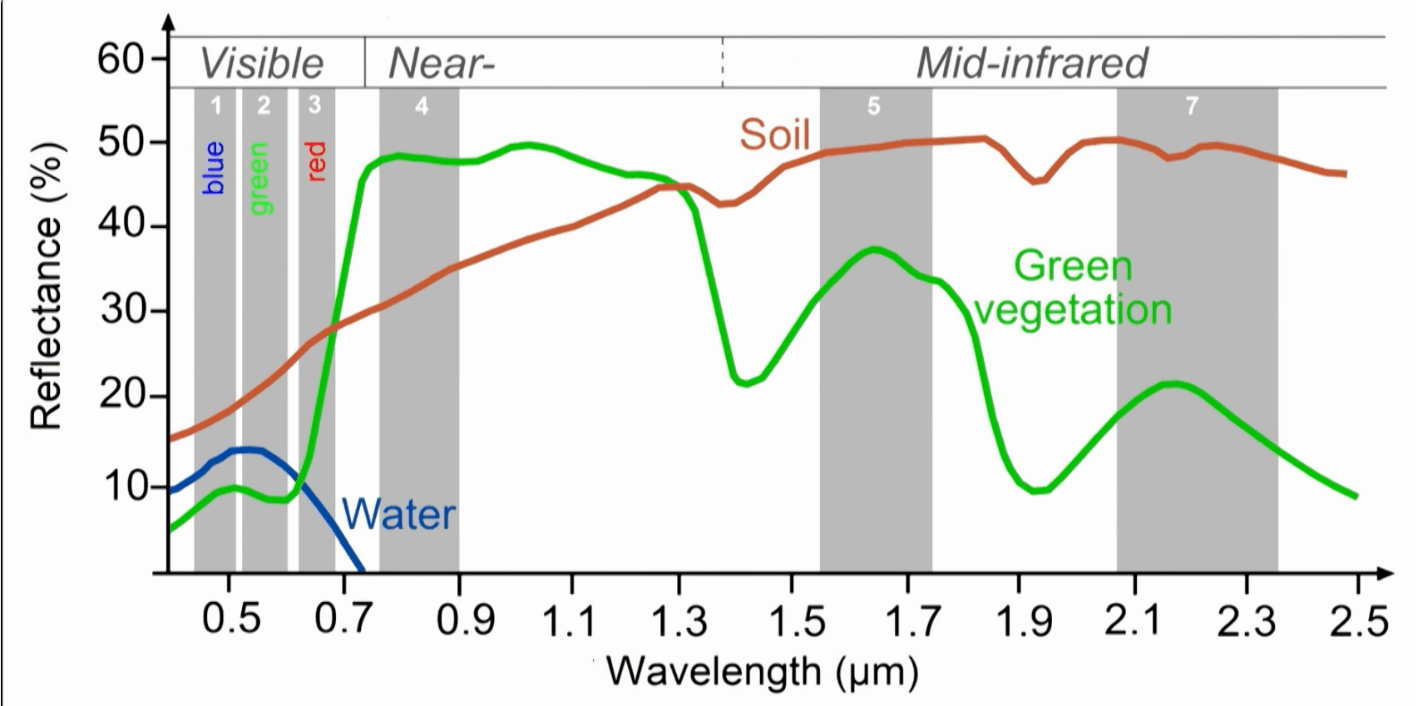
Vegetation reflects highest in the near infrared band (not in the visible band)
The energy carried by an electromagnetic wave
Radiant energy
As shown in this figur, the Sun's temperature of 6000 degrees Kelvin causes its blackbody radiation to peak in this portion of the spectrum explainig why passive remote sensing relies heavily on reflected solar energy during daytime.
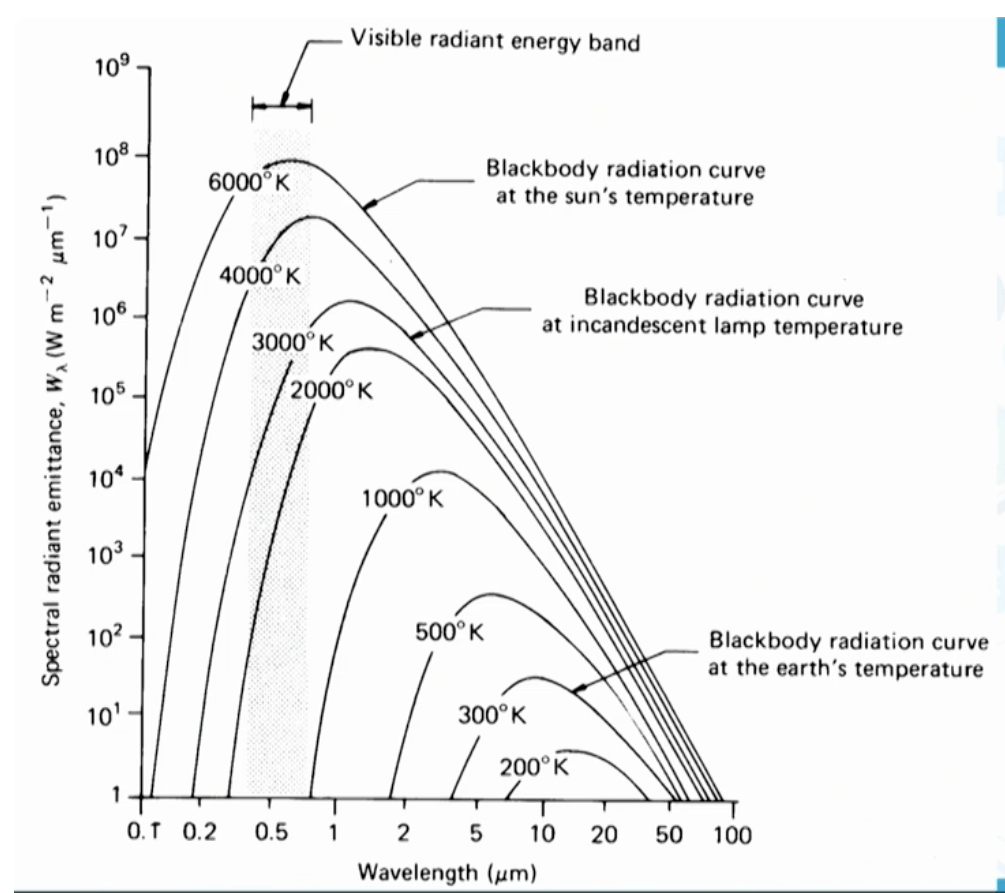
What is the visible region (or visible light)
The figure demonstrates this principle from Wien's displacement law: as temperature increases from 300 K (Earth) to 6000 K (Sun), the peak emission wavelength does this, shifting from the infrared into the visible spectrum.
Figure also illustrates that the Sun at 6000 K has a spectral radiant emittance peak that is many orders of magnitude higher than Earth at 300 K,
This orbital parameter, ranging from 0 for a perfect circle to values approaching 1 for highly elongated paths, is kept near zero for MEO navigation satellites to ensure consistent coverage and signal strength.
What is eccentricity?
Use this sensor to measure sea level rise (Jason-2 had Poseidon-3 for this)
Radar Altimeter -
Radar altimetry is defined as a remote sensing technique that measures the height of the ocean surface and other topographic features using radar signals, enabling the study of surface waves and the relationship between water level and subsurface pressure.
The Poseidon-3 altimeter emits pulses at two frequencies 13.6 and 5.3 GHz to measure the distance from the satellite to the surface
NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) index is calculated in this way using this figure 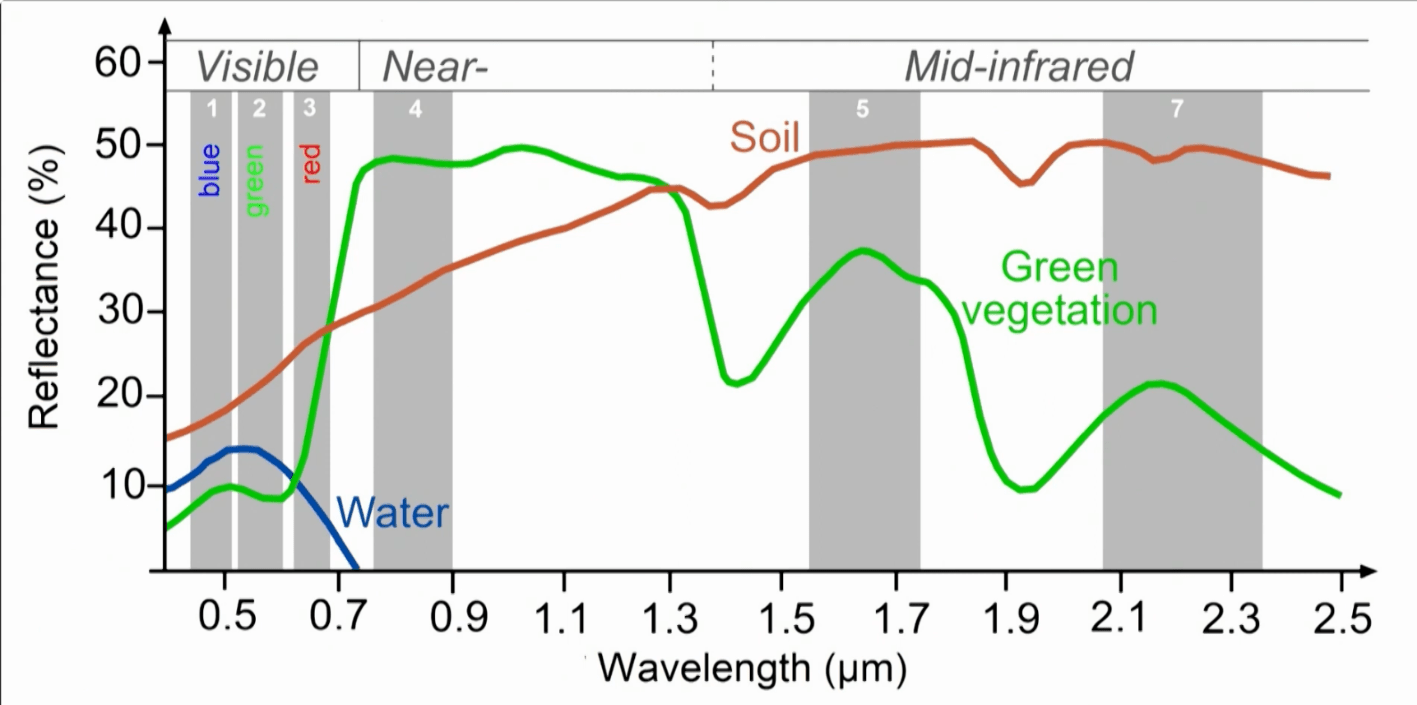
normalized values of the
Landsat Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) is used to quantify vegetation greenness and is useful in understanding vegetation density and assessing changes in plant health.
NDVI is used to quantify vegetation greenness and is useful in understanding vegetation density and assessing changes in plant health. NDVI is calculated as a ratio between the red (R) and near infrared (NIR) values in traditional fashion:
(NIR - R) / (NIR + R)
In Landsat 4-7, NDVI = (Band 4 – Band 3) / (Band 4 + Band 3).
In Landsat 8-9, NDVI = (Band 5 – Band 4) / (Band 5 + Band 4).
NDVI is delivered as a single band product, specified as shown in the table below.