
What is Fabry Disease
2 types of K secretory channels
What are BK Voltage-dependent and ROMK leak-dependent
The only approved treatment for Calciphylaxis
What is Sodium Thiosulfate
EBV sero-negative patients shouldn't receive this drug
What is Belatacept?
DOUBLE POINTS
An IS drug should be stopped before pregnancy
What is MMF?
DOUBLE POINTS
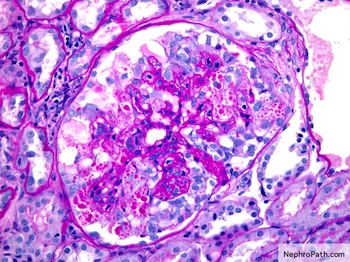
What is Collapsing FSGS?
Amiloride potassium sparing mechanism
What is blocking sodium transport, inhibiting sodium-potassium exchange.
The mechanism of action of amiloride is independent of aldosterone
The difference between home and in-center hemodialysis targeted Kt/v
What standard Kt/v and spKt/v
Cases where Rituximab could be used in transplant
What Are ABO incompatible, desensitization and late ABMR
CS Maintenance period after achieving remission in Adults with MCD
What is 6 months
What is Anti-GB GN
DOUBLE POINTS
Mechanism of hypomagnesemia causing hypokalemia
What is ROMK channel unblocking?
The maximum CVVH filtration fraction
What is 30%
DOUBLE POINTS
Could cause gingival hyperplasia and increase Cyclosporine level
What is Diltiazem?
Epstein syndrome
What is Megathrombocytopenia and autosomal dominant Alport syndrome?
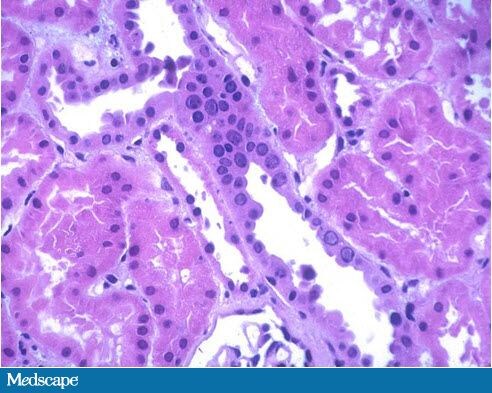
What is BK Nephropathy?
Genes mutations cause familial hyperaldosteronism type II
What are WNK1 and WNK2?
The maximum colony-forming units and an endotoxin concentration allowed in dialysis water
What are 100 (CFU)/mL and 0.25 units (EU)/mL
2 CMV infection conditions, Foscarent should be used as treatment
What Are UL54 mutations and UL97 mutations with 5-10-fold increase in ganciclovir resistance?
LN classes the majority of patient had in ALMS trial
What are LN classes 3 and 4

What is Karyomegalic Nephropathy?
Gene mutation causes hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis with hypomagnesemia and hypocalciuria
What is SLC12A3 mutation?
DOUBLE POINTS
Anticonvulsant with large volume of distribution and highly protein bound could need serial HD or CRRT
What is Carbamazepine?
The majority of studies showed that ATG superior to Basiliximab
What is acute rejection prevention?
Mutation causes familial FSGS, presents at a later age (adolescence or early adulthood)
What is INF2 Mutation?
(encodes a member of the formin family of actin-regulating proteins )
FSGS caused by NPHS1 and NPHS2 mutations, typically present at a very early age
