An organism that reproduces asexually will have offspring that have
(a) The same genetic information as both of its parents
(b) Different genetic information from either of its parents
(c) The same genes as its parent
(d) Different genes from its parents
(c) The same genes as its parent
Which human sex (male or female) does this diagram represent?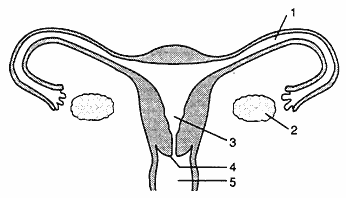
Female
The bud shown in the diagram below was produced by asexual reproduction.

Which process is responsible for the formation of the bud?
A) fertilization
B) recombination
C) mitosis
D) meiosis
C) mitosis
Which sequence represents the correct order of processes that result in the formation and development of an embryo?
a) Meiosis → fertilization → mitosis
b) Mitosis → fertilization → meiosis
c) Fertilization → meiosis → mitosis
d) Fertilization → mitosis → meiosis
a) Meiosis → fertilization → mitosis
Warts result when certain viruses cause skin cells to reproduce at a high rate. What can this rapid reproduction of skin cells be attributed to?
A) cellular digestion
B) mitotic cell division (mitosis)
C) synthesis processes
D) meiotic cell division (meiosis)
B) mitotic cell division (mitosis)
You would expect to see variation in organisms produced
a) Sexually, only b) Asexual, only
c) Both sexually and asexually d) Neither
a) Sexually, only

The process of meiotic cell division begins within this structure.
Number and Name the structure
2, Ovary
Which cell process occurs only in organisms that reproduce sexually?
A) mutation
B) replication
C) meiosis
D) mitosis
C) meiosis
Base your answer on the diagram below, which represents some stages in the development of an embryo, and on your knowledge of biology.

This entire sequence (A through embryo) started with
A) the periodic shedding of a thickened uterine lining
B) mitotic cell division in a testis
C) meiotic cell division in the placenta
D) the process of fertilization
D) the process of fertilization
Regulation of sexual reproductive cycles of human males is related most directly to the presence of which hormone?
testosterone
A pattern of reproduction and growth in a one-celled organism is shown below.
Which statement best describes this pattern of reproduction?
a) All genetic material comes from one parent
b) Only some of the genetic material comes from one parent
c) The size of the parent determines the amount of genetic material
d) The size of the parent determines the sources of the genetic material.
a) All genetic material comes from one parent

Fertilization occurs in this structure
(Number and name the structure)
1, The fallopian tubes
During meiosis, crossing-over (gene exchange between chromosomes) may occur. Crossing-over usually results in
A) overproduction of gametes
B) fertilization and development
C) the formation of identical offspring
D) variation within the species
D) variation within the species
The development of specialized tissues and organs in a multicellular organism directly results from what process?
Differentiation
Where does this process occur?
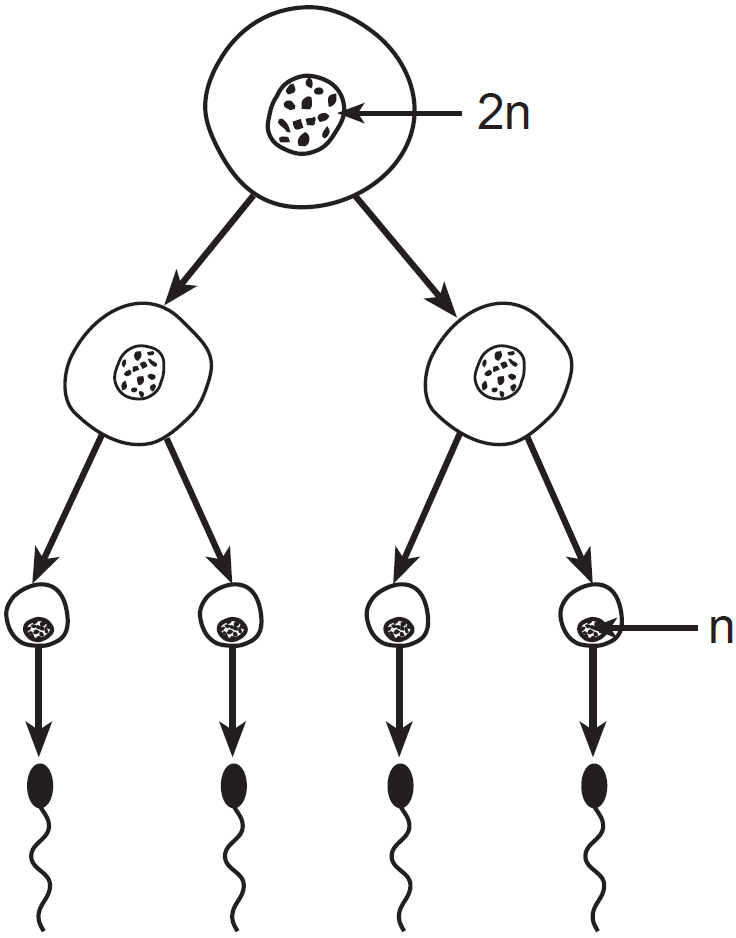
Testes
Provide an example of asexual reproduction
Many possible answers:
Budding, Binary Fission, Regeneration, A flower fertilizing itself, and more
A reproductive system is represented in the diagram below.
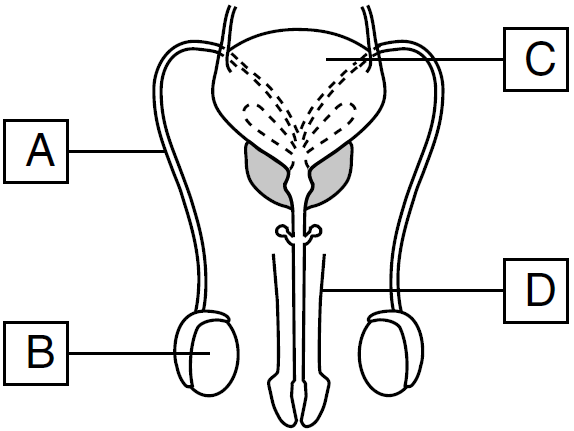
Which structure is correctly paired with its reproductive function?
A) A – pathway of gametes
B) B – synthesis of progesterone
C) C – production of sperm
D) D – regulation of homeostasis
A) A – pathway of gametes
the Vas Deferens
How do human cells resulting from meiotic division differ from human cells resulting from mitotic division?
A) they have twice as many chromosomes
B) they have the same number of chromosomes
C) they have one-half the number of chromosomes
D) they have one-quarter as many chromosomes
C) they have one-half the number of chromosomes
What is the function of the placenta during the internal development of an offspring?
(Name 2)
- Oxygen and nourishment for the developing offspring diffuse across the placenta.
- The placenta allows the exchange of materials, including wastes, between the mother's blood and her developing fetus.
- The placenta protects the fetus from some infections by not allowing blood from the mother to flow to the fetus
Explain how harmful substances in the blood of a pregnant female can enter a fetus even though the blood vessels of the mother and fetus are not directly connected.
- Harmful substances can diffuse/pass through the walls of blood vessels and the placenta.
What are the disadvantages of asexual reproduction?
Without genetic variation, a population is more likely to die out because it cannot adapt to change.
Cancer of the ovary is not common, but when it occurs, the cancer can cause the ovary to malfunction. Identify one possible result of an ovary not performing its intended function in the body.
— No eggs would be produced
— A female might not produce estrogen/progesterone.
— A woman might have difficulty becoming pregnant.
— disrupts the female's menstrual cycle

Explain how process 2 increases genetic variation.
Process 2 combines genetic material from 2 individuals to create offspring that are not the same as the parents.
Identify one way in which the process of growth of a human embryo is similar to the process of reproduction in a single-celled organism.
– They both involve mitosis.
– Both processes produce cells containing identical genetic information.
– The cells are produced asexually.
When a pregnant woman ingests toxins such as alcohol and nicotine, the embryo is put at risk because these toxins can
A) diffuse from the mother's blood into the embryo's blood within the placenta
B) enter the embryo when it eats
C) transfer to the embryo since the mother's blood normally mixes with the embryo's blood in the placenta
D) enter the uterus through the mother's navel
A) diffuse from the mother's blood into the embryo's blood within the placenta