This perspective focuses on unconscious drives and early childhood experiences.
What is the psychodynamic perspective?
The branch of mathematics used for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data.
What are statistics?
A type of study that looks for a relationship between two variables without manipulating them.
What is a correlational study?
The group in an experiment that receives the treatment or manipulation.
What is the experiment group?
The ethical guideline that requires subjects to understand the nature of the study and agree to participate.
What is informed consent?
This perspective emphasizes personal growth and self-actualization.
What is the humanistic perspective?
This measure of central tendency helps us find our average, as in what is my average in this class.
What is mean?
A relationship where as one variable increases, the other decreases.
What is a negative correlation?
The variable that is measured in an experiment.
What is the dependent variable?
The ethical guideline that ensures the identity and information of participants will not be revealed.
What is confidentiality?
This perspective studies mental processes like memory, problem-solving, and perception.
What is the cognitive perspective?
The shape of a symmetrical distribution where most data points are near the mean.
What is a bell curve?
This shows what kind of relationship?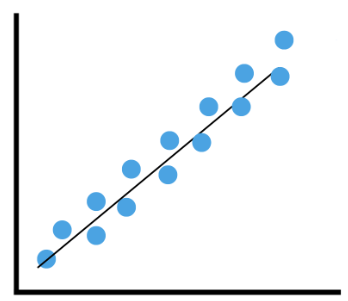
What is a positive correlation?
The group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment.
What is the control group?
A session at the end of a study where the researcher explains the study's true purpose to the participants
What is debriefing?
This perspective explores the links between brain, body, and behavior.
What is the biological perspective?
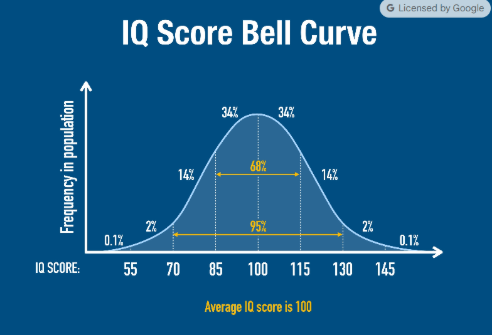
What is the standard deviation in the graph?
The concept that a relationship between two variables does not prove one causes the other.
What is correlation does not mean causation?
Factors other than the independent variable that might affect the dependent variable.
What are confounding variables?
The ethical principle that states researchers must take every precaution to prevent harm to their subjects, both physically and psychologically.
What is protection from harm?
This perspective examines how culture and social norms influence behavior.
What is the sociocultural perspective?
DOUBLE JEOPARDY!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
p < 0.05
What is statistically significant?
In correlation, the idea that correlation does not equal causation because of this hidden variable.
What is a third variable?
The type of music the students listen to, as in this experiment: A researcher wants to investigate if students who listen to classical music before a test perform better than those who listen to pop music.
What is the independent variable?
Professional organization of psychologists.
What is the APA?