This dome-shaped muscle plays a key role in the breathing process.
The Diaphragm
What physical principle is driving air into the lungs during inhalation
Pressure gradient created by the expansion of the thoracic cavity.
This respiratory disorder is characterized by inflamed and narrowed airways, leading to symptoms like wheezing and shortness of breath
Asthma
Name the Law that describes the pressure-volume relationship of gases in a closed system.
Boyle's Law
This organ is responsible for producing sound during speech.
The vocal cords.
The trachea bifurcates into these two tubes
The left and right bronchi
Name the process by which oxygen is transported from the alveoli to the blood.
Pulmonary diffusion
Give the full name of this small device, commonly used by individuals to deliver a short burst of medication in droplet form to help open up airways
Pressurised metered-dose inhaler (pMDI)
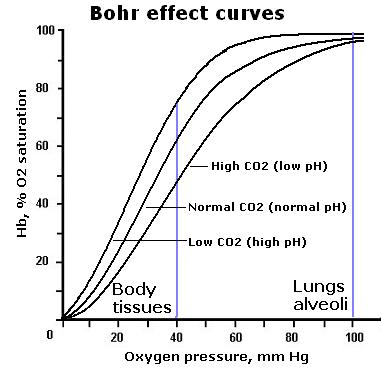
What is the Bohr effect, and how does it relate to respiration?
The effect of pH on oxygen binding to hemoglobin; it facilitates oxygen release in tissues with lower pH
What depth was reached during the deepest free dive on record (without the use of external breathing devices)?
213,9 meters
2007 by Herbert Nitsch
Name two pleural layers that form a pleura space which contains a small quantity of fluid.
The visceral and parietal pleura
These are the primary muscles used during forced exhalation.
The internal intercostal muscles and the abdominal muscles
This therapy is commonly used to treat sleep-related breathing disorder
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
In cases of atelectasis (lung collapse), the pressure in the pleural cavity is typically higher/lower/same than normal.
Higher
Explain what the term "dead space" means in respiratory physiology.
Provide a value.
Space in anatomical airways where no gas exchange occurs (trachea, bronchi).
130 to 180 mL
This part of the brain regulates breathing rhythm and rate
The medulla oblongata
What is surfactant composed of?
90% lipid and 10% protein
What procedure is used to visualize and diagnose conditions inside the airways, obtain tissue samples, remove foreign objects, or treat obstructions
Bronchoscopy
The partial pressure of a gas in a mixture is proportional to this
The concentration of that gas in the mixture
What is the average respiratory rate of a newborn? Provide a range of values. Tolerance +-3 bpm
40-60 bpm
The Hering-Breuer reflex, which prevents overinflation of the lungs, is triggered by stretch receptors located in?
The bronchi and bronchioles
What is the primary driver of respiration in a healthy individual?
Level of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood
What technique is using small, rapid oscillations to deliver breaths at a much higher frequency, aiming to improve oxygenation while minimizing lung injury?
High-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV)
Provide the Re number along with its corresponding unit at the point where airflow transitions into turbulence.
Reynolds number for turbulent flow is >3500.
Dimensionless quantity.
The inertial forces dominate over the viscous forces
The act of sneezing is a powerful reflex, often triggered by irritants. What is the approximate speed at which air can exit the nose during a sneeze?
Provide your gues in km/h
160 km/h