The recommended time it takes while breathing 100% O2 to achieve full de-nitrogenation prior to ETI.
What is 3 minutes?
This is what the acronym SCAPE stands for.
What is Sympathetic Crashing Acute Pulmonary Edema?
A respiratory disease affecting younger children caused by a viral infection and accompanied by a fever, barking cough and may present with stridor.
What is croup?
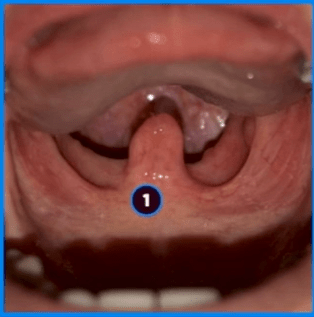
What is the Uvula?
This medication can be continuously given for both hyperkalemia and asthma.
What is albuterol?
This uses a nasal canula that is kept in place and flowing "flush rate" O2 during the ETI attempt and has been shown to decrease the rates of peri-intubation hypoxemia.
What is apneic oxygenation?
This is a measurement of the percentage of blood that is pumped out of the heart with each beat.
What is ejection fraction?
A disease characterized by chronic inflammation, airway narrowing, decreased lung recoil that often presents with dyspnea, productive cough and classically caused by smoking.
What is COPD?
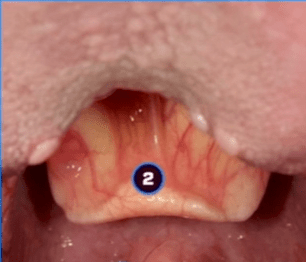
What is the epiglottis?
The dose/kg of IM 1:1,000 epi used to treat severe asthma in a pediatric patient.
What is 0.01mg/kg?
This general position is designed to optimize the view of the cords during laryngoscopy.
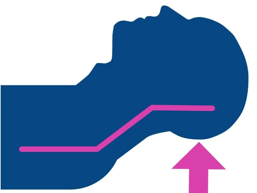
What is flextension?
A type of heart failure defined by stiff ventricles that don't properly relax during the resting phase of the heart beat and therefore results in a low preload and poor cardiac output.
What is diastolic heart failure?
This is the classic EtCO2 wave form in obstructive airway disease.
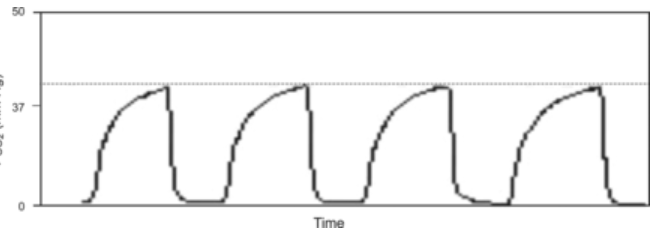
What is a shark fin?
#3
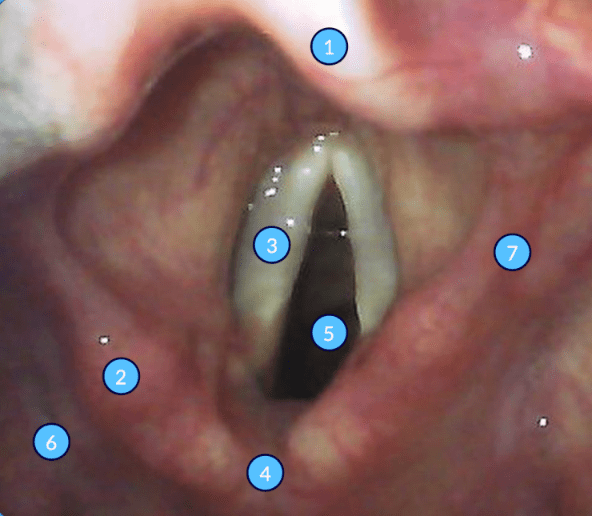
What are the vocal cords?
An anticholinergic that is indicated for bronchospasms secondary to reactive airway disease.
What is Ipratropium Bromide?
This is a technique that uses procedural sedation for the purpose of preoxygenation prior to ETI.
What is Delayed Sequence Intubation?
This is a form of cardiogenic pulmonary edema defined by moderate respiratory distress, slow gradual onset, likely missed dialysis or Lasix Rx, rales, and an SpO2 greater than 90%
What is FOSPE?
A disease characterized by narrowing of the airway lumen caused by smooth muscle contraction, bronchospasms, edema, and mucus production, all contributing to varying levels of recurring airway obstruction.
What is asthma?
#6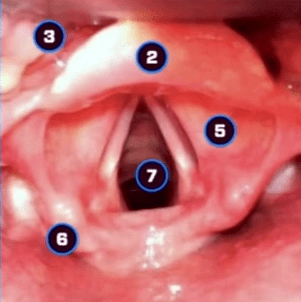
What is the arytenoid cartilage?
This medication causes the relaxation of smooth muscle within the blood vessels resulting in vasodilation.
What is Nitroglycerin?
Hypotension, Hypoxemia and Acidosis
What are the HOP killers?
The starting dose of a nitro drip that is given to a SCAPE patient with a SBP >200mm Hg.
What is 150mcg/min?
The treatment for a complete airway obstruction that is not visible above the level of the vocal cords?
What is ETI to push the obstruction right mainstem?
#4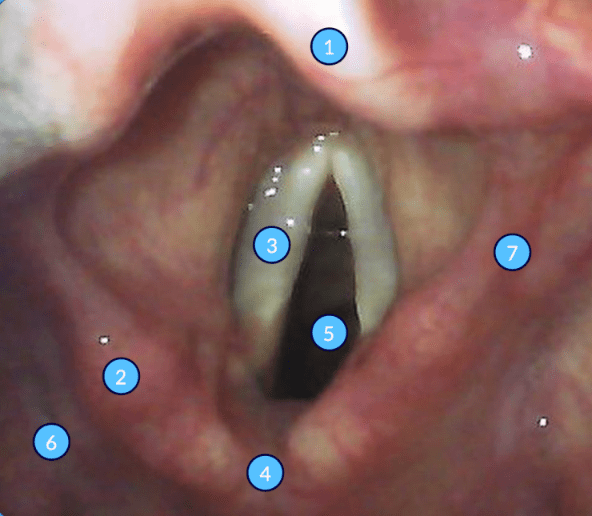
What is the Interarytenoid Notch?
The 3 choices of FiO2 delivery available in the Pulmodyne O2-Max CPAP.
What are 30%, 60% and 90%?