What is normal ETC02?
35-45 mmHg
Difference between oxygenation & ventilation?
Ventilation is the mechanical process of moving air into and out of the lungs, while oxygenation refers to the delivery of oxygen from the lungs to the bloodstream and subsequently to the body's tissues
What is the difference between a pulse ox & end tidal?
Pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation in the blood, while end-tidal CO2 measures the amount of carbon dioxide in exhaled air
Which river is considered the longest in South America?
Amazon River
What is considered Hypercapnia? Most common cause?
-above 45 mmHg
-Hypoventilation
2 diseases under the COPD umbrella?
Chronic Bronchitis & Emphysema
The Shape of a waveform should be..
Rectangular with rounded corners
What has a head, and a tail, is brown, and has no legs?
a penny
What is considered Hypocapnia? Common causes?
-below 35 mmHg
-Hyperventilation or poor metabolic state (shock)
What is the MOA of albuterol?
Beta 2 agonist
Describe how we document ETCO2/Capnography at cars
End-tidal must be documented under "Procedures" in Image Trend
"Z-End tidal carbon dioxide concentration" - nasal ETCO2 placement
"Confirm - ETCO2 capnography" - confirmation of advanced airway placement
Under the "Rx" section of the narrative, provide a rationale for utilizing ETCO2.
When validating data from Lifepak, look for erroneous respiratory rates and ETCO2 values and delete them.
What is the tallest tree species in the world?
The coast redwood
What could this waveform mean? What treatments might you do?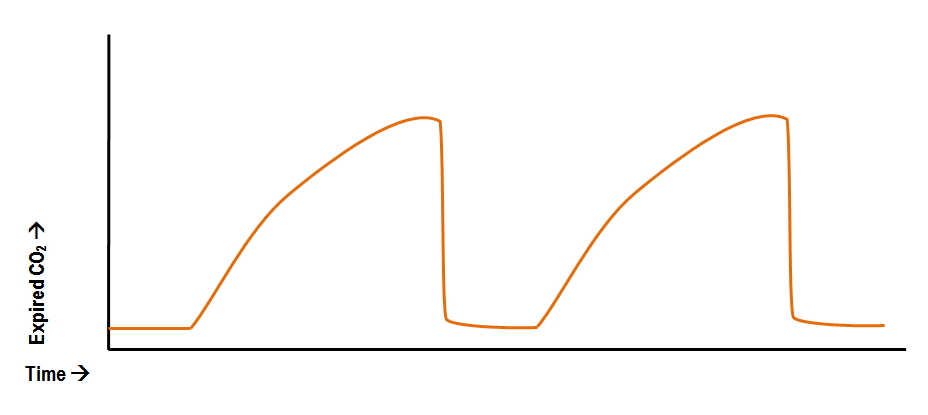
-bronchospasm
-Bronchodilators/epi
Is Asthma an oxygenation or ventilation problem?
When would you give epi?
Ventilation
-Fatiguing patient/ silent chest
If a patient begins to metabolize anaerobically and they become unstable, what is their body most likely deprived of?
oxygen
which blood type is universal recipient?
AB positive
In severe asthmatics, what could a normal wave form/rate mean?
Could mean your patient is tiring out. Attacks start with hyperventilation, as they get tired it normalizes and then will start to retain, having air trapping/acidosis/hypercapnia.
What happens in anaphylaxis? (S&S)
-Exposed to a source/immune response
- edema -Hypotension. -SOB
-swelling. -Urticaria -Tachycardia
-Gi S/S -Diaphoresis
What are some of the specific accessory muscles used in forceful inspiration and expiration?

How many time zones are in the world?
24