Which of the following air passages is the most distal part of the conducting portion of the patient’s lungs?
a. Alveolar ducts
b. Respiratory bronchioles
c. Secondary bronchi
d. Segmental bronchi
e. Terminal bronchioles
e. Terminal bronchioles
A 29-year-old opera singer complains about recent changes in the quality of her vocal sound. Which of the following types of epithelia covers the vocal folds in this patient?
a. Pseudostratified columnar
b. Stratified squamous
c. Simple columnar
d. Simple squamous
e. Stratified columnar
b. Stratified squamous
The squamous epithelial cells that cover most (95%) of the surface area of the pulmonary alveoli are connected to one another through junctions that prevent the leakage of interstitial fluid into the alveolar air spaces. Which of the following types of intercellular junctions serve this important biological function?
a. Cadherins
b. Hemidesmosomes
c. Zonula occludens
d. Macula adherens
e. Zonula adherens
c. Zonula occludens
The respiratory portion of the respiratory system begins at which of the following locations in the lungs?
a. Alveolar ducts
b. Alveolar sacs
c. Alveoli
d. Respiratory bronchioles
e. Terminal bronchioles
d. Respiratory bronchioles
A 19-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of a gunshot wound to the chest. An emergency thoracotomy is performed and, in order to stop bleeding, a segment of the lung is removed. A photomicrograph of a section of resected lung is shown. Which of the following products is produced by the cells indicated by the letter C?
a. Alkaline phosphatase
b. Immunoglobulin
c. Mucus
d. Surfactant
e. Tubular myelin
d. Surfactant
A 15-year-old girl is hospitalized for a new onset of seizures. Tests reveal that she has a concealed 7 months pregnancy. She soon delivers a 1500-gram baby by emergency C-section. The neonatal examination reveals tachypnea, nasal flaring, cyanosis, and expiratory grunting. Which of the following cells are responsible for this condition?
a. Alveolar macrophage
b. Alveolar cells type I
c. Alveolar cells type II
d. Bronchiolar Clara cells
e. Goblet cells
c. Alveolar cells type II
A 4-year-old girl is referred to an allergist for evaluation of wheezing and postnasal drip. Her mother mentions recurrent bouts of bronchitis, but there is little information about birth history due to adoption. On examination nasal polyposis is identified. The girl is diagnosed to have cystic fibrosis. Which of the following cells are responsible for this condition?
a. K cells
b. Goblet cells
c. Ciliated cells
d. Pneumocyte type I
e. Brush cells
b. Goblet cells
A 14-year-old girl with the common cold presents with a “stuffy nose” due to nasal congestion. Which of the following represents a hallmark of the lamina propria in the nasal cavity?
a. Elastic fibers
b. Loose connective tissue
c. Lymphocytes
d. Reticular fibers
e. Rich vascular plexus
e. Rich vascular plexus
A 54-year-old man with a history of smoking presents with hemoptysis and chest pain diagnosed as having adenocarcinoma. The mass is removed, and examination of the tumor margin shows an intrapulmonary bronchus. Which of the following histologic features distinguishes this intrapulmonary bronchus from an extrapulmonary primary bronchus?
a. Absence of submucosal glands
b. Adventitia composed of connective tissue
c. Lack of cartilage in the bronchial wall
d. Loss of respiratory epithelium
e. Presence of cartilage plates
e. Presence of cartilage plates
Which of the following best describes the function of the structure identified in by the arrow in the opposite micrograph?

a. Conditioning of inhaled air
b. Polypeptide hormone secretion
c. Production of secretory IgA antibody
d. Source of pulmonary surfactant
e. Substrate for inflammatory cell adhesion
a. Conditioning of inhaled air
A portion of olfactory mucosa is obtained at autopsy and examined by light microscopy (shown in the image). Identify the structure indicated by the arrow.
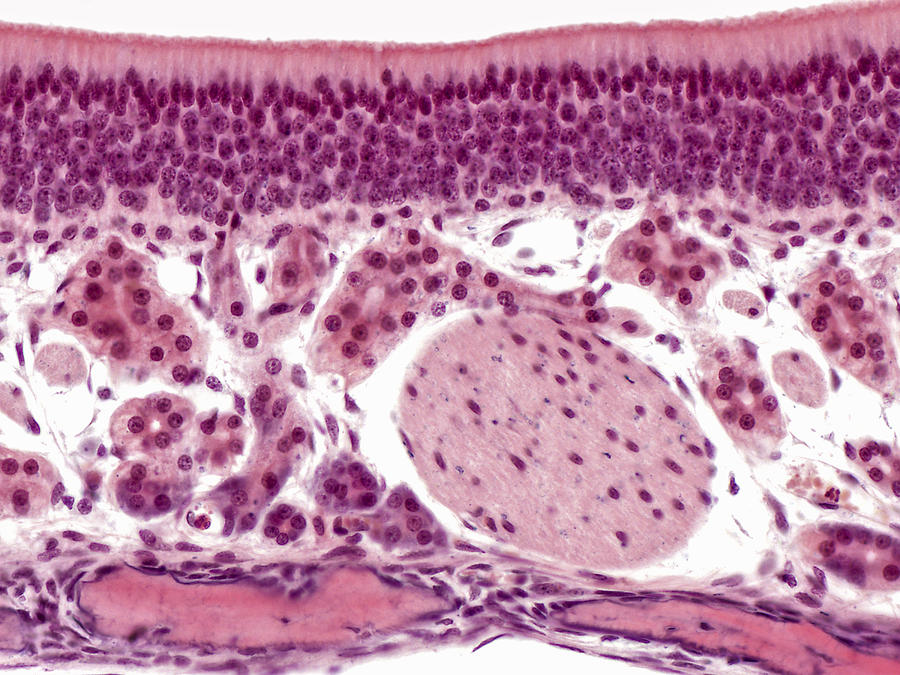
a. Blood vessel
b. Lymphatic nodule
c. Mucous gland
d. Olfactory nerve
e. Bowman`s gland
e. Bowman`s gland
The lung specimen is examined at higher magnification (shown in the image). Identify the structure indicated by the arrow number 3.

a. Basement membrane
b. Dense connective tissue
c. Lamina propria
d. Muscularis mucosa
e. Submucosa
d. Muscularis mucosa
Sections through an intrapulmonary bronchus and a pulmonary artery (shown in the image) are examined in the pathology department. Which of the following tissue components is responsible for the folded appearance of the mucosa in this bronchus?

a. Basement membrane
b. Cartilaginous plates
c. Elastic fibers in the adventitia
d. Fibroelastic tissue in the lamina propria
e. Muscularis mucosa
e. Muscularis mucosa
A 50-year-old woman with leukemia undergoes chemotherapy. During treatment, she develops increasing cough and shortness of breath. Sputum cultures are negative, and the patient does not respond to antibiotic therapy. If this patient has acquired a viral pneumonia, with alveolar damage, which of the following cells can regenerate the alveolar epithelium during healing?
a. Clara cells
b. Enterochromaffin cells
c. Small granular cells
d. Type I alveolar cells
e. Type II alveolar cells
e. Type II alveolar cells
An electron micrograph of the alveolus is examined for evidence of structural changes. The barrier that separates atmospheric gasses from blood features which of the following important biological adaptations?
a. Fusion of epithelial and endothelial basal laminae
b. Gap junctions between epithelial and endothelial cells
c. Interdigitation of microvilli on adjacent epithelial and endothelial cells
d. Sinusoidal alveolar capillaries
e. Tight junctions between epithelial and endothelial cells
a. Fusion of epithelial and endothelial basal laminae
A 72-year-old woman with a history of heavy smoking dies of congestive heart failure. The patient’s lungs (shown in the image) are examined at autopsy. Identify the cells indicated by the arrows.
a. Clara cells
b. Macrophages
c. Neutrophils
d. Plasma cells
e. Type II alveolar cell
b. Macrophages
During cadaver dissection, a student notices that the lymph nodes at the hilum of her cadaver’s lungs appear black. Which of the following best explains the dark color of these hilar lymph nodes?
a. Acute inflammatory cell infiltrate
b. Aggregates of senescent red blood cells
c. Carbon particles within macrophages
d. Pollen and dust within the lymph fluid
e. Primary and secondary lymphoid nodules
c. Carbon particles within macrophages
A 67-year-old smoker presents with increasing shortness of breath and dry cough. He is constantly “gasping for air” and walks with difficulty because he becomes breathless after only a few steps. A chest x-ray discloses hyperinflation of the lungs, and the patient is diagnosed with pulmonary emphysema. This disease is caused by smoking-related injury to which of the following components of the respiratory system?
a. Capillary endothelial cells
b. Respiratory epithelial cells
c. Alveolar septa
d. Submucosal cartilage plates
e. Submucosal mucous glands
c. Alveolar septa
A 71-year-old woman admitted to ICU with pneumonia. She has a history of COPD and CHF. A tracheostomy was inserted to facilitate long-term mechanical ventilation. Mention the right sequence of the tracheal layers that the surgeon cut through?
a. Mucosa, submucosa, cartilage, adventitia.
b. Submucosa, mucosa, cartilage, adventitia.
c. Adventitia, cartilage, submucosa, mucosa
d. Mucosa, cartilage, submucosa, adventitia.
e. Adventitia, mucosa, submucosa, cartilage
c. Adventitia, cartilage, submucosa, mucosa
A 24-year-old man presents with infertility, recurrent sinus infections (sinusitis), and a chronic productive cough. He has had recurrent sinusitis and numerous lower respiratory tract infections since childhood. The cilia of the respiratory tract have which of the following function?
a. are located from the terminal bronchioles to the alveolar sacs
b. beat in a coordinated fashion between 10 and 20 times per second
c. eliminate particles of < 2 um in diameter from the lungs
d. propel mucus and trapped particles toward the alveolar macrophages
e. secrete a thick mucus material that lines the respiratory tract
b. beat in a coordinated fashion between 10 and 20 times per second