The respiratory system is made up of these two functional components.
What are the conducting and respiratory parts?
These structures collectively form the upper part of the respiratory system.
What are the nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx?
These structures collectively form the lower part of the respiratory system
What are the trachea, lungs, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli?
This membrane covers the lungs
What is the pleura?
This is considered the mechanical act of breathing.
What is pulmonary ventilation?
This is the place where air is moistened and warmed before entering the respiratory tract
What is the nasal cavity?
This structure (#8) is shared by both the digestive and respiratory system.
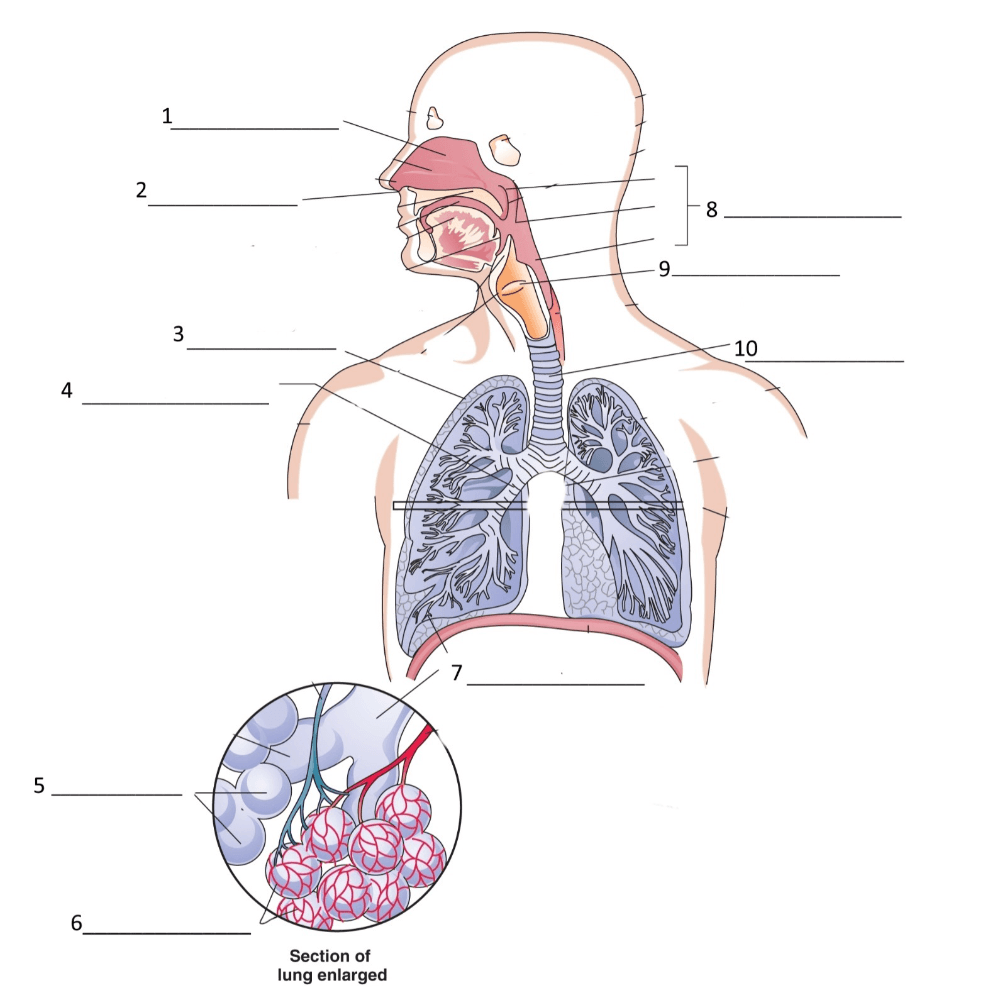
What is the pharynx?
This structure is kept open by C-shaped cartilage and also referred to as the 'windpipe'
What is the trachea?
These structures (#4) are the largest passageways in the lungs.
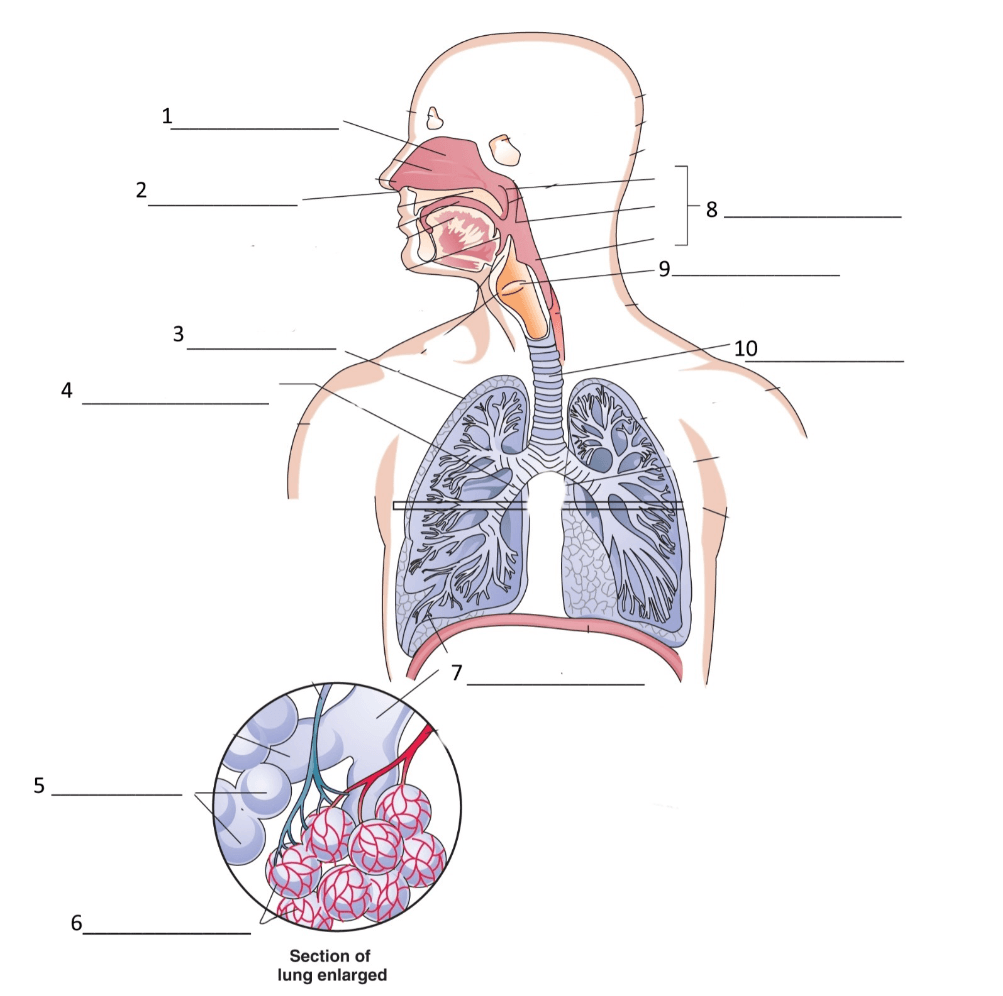
What are the bronchi?
This is the passive part of breathing
What is exhalation/expiration?
Lining of the nasal cavity that is composed of cilia and goblet cells to help filter and warm air as it enters the respiratory tract.
What is the nasal epithelium?
Also known as the voice box, this organ in the throat houses the vocal cords and plays a key role in speech production and preventing food from entering the trachea.
What is the larynx?
The lungs are divided into these distinct sections by deep fissures
What are lobes?
These tiny air passages in the lungs, branching off from the bronchi, play a crucial role in regulating airflow and ensuring efficient gas exchange.
What are the bronchioles?
This muscle is domed-shape and responsible for contraction and relaxation of breathing
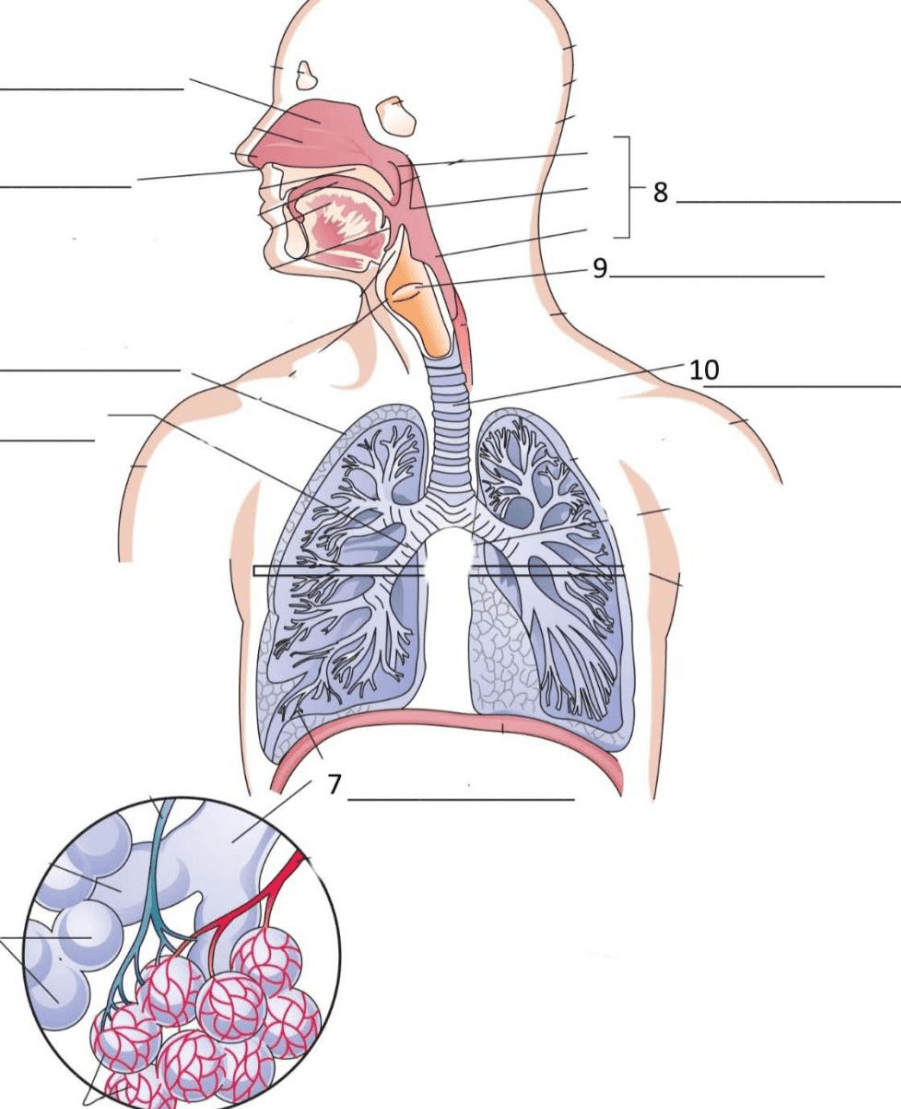
What is the diaphragm?
This lymphatic tissue is located in the throat, but not actually part of the respiratory system.
What are the tonsils?
This automatic response helps clear the airways by forcefully expelling air, mucus, or irritants.
What is the cough?
These tiny hair-like structures, found on the surface of respiratory mucosa, play a key role in moving mucus and trapped particles out of the respiratory tract.
What are mucosal cilia?
These structures are at the end of the bronchial tree and fill with air for the purpose of gas exchange
What are the alveoli?
This gas exchange occurs within the systemic capillaries?
What is internal respiration?
This vital function of the respiratory system involves the coordinated action of the lungs, diaphragm, and structures like the larynx, enabling humans to produce speech and various vocalizations
What is sound production?
This flap-like structure in the throat prevents food and liquids from entering the windpipe during swallowing.
What is the epiglottis?
This thin barrier consisting of the alveolar + capillary walls, is essential for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What is the respiratory membrane?
These delicate structures (#6) are responsible for gas exchange between the air in the lungs and the surrounding blood
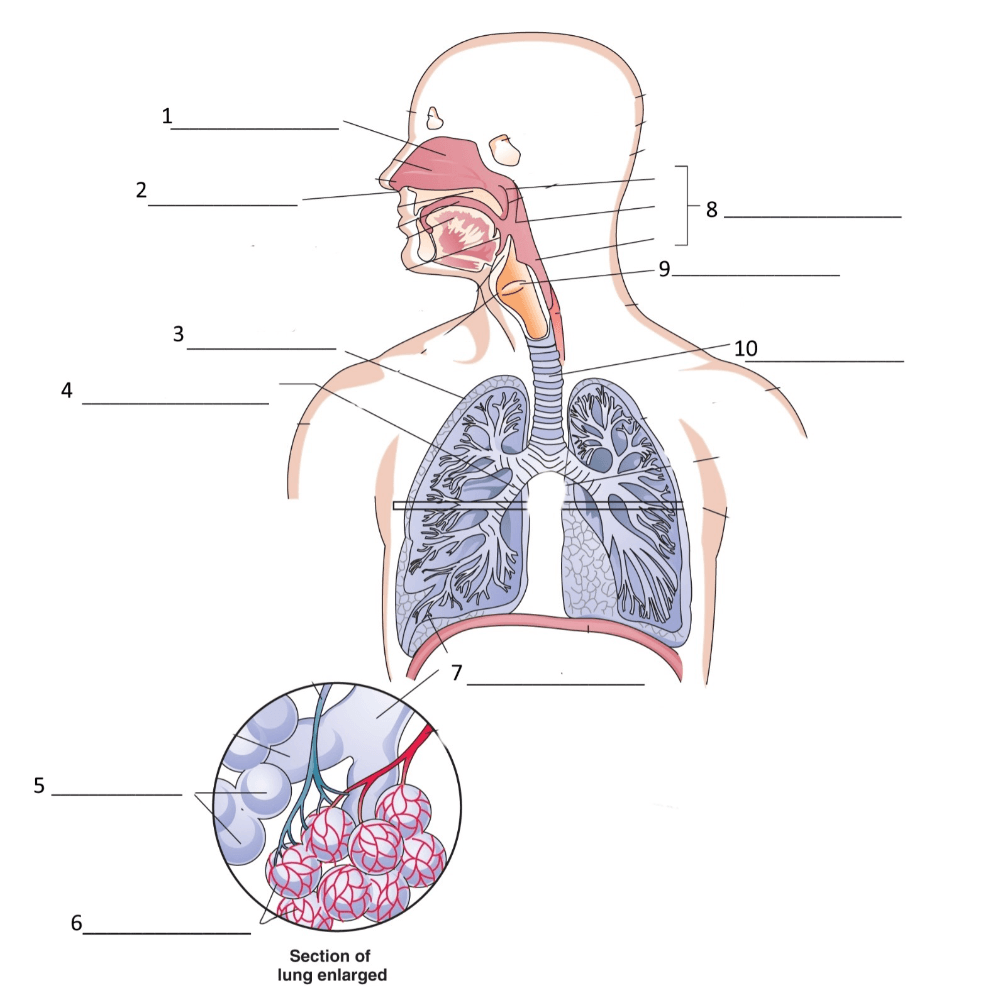
What are the capillaries?
Metabolic reactions generate an excess of this gas, requiring rapid elimination from the body through exhalation.
What is carbon dioxide?