pH 7.35 - 7.45
CO2 35- 45
HCO3 22 - 26
What are normal ABGS ranges.
This measurement represents the percentage of oxygen in the red blood cells.
What is oxygen saturation?
An umbrella term used to refer to Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema
What is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or COPD?
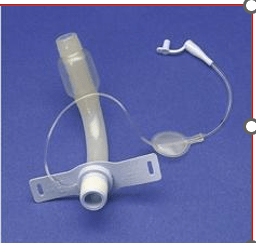
This type of trach allows air to flow freely around the tracheostomy tube and through the larynx, reducing the risk of tracheal damage. You can't use this type of tube in a patient who's receiving mechanical ventilation because oxygen may escape around the tube.
What is an uncuffed trach tube?
A catheter inserted into a large vein to deliver medications, fluids, or nutrition, or to monitor hemodynamics. Common insertion sites include:
- Internal jugular vein
- Subclavian vein
- Femoral vein
Central line or Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
A nurse is caring for a patient with a temporary hemodialysis catheter in the internal jugular. Which action by the nurse requires correction?
A. Dressing the catheter site with a transparent sterile dressing.
B. Using the catheter to administer IV antibiotics.
C. Observe the site for redness, swelling, or drainage during each shift.
D. Flushing the catheter with heparin after the dialysis session.
B. Using the catheter to administer IV antibiotics.
Rationale:
Hemodialysis catheters should not be used for anything other than dialysis unless specifically ordered by the provider in emergencies. This minimizes the risk of infection and catheter dysfunction.
Your patient has a right UE PICC line, and you need to give an IVP medication. The medication will be 1mL in volume. Collect all supplies needed to administer this medication (no vial or blunt needed).
pH 7.57
CO2 28
HCO3 25
What is Respiratory alkalosis?
This measures the acidity levels of oxygen, and carbon dioxide in arterial blood.
What are ABGs or arterial blood gases?
An inflammatory illness of the lung resulting in alveolar fluid accumulation, it is the leading cause of infectious disease in the US
What is pneumonia?
This type of tube allows the adequacy of mechanical ventilation by helping seal the area between the tube and trachea, decreasing a patient's risk of aspiration.
What is a cuffed trach tube?
Regularly monitor the cuff pressure, this type of tube may erode the trachea if the cuff is over-inflated. If the cuff is inflated, the patient can't talk and needs an alternate means of communication.
A serious healthcare-associated infection that occurs when pathogens enter the bloodstream through a central line. It can lead to severe complications, including sepsis, organ failure, or death.
CLABSI (Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infection)
Type of failure of the lungs to eliminate adequate CO2.
What is hypercapnic respiratory failure?
If your patient has a trach, you need to apply oxygen. The patient's order is to apply a humidified trach collar at 50%FiO2.
Gather your supplied and properly hook up your patient to oxygen.
pH 6.96
CO2 71
HCO3 26
What is respiratory acidosis?
Oxygen delivery device used in emergencies and as short-term therapy to patients requiring a high FIO2, the bag must be fully inflated and flow rate set at 10-15L/min
What is a non-rebreather?
Providing good oral care to a patient with a compromised respiratory system can prevent this condition.
What is pneumonia?
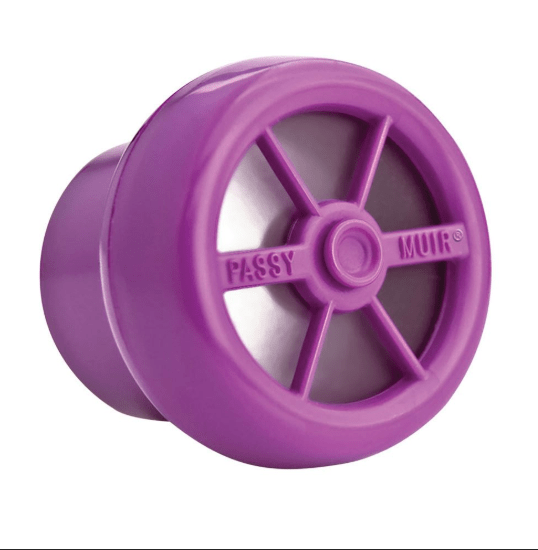
This device attaches to the opening of the trach and allows air flow into the tracheostomy but not out of it. Air is forced around the trach tube and up over the vocal cords allowing sounds to be made.
What is the Passy-Muir valve?

Type of central line for the patient in need of long-term antibiotics, Infusion of Irritant or Vesicant Medications, TPN, Chronic Illness, Frequent blood draws.
What is a PICC line?
A PICC line (Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter) is a type of central venous catheter inserted into a peripheral vein (usually in the arm) and advanced to a large central vein near the heart. It is used for medium- to long-term intravenous (IV) access.
Vital parameter used to determine the concentration of oxygen delivered to patients receiving supplemental oxygen.
The percentage or concentration of oxygen in the gas mixture of room air that a person inhales.
•(FiO2) fractional concentration of inspired oxygen
The gas mixture at room air has a fraction of inspired oxygen of 21%, meaning that the concentration of oxygen at room air is 21%
Your patient has an oxygen saturation of 87% on RA, and RR of 22, and they have a history of COPD.
You have an order to apply O2 as needed to keep sats above 92%.
Choose an oxygen modality and apply it as you would to the patient in bed 1.
pH 7.30
CO2 36
HCO3 16
What is Metabolic acidosis
This Oxygen Delivery device:
Utilizes adapters that twist to set specific FiO2 ranging from 24-50%
Has a set flow according to FiO2 specified on adapter.
Does NOT use a humidifier!
What is a Venturi Mask?
A chronic inflammatory disease of the airway causing airflow limitation and bronchospasm, often triggered by environmental exposure.
What is Asthma?
This type of trach tube permits speech through the upper airway when the external opening is capped and the cuff is deflated.
What is a Fenestrated tube?

Location of a central line that increases the risk of infection.
What is femoral access?
The process of adjusting the concentration or flow of oxygen a patient receives to achieve a specific target oxygen saturation level, typically measured using pulse oximetry. The goal is to ensure the patient receives adequate oxygenation without over-supplying oxygen
What is oxygen titration?
On Chester Chest, identify the central venous cath that is always present but requires an additional intervention to access.
pH: 7.54
PaCO₂: 48 mmHg
HCO₃⁻: 39 mEq/L
What is Metabolic Alkalosis?
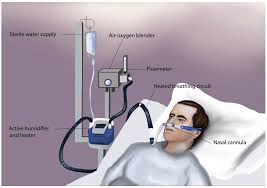
This oxygen device is a newer form of respiratory care with four key benefits:
Accurate delivery of up to 100% oxygen. Washout of anatomical dead space. Delivery of positive airway pressure. Optimized mucociliary clearance
What is High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC)
Collection of air or gas in the pleural cavity between the chest wall and the lung causes include spontaneous rupture of a bleb, bullous emphysema or chest trauma
What is a pneumothorax?
Something that is added to the oxygen delivery system for a patient with a trach.
What is humidification?
Humidification is used to moisten the air, which is essential for patients with a tracheostomy as the air bypasses the natural humidification provided by the nose and mouth.
Nursing interventions to decrease the risk of CLABSI. (Name as least 4)
- Perform daily assessments of the line's necessity. Including the interdisciplinary team.
- Follow aseptic technique when accessing the line.
- Use a chlorhexidine(CHG)-impregnated dressing or antiseptic cap.
- Scrub the hub for 15 seconds prior to every access.
- Perform regular flushing to maintain line patency.
- Ensure sterile technique for dressing changes.
- Use of CHG wipes as indicated by facility policy.
Equipment needed at the bedside for all trach patients (name at least 3)
What is:
Extra tracheostomy tube and obturator (same size, and one size smaller)
· Resuscitation bag attached to an oxygen source (readily available for easy access in case of an emergency)
· Humidification device, oxygen monitoring equipment. (as ordered- consult with Respiratory Therapy)
· Suction equipment (canister, connecting tubing, gauge, catheters)
· Disposable inner cannula (if using disposable system)
· Trach cleaning kit (if non-disposable system is used)
sterile water for rinsing inner cannula or suction catheter
Gather supplies and set up suction. You have orders for low continuous suction.