Conditions
Conditions
Conditions
This process leads to a narrowing of the airway due to contraction of the bronchial smooth muscle.
What is bronchospasm?
This chronic respiratory disease is characterized by persistent airflow limitation due to exposure to noxious gases and particles.
What is COPD?
A pH below 7.33, a PaCO2 above 47 mm Hg, and HCO3 24 indicate this imbalance.
What is respiratory acidosis?
These are effective dietary recommendations to promote wound healing.
What is a high-protein diet with vitamin C?
The gradual loss of this type of vision is one of the hallmark symptoms of glaucoma.
What is peripheral vision?
A fracture in one of the long bones of the body places the client at risk for this life-threatening complication.
What is a fat embolism?
This term describes the swelling of the airway lining due to inflammation, leading to a reduced airway diameter.
What is mucosal edema?
This device is often given to clients with asthma to monitor their airway status at home.
What is a peak flow meter?
The nurse should wear this type of mask when caring for a client with TB.
What is an N95 respirator?
This method is used to estimate the total body surface area (TBSA) affected by burns.
What is the Rule of Nines?
This common symptom of glaucoma creates a bright ring around lights.
What is the halo effect?
A client in skeletal traction must have weights positioned in this way.
What is hanging freely?
This is a priority when treating a client with carbon monoxide poisoning.
What is "pure" oxygen or hyperbaric oxygen?
This pathophysiological condition in COPD is characterized by increased mucus secretion, goblet cell hyperplasia, and submucosal gland enlargement.
What is chronic bronchitis?
This physical finding, characterized by an increased anteroposterior chest diameter, is a feature of severe COPD.
What is barrel chest?
A client presents with burns covering the entire left arm, right arm, and front torso. Using the Rule of Nines, this is the estimated percentage of body surface area burned.
What is 36%?
This common age-related change in vision affects the ability to focus on close objects.
What is presbyopia?
This complication occurs when increased pressure within the fascia compresses nerves and blood vessels, reducing perfusion to the affected limb.
What is compartment syndrome?
These white blood cells release leukotrienes and contribute to the late-phase inflammatory response in asthma.
What are eosinophils?
In emphysema, destruction of this structure leads to airway collapse and loss of elastic recoil.
What are alveolar walls?
A pH above 7.49, normal PaCO2, and HCO3 30 indicate this acid-base disturbance.
What is metabolic alkalosis?
Position changes should be done this often to prevent pressure ulcers.
What is every 2 hours?
A client recovering from cataract surgery should immediately report this symptom to their provider.
What is severe eye pain?
To reduce swelling and pain, ice should be applied intermittently for this recommended timeframe after a soft tissue injury.
What is the first 24 to 48 hours?
A hallmark sign of an acute asthma attack, this high-pitched whistling sound occurs due to narrowed airways.
What is wheezing?
Influenza is primarily spread through this transmission route.
What is droplet transmission?
Clients with advanced COPD commonly sit in this position to facilitate breathing.
What is leaning forward (tripod position)?
A client with a suspected inhalation injury from a fire should be monitored for this respiratory sound, which is considered a medical emergency.
What is stridor?
A nurse administering timolol eye drops for glaucoma should monitor for this systemic adverse effect.
What is bradycardia?
These three types of injuries are commonly used to describe damage to soft tissues.
What are strains, sprains, and contusions?
This process, characterized by rapid breathing, occurs in response to hypoxemia and leads to a decrease in carbon dioxide levels.
What is hyperventilation?
A severe, life-threatening asthma attack that does not respond to standard treatment.
What is status asthmaticus?
This pulmonary function test is the gold standard for diagnosing COPD.
What is spirometry?
A patient recovering from chickenpox is at risk of developing this condition later in life due to the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus.
What is shingles?
Hearing impairment can lead to social isolation due to difficulty in engaging in this essential aspect of human interaction.
What is communication?
The "six P's" used to assess for compartment syndrome include pain, paresthesia, paralysis, pallor, pulselessness, and this condition, which refers to abnormal temperature regulation of the limb.
What is poikilothermia?
This is the most common type of asthma, often associated with a history of hay fever, eczema, or allergic rhinitis.
What is allergic asthma?
Clients with tuberculosis must be placed in this type of precaution.
What is airborne precautions?
The ratio of these two spirometry values is used to determine airflow limitation in COPD.
What are forced expiratory volume (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC)?
This stage of pressure ulcer involves full-thickness loss of skin, exposed adipose tissue and undermining or tunneling may occur.
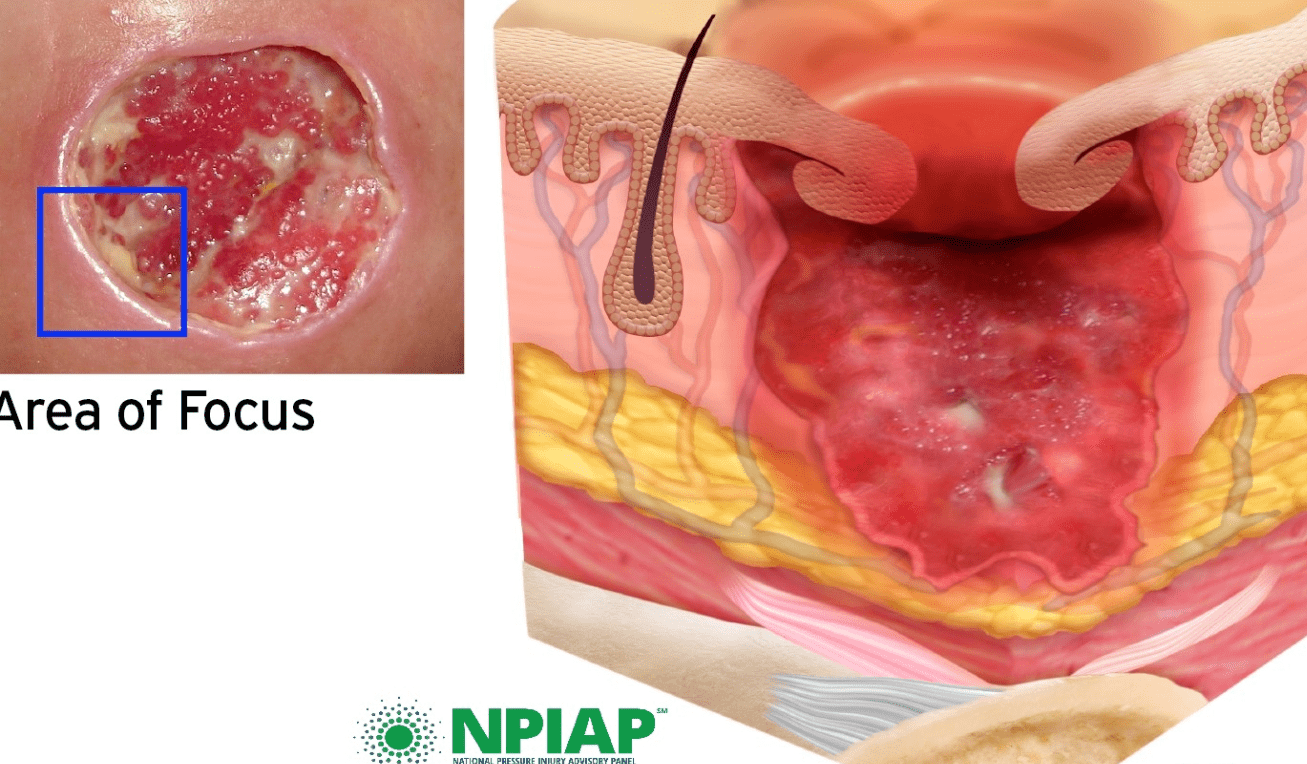
What is a Stage 3 pressure ulcer?
To improve understanding, a nurse or caregiver should ensure that the client has a clear view of this facial feature when speaking.
What is the speaker’s mouth?
Weight loss is a recommended intervention for both gout and this degenerative joint disease to reduce stress on affected joints.
What is osteoarthritis (OA)?
Shallow respirations and bradypnea will most likely result in this acid-base imbalance.
What is respiratory acidosis?
This is the single most important risk factor for developing COPD.
What is smoking?
This non-invasive test measures oxygen saturation in the blood and is commonly used to monitor COPD severity.
What is pulse oximetry?
Inhalation injuries from burns can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning because CO binds to this molecule in the blood.
What is hemoglobin?
This seemingly harmless movement should be avoided after surgery because it can increase intraocular pressure.
What is bending over?
This form of arthritis results from the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and severe pain episodes.
What is gout?
This pulmonary function test is used to assess lung function and often reveals an obstructive pattern that improves with bronchodilators.
What is spirometry?
COPD prevalence is highest among this age group.
What is adults over 60 years old?
This class of medications is used for both immediate relief (short-acting) and long-term management (long-acting) of COPD by relaxing airway muscles.
What are beta-2 agonists?
A pressure ulcer characterized by non-blanchable erythema but no skin breakdown is classified as this stage.
What is Stage 1?
Following cataract surgery, clients should avoid strenuous activities such as bending over or lifting more than this weight limit to prevent increased intraocular pressure.
What is 10 pounds?
This type of arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation of the synovial membrane, leading to joint damage.
What is rheumatoid arthritis (RA)?
This class of medication is considered a quick-relief treatment for asthma, working by relaxing the airway muscles.
What are short-acting beta-agonists (SABAs)?
This symptom is an early indicator of impaired oxygenation in a client with respiratory distress.
What is restlessness or agitation?
This class of drugs, commonly used in COPD, blocks M3 receptors in smooth muscle to prevent bronchoconstriction.
What are antimuscarinics?
This burn classification destroys both the epidermis and dermis and requires a skin graft for healing.
What is a full-thickness (third-degree) burn?
Clients should notify their healthcare provider if they experience any of these postoperative complications, such as purulent drainage, floaters, or sudden eye pain.
What are signs of infection or complications?
A diagnostic test for gout involves analyzing synovial fluid for these needle-shaped crystals.
What are uric acid crystals?