Concepts
Functions of this structure include to warm air, detect odors, and amplify the voice.
What is the nose?
Commonly called the Adam's apple.
What is the laryngeal prominence?
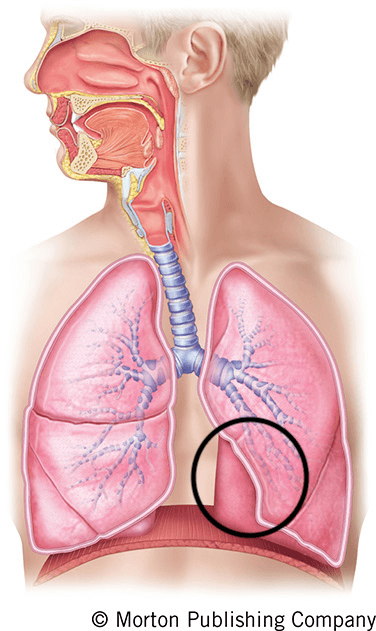
What is the cardiac impression?
The primary function of this structure is gas exchange.
What are the alveoli?
When you inhale, the diaphragm ________.
contracts
The soft "punching bag" found in the nasopharynx.
The flap that prevents food and drink from going down the trachea.
What is the epiglottis?
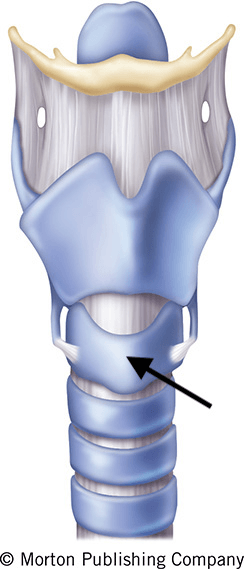
What is cricoid cartilage?
Nasal cavity --> ______ --> oropharynx
What is the nasopharynx?
During exhalation, pressure ______ while volume ________.
The final portion of the pharynx.
What is the laryngopharynx?
The final ring of the trachea.
What is the carina?
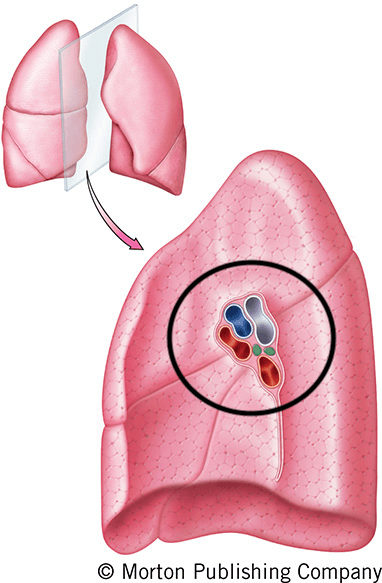
What is the hilum?
Trachea --> primary/main bronchus --> ___________
What are secondary/lobar bronchi?
Inhalation is a/n _______ process. Exhalation is a/n ______ process.
active; passive
This structure represents the end of the conducting division.
What are the terminal bronchioles?
Lie inferior to the vestibular folds and produce sound.
What is the true vocal cord?
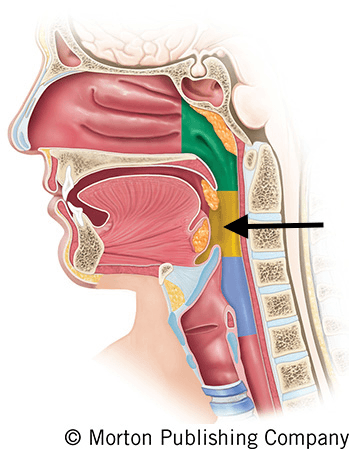
What is the oropharynx?
Bronchiole --> __________ --> respiratory bronchiole
What is terminal bronchiole?
A graph that represents the percent of total hemoglobin that is saturated at a given partial pressure of oxygen.
What is the O2-Dissociation Curve?
These are 3 folds in the nasal cavity that increase surface area and help trap pathogens.
What are nasal conchae?
Ciliated pseudostratified epithelium in the trachea helps bring up mucous to be expelled or swallowed.
What is the mucociliary escalator?
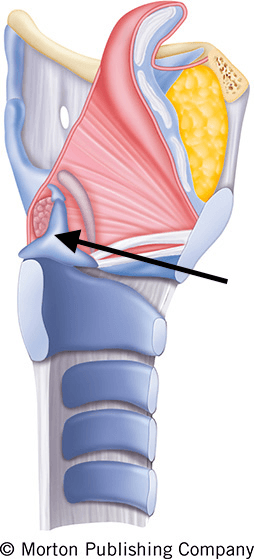
What is arytenoid cartilage?
The type of blood cell that oxygen attaches to after traveling through the alveoli.
What is an erythrocyte (RBC)?
If the blood pH decreases there will be a _____ shift on the O2 dissociation curve.
A right shift