What is lead 2.
What is the difference between a STEMI and a NSTEMI?
ST Elevation on a 12-lead ECG.
The dose of Diphenhydramine
2mg/kg IM IV or PO Max 50mg
List two parts of a neuro assessment.
Pupils
CMS
GCS
Amiodarone
What is an antiarrythmic?
Medication and dose given for cardiac chest pain.
What is 0.4mg Nitro SL?
Where do we place V1?
4th intercostal space on the right side of the chest.
2 Contraindications of Salbutamol.
Allergy
Ischemic Chest Pain
Demonstrate a cincinnati stroke assessment.
Speech, Arms, and Face
Xarelto
What is a blood thinner?
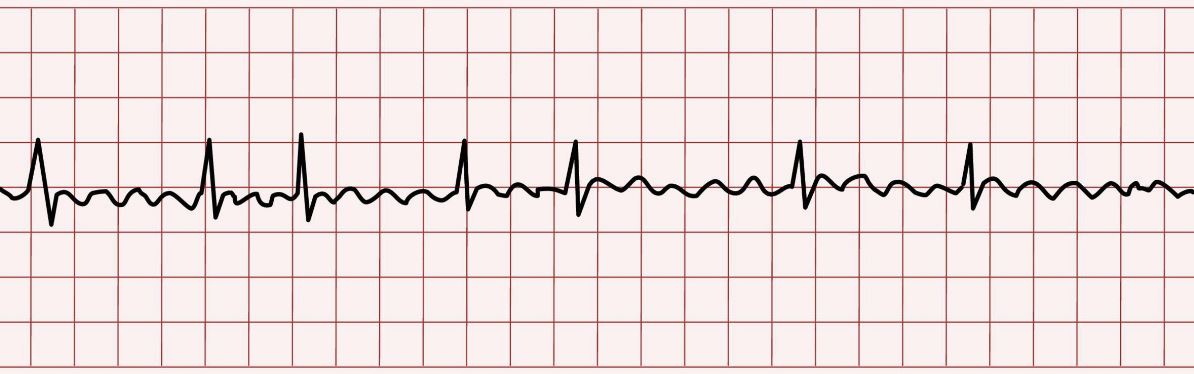
Afib
Where do we place V4?
Mid clavicular - 5th intercostal space.
What is the epinepherine dose for a 100kg Female with angioedema?
0.5mg IM q 5 min max 3 doses
What are the 3 categories of GCS?
Verbal Response
Motor Response
Eye Opening
What is another name for Lorazepam?
Ativan
What cardiac enzyme is used to determine if a patient is having a heart attack?
Troponin
Clear lung sounds and pinpoint chest pain.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Which type of MI is a precaution for Nitroglycerin?
Inferior wall MI
What are the 2 most important questions to ask family when dealing with a possible CVA?
Do they take blood thinners?
When were they last seen normal?
Bisoprolol
What is a Beta blocker / HTN / Afib?
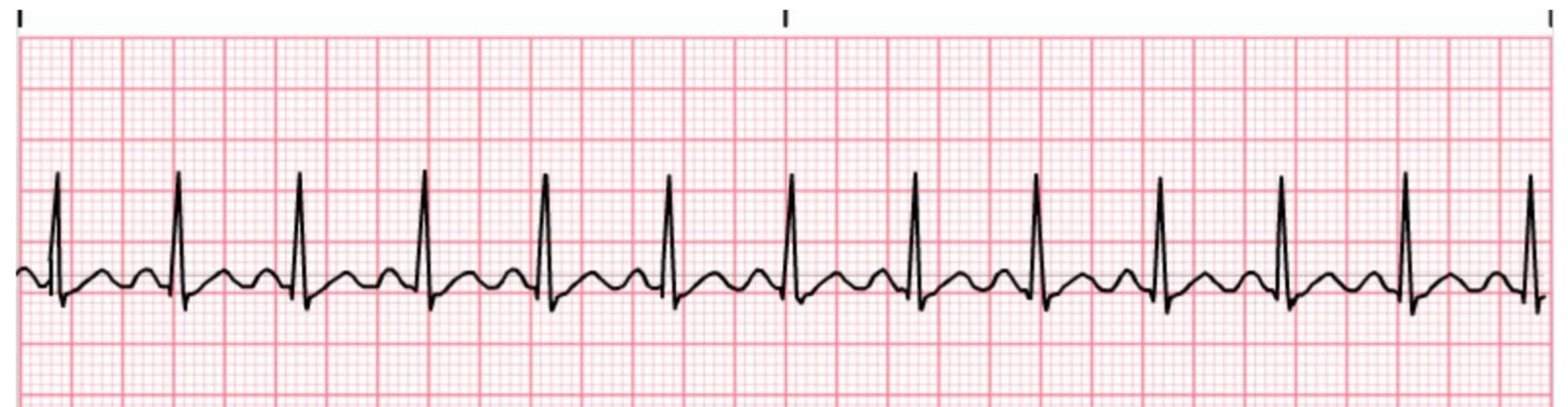
Sinus Tachycardia
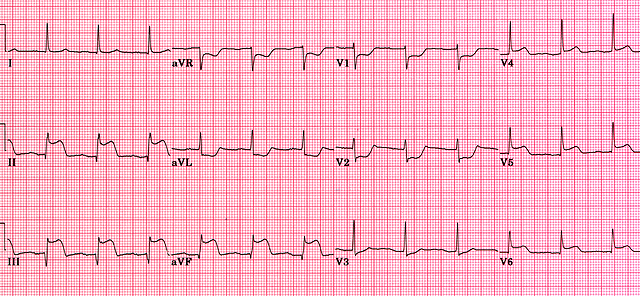
Inferior MI
List 4 contraindications of Ketorlac.
Allergy to asa or nsaids
Hypovolemia
Anticoagulants
CVA or head trauma
Peptic ulcer disease
Pregnancy (3rd Trimester)
Known Renal Insufficiency
Suspected long bone fractures
What is the targeted EtC02 for patients showing signs of cerebral herniation?
30-32 mmHG
Rosuvistatin
Dyslipidemia (High Cholesterol)