A positive modified Allen test indicates this presence
a patent ulnar artery.
As alveolar ventilation increases, PaCO2...
Decreases
A sinus rhythm with a long PR interval of 0.26 seconds is call sinus rhythm with
1st degree AV block
This type of medicine is given to treat acute bronchoconstriction due to its ability to rapidly reduce smooth muscle constriction
SABA
Patient is in PEA. RN is unable to obtain IV access. Which is the next preferred route?
IO
The renal system compensates for a respiratory acid-base imbalance what time period
Several hours to days
Normal HCO3- to dissolved CO2 ratio
20:1
A regular rhythm with narrow QRS complexes, no identifiable P wave, and a heart rate of 190 would be consistent with:
SVT
This part of the brain is responsible for involuntary respiratory function
Medulla oblongata
An 8-year-old boy with status asthmaticus in the ER, needs a continuous neb. The physician orders 10 mg/hr. for 2 hours. How many unit doses of albuterol does the RCP need?
8 unit doses
A 21 year old woman presents with a five day history of vomiting and lethargy. She is confused and hypotensive. Interpret the following ABG:
pH: 7.30
PaO2: 97
PaCO2: 30.8
HCO3: 13
BE: -5
Partially compensated metabolic acidosis with normal oxygenation
A 24 year old asthmatic patient presents with a wheeze and shortness of breath. Interpret the following ABG:
pH: 7.49
PaO2: 82.5 mmHg
PaCO2: 30.8 mmHg
HCO3: 24 mEq/L
BE: +1
Uncompensated Respiratory Alkalosis with normal oxygenation

Complete Heart Block
Agent used to induce bronchoconstriction during bronchoprovocation and works by mimicking the pulmonary effects of acetylcholine
Methacholine
Medication considered the gold standard for sedation in RSI
Etomidate
Hazards/complications of arterial puncture
1. vessel obstruction
2. infection
3. hematoma
4. hemorrhage
A 52 year old with severe COPD is reviewed in a pulmonary clinic. Interpret the following ABG:
pH: 7.35
PaO2: 54 mmHg
PaCO2: 56 mmHg
HCO3: 33 mEq/L
BE: +6
This is an ABG of a chronic CO2 retainer showing chronic respiratory acidosis
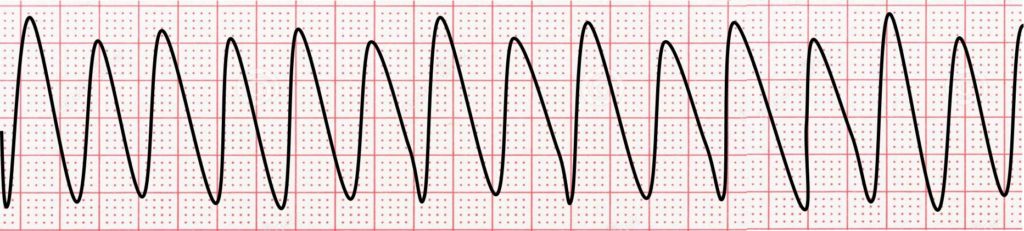
VTACH (monomorphic)
Typically used to treat hypervolemia in CHF patients
Diuretics
This type of diabetes is primarily due to insulin resistance and a progressive loss of β-cell insulin secretion
Type 2
Contraindications for arterial puncture
1. presence of a surgical shunt in the selected extremity
2. negative modified Allen's test
3. infection involving the selected extremity
Interpret the following ABG:
pH: 6.90
PaO2: 127
PaCO2: 69 mmHg
HCO3: 16 mEq/L
BE: -12
Mixed Respiratory and Metabolic Acidosis with Hyperoxia

VFib
You are responding to a cardiac arrest in the emergency department. The physician asks for epinephrine administration via the endotracheal tube. What dose should be administered via the endotracheal tube?
2 mg
Acceptable methods of decreasing HR for a pt with SVT
Adenosine and the Valsalva maneuver