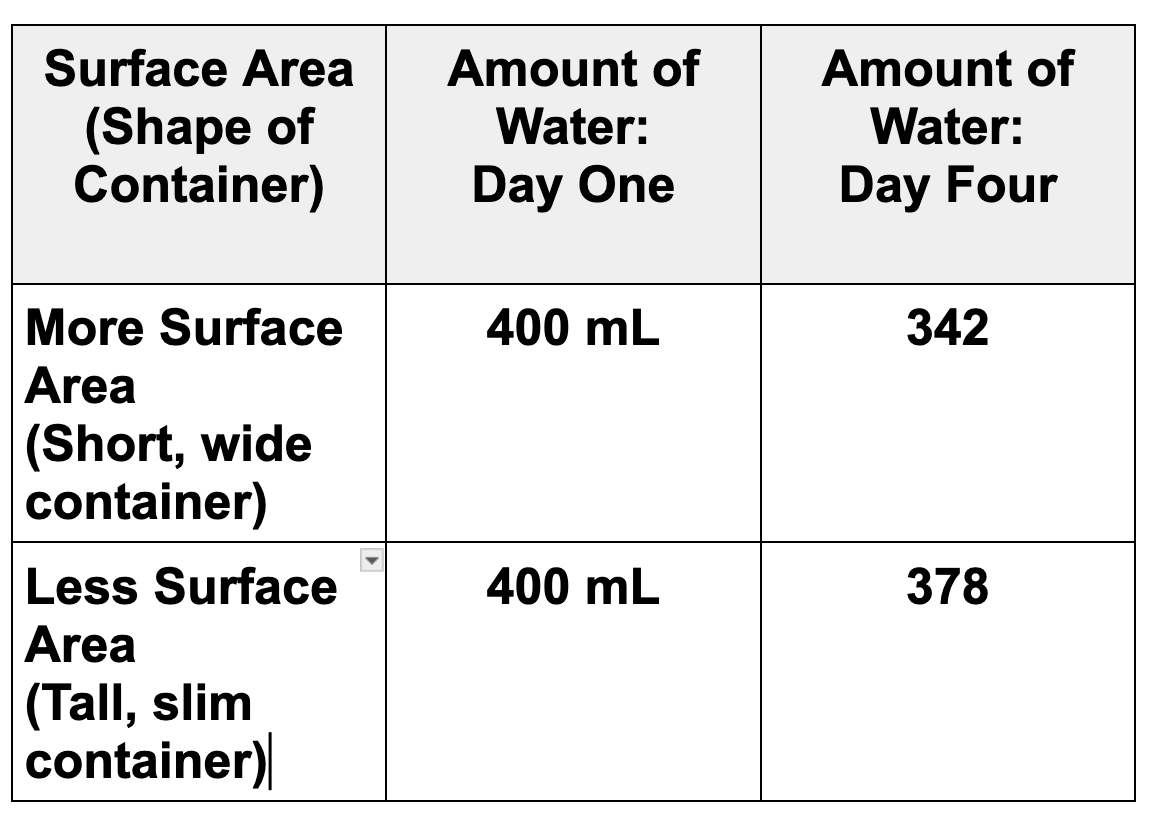
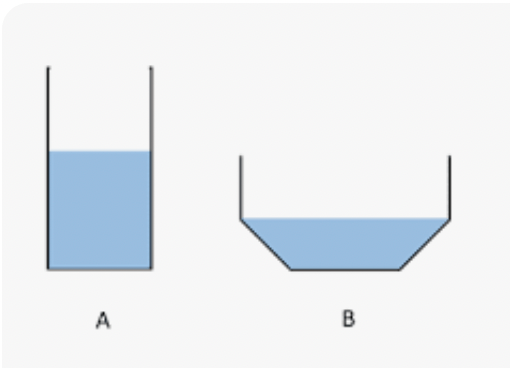
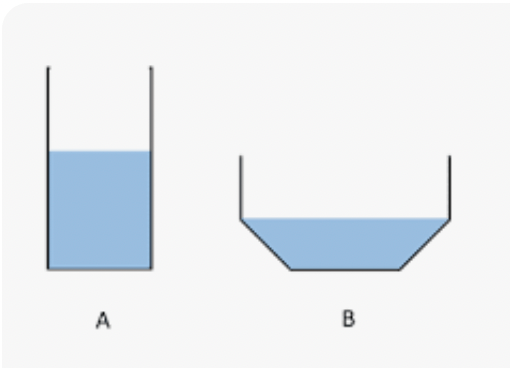
Students wanted to find out how surface area (the amount of water in contact with the air) would affect evaporation rate. They set up two containers. Which container has more surface area?
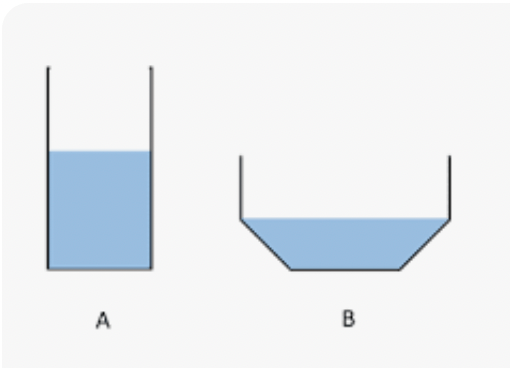
Container B.
Aside from keeping all of the variables constant except one, what else should students do to make sure they get accurate results?
Do multiple trials
In this model of evaporation, what do the circles represent?
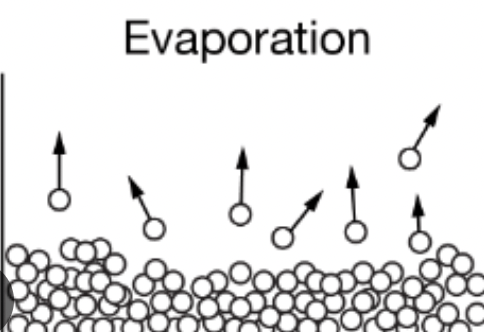
molecules of water
Hurricanes usually occur where the ocean water is over 80 degrees. What color on this visual indicates this area on Earth?
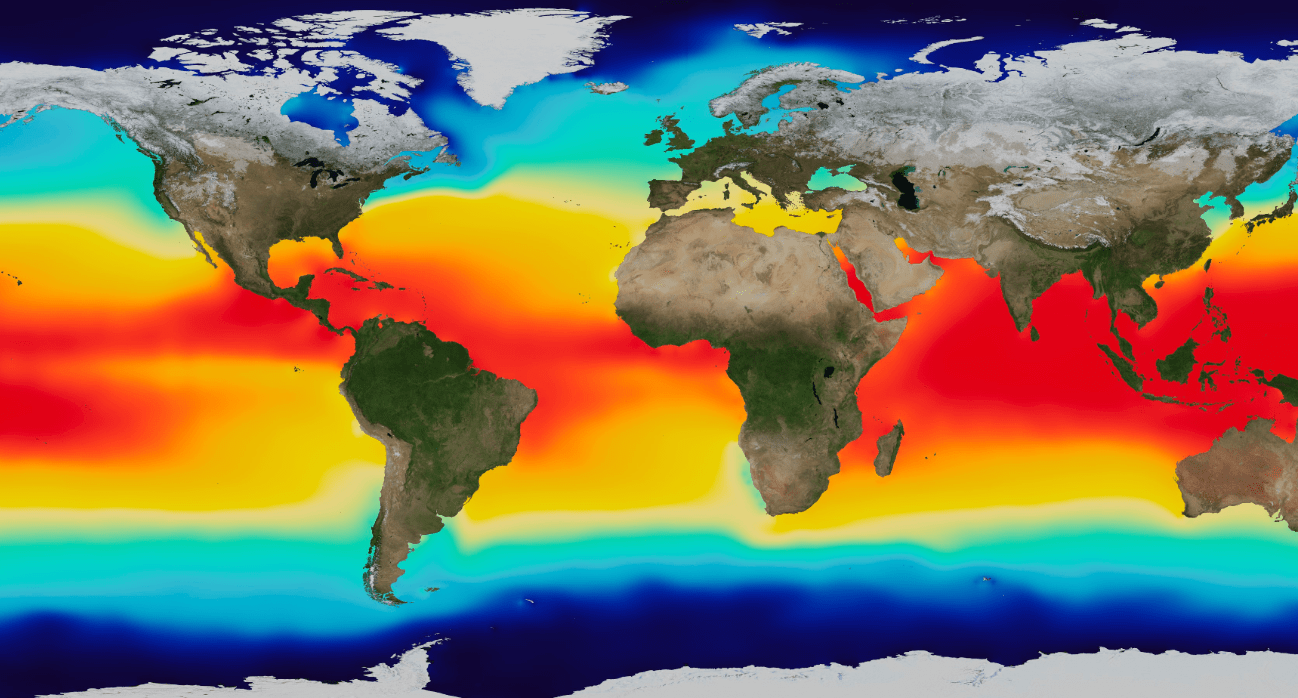
Red
___________ is a tiny particle made up of two or more atoms that are connected together. These atoms can be the same type, like in oxygen (O₂), or different types, like in water (H₂O). The atoms are joined by chemical bonds, which hold it together.
molecule
What should be the fair test question for this experiment?
How does the amount of surface area affect evaporation rate?
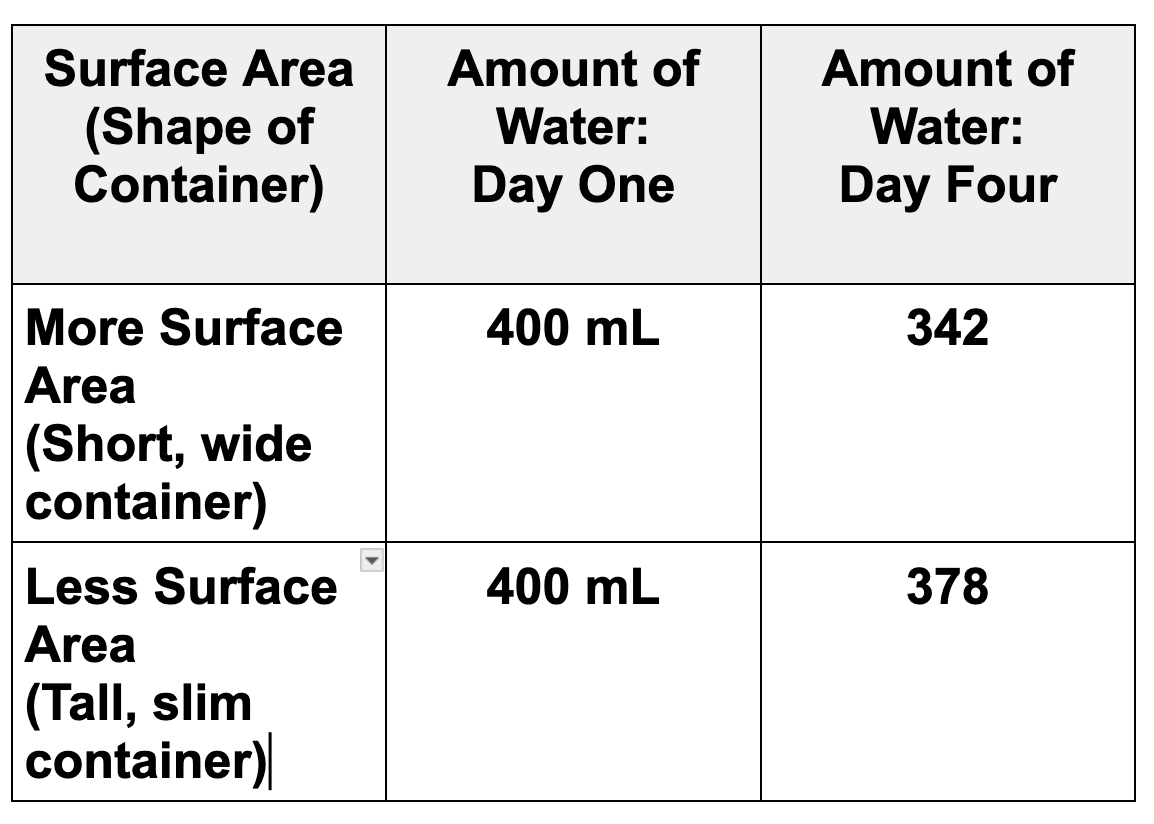
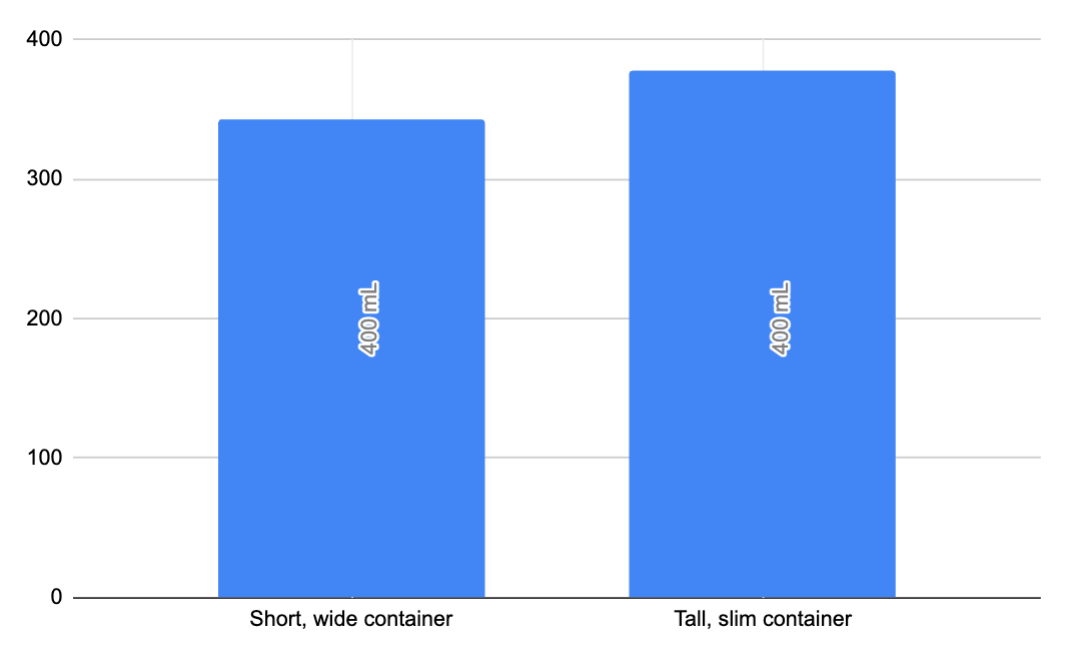
What conclusion could be drawn based on this data? Be sure to use the words "surface area."
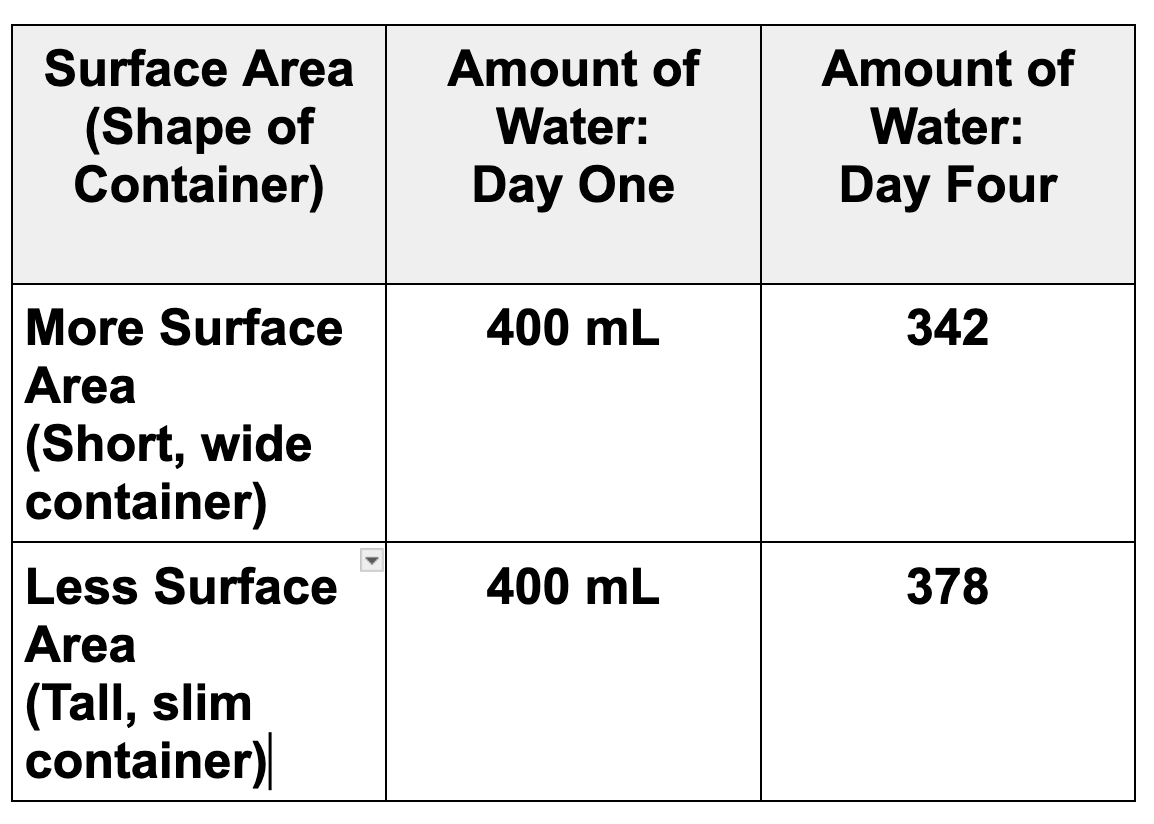
The container with more surface area had a faster evaporation rate than the container with less surface area.
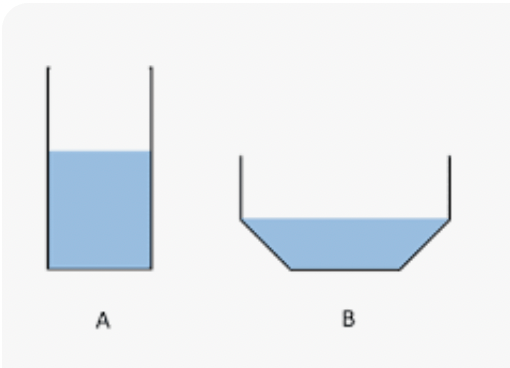
Which of these models shows water in its liquid form?
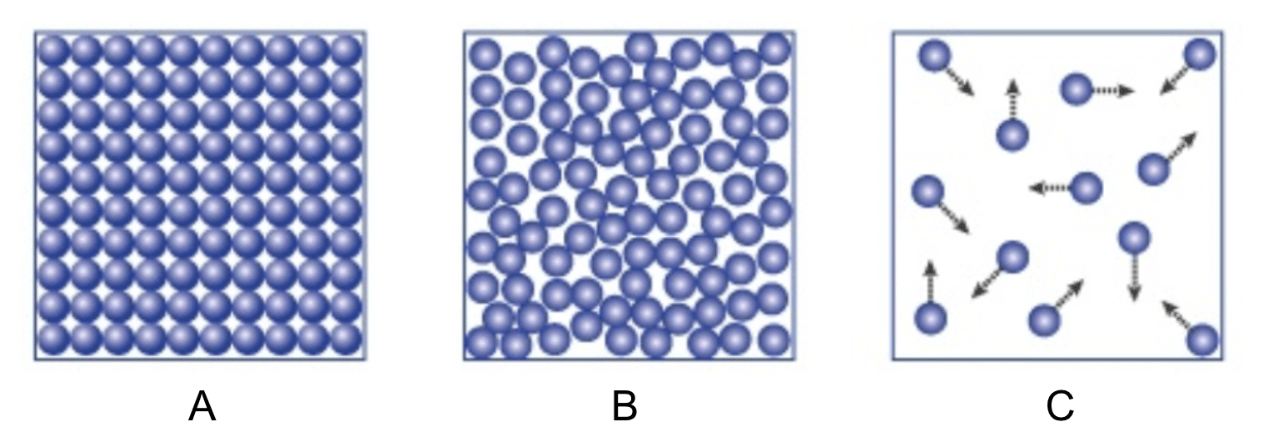
B.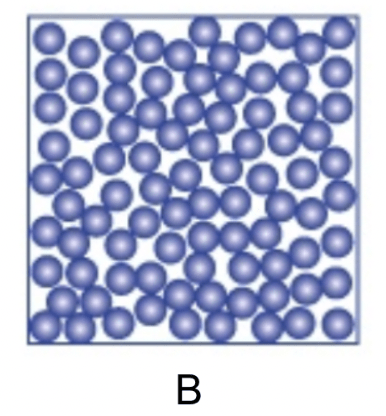
According to the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, what number category is the most powerful?

Category 5
_______________ describes how much matter there is in a given space (how closely packed together the molecules are).
density
What is the independent variable (the ONE variable that is changed) in this investigation?
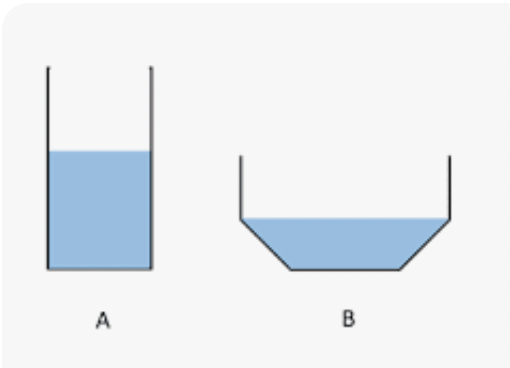
surface area
What should the title of graph be for this data?
The Effect of Surface Area on Evaporation Rate
What phase change occurs during evaporation?
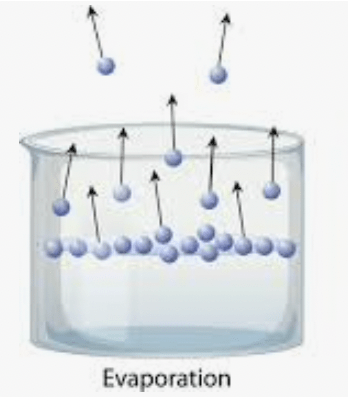
liquid to gas
Why do hurricanes weaken when they reach land?
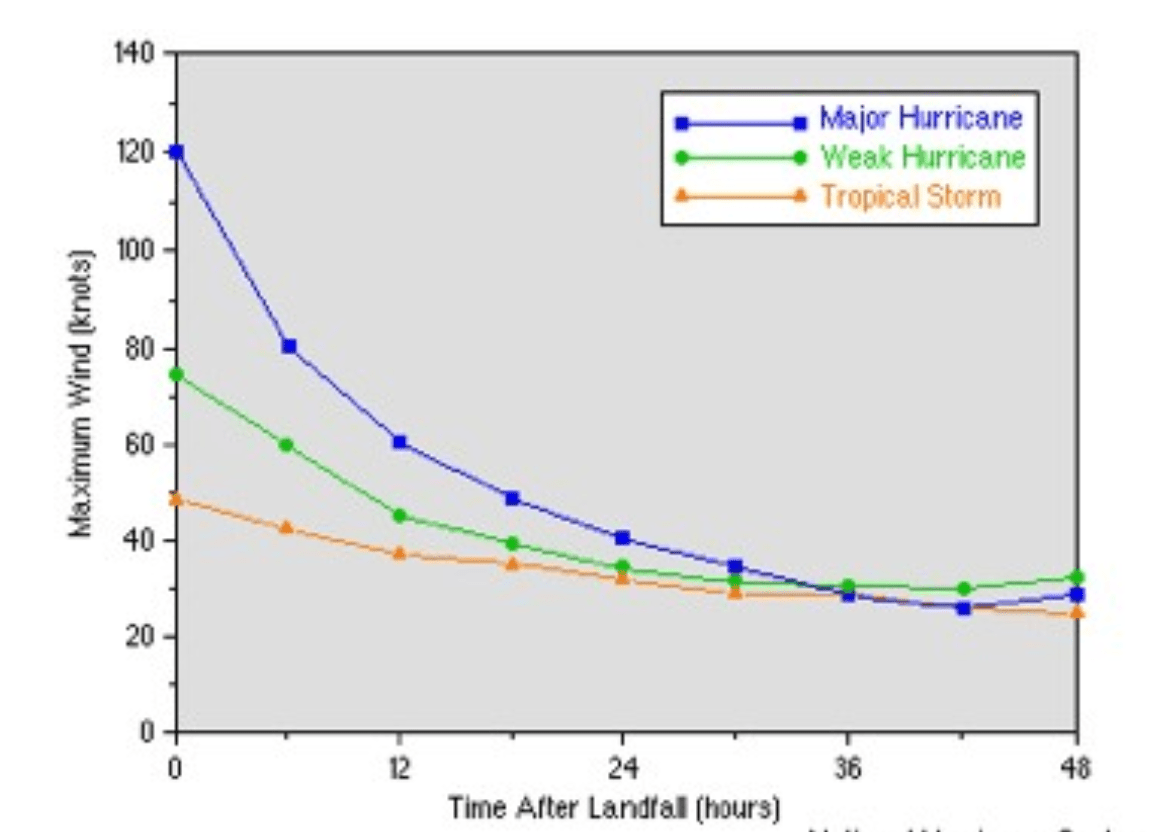
Because they don't have access to the ocean water, so there is less evaporation. Water is like the "fuel" of the hurricane.
Also accepted: The ground itself is rougher than the smooth ocean, which slows down the hurricane’s winds.
__________ is anything that takes up space and has mass. Everything around you—like your desk, the air you breathe, and even your body—is made of this. It can exist in three main forms: solid, liquid, or gas.
Matter
What is the dependent variable in this investigation?
evaporation rate
What variable should go on the x-axis of the graph?
Surface Area (the independent variable)
Name two variables that make water evaporate quicker.
heat and wind
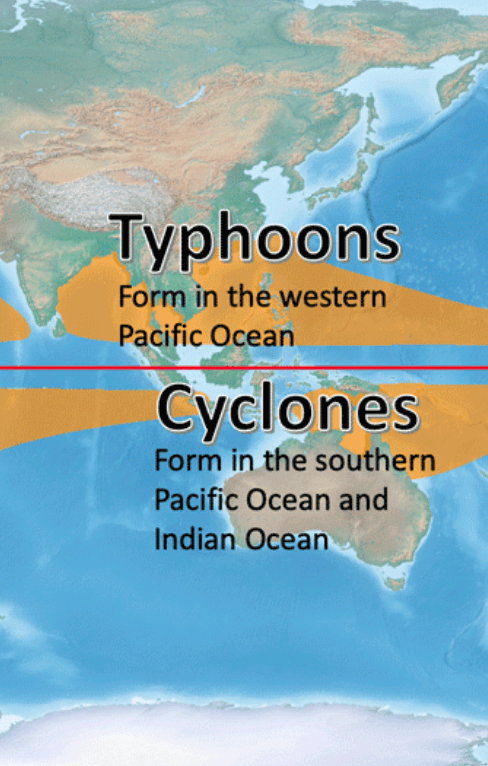
We call these storms "hurricanes" here in the Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Ocean. What are these storms called in the Western & Southern Pacific and Indian Ocean? Name TWO.
____________ is the process by which a liquid turns into a gas. This happens when the molecules in the liquid get enough energy (usually from heat) to break free from the surface and escape into the air.
Evaporation
Name three variables that should be kept constant in this investigation.
amount of water
temperature of water
placement of the containers (whether near heat sources or not)
humidity of the area
material of container
What should we label the y-axis of this graph?
Amount of Evaporation in mL
When liquid water evaporates, what does it become? Be more specific than "gas."
water vapor
The people of this Caribbean island have shown great resilience when recovering from hurricanes in recent years. They supported each other and rebuilt their communities in innovative ways.
Puerto Rico
__________________ is the part of an experiment or investigation that you change on purpose to see how it affects something else. It’s the "cause" in a cause-and-effect relationship.
Independent Variable