What is molecular biology?
Molecular biology is used to explain processes in terms of the chemical substance involved.
What are the two solubility groups of water?
Hydrophilic- Easily dissolvable in water, attracts water molecules "water loving"
Hydrophobic- "water-hating" substances that don't dissolve in water, repels water molecules
Give two examples of monosaccharides
Answers may vary: glucose/galactose/fructose
What group determines if an amino acid is polar or not?
Polar and non-polar amino acids are determined by the "R" group.
polar= hydrophilic "R"group
non-polar= hydrophobic "R" group
What is an enzyme?
Enzyme- 3D globular protein with long polypeptide chains
Amino acid R groups of the active site interact with the substrate.
Structure = Function
Enzyme is never permanently altered by the reaction. Can be reused!
1) carbon
2) hydrogen
3) oxygen
4) nitrogen
Why is water important?
Water is a versatile molecule that is the main component of living things in all levels of organization. Water also helps organisms maintain homeostasis.
Name the two different forms of starch and contrast them
Amylose: 1-4 glycosidic bonds (linear). Amylopectin: 1-6 glycosidic bonds (branch)
What are polypeptides?
Polypeptides are a chain of amino acids, which form to create more complex proteins. All proteins are polypeptides.
What are the four parts of an enzyme?
-Enzyme (C)- a globular protein which acts to catalyze a chemical reaction
-Active site (A)- the region on the surface of an enzyme to which substrates bind.
-Substrate/s (B)- the substance that an enzyme acts on- the reactant/s
-Allosteric Site (D)- Where a non-competitive inhibitor will bind
What is the difference between an organic and inorganic compound?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are found in organic molecules such as proteins and carbohydrates.
Any compound that does not contain carbon is said to be inorganic.
What makes water a polar molecule?
It's unusual structure of two hydrogen atoms with a (+) charge and an oxygen atom with a (-) charge
Contrast saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated- every carbon atom in the hydrocarbon chain has the maximum number of H atoms bonded.
Unsaturated- the Hydrocarbon chain does not have the maximum number of H carbons bonded due to the inclusion of three double bonds
What are the four structural levels of proteins?
Primary structure- order of amino acids, primary structure relates directly to how a protein will fold
Second structure- either helical or pleated sheet, due to hydrogen bonding only
Tertiary structure- more folding, once again due to the order of amino acids
Quaternary structure- an association of two or more peptides
What are the three factors that affect enzyme action?
Temperature- optimal temp is 37°C
Decreased temp: slower-moving molecules = less likely interactions between enzymes and substrates.
Increased temp: atoms within the enzyme molecule move more energetically and stress/break 3D bonds (in this case, the enzyme is destroyed, or denatured)
optimal pH- depends on the type of enzyme (most work at pH 7, the pH of cells’ cytoplasm).
Concentration of substrate OR enzymeMore substrate OR enzyme = greater chance of collision between the two
Define condensation and hydrolysis. What types of reactions are they?
Condensation- In a condensation reaction, two molecules are combined to create a larger molecule held together by a covalent bond. This is an example of an anabolic reaction in which monomers are used to form macromolecules.
Hydrolysis- The breaking down of polysaccharides, polypeptides, and triglycerides to create monomers. Hydrolysis is a catabolic reaction; water molecules are used (reverse of condensation reactions).
What is a hydrogen bond? What does it form between?
A weak bond that forms between the negative charge of one water molecule and a positive charge of another
Name and contrast the different types of unsaturated fatty acids.
Cis- two H atoms are absent from the same side of the hydrocarbon chain.
Trans- one H atom is absent from each side of the hydrocarbon chain
What types of proteins are shown in the diagram below?
a) Fibrous protein: long, narrow shape, mostly insoluble in water
b) Globular protein: rounded shape, often soluble in waterThis graph shows which environmental condition that can impact enzymes?
a) pH
b) enzyme concentration
c) substrate concentration
What type of reaction is this and what molecules are being used?
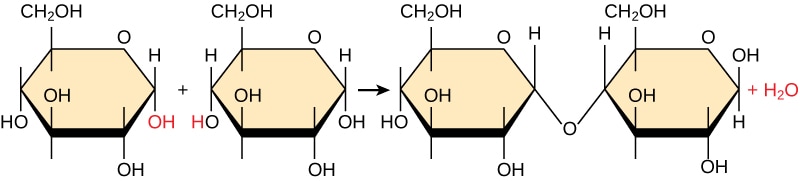
This is a condensation reaction where two glucose molecules are being combined to create maltose.
Two glucose monomers are combined, and one H20 molecule is released in the condensation reaction to create a glycosidic bond.
What is the difference between cohesion and adhesion?
Cohesion allows water molecules to hold together in a network.
Adhesion allows water molecules to hold onto different molecules in a vessel
How are triglycerides formed?
By the condensation of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule.
What is the denaturation of proteins and what factors cause it?
Denaturation- This occurs when the structure of a protein is destroyed causing it to lose its function
Change in Heat and pH will cause the protein to lose hold of its folds and the function of the protein is lost.
What is an example of an industry enzyme and what is its function?
Pectinase- used in fruit juice production.
Protease- breaks down proteins
Enzymes in detergent- used to break down organic molecules