This is to give points
What word describes the blue points?
hint: points K and J are the _______ of Circle F and Circle I

intersections
What is the next step in the perpendicular bisector construction?

Draw a line through the intersection of the circles.
The red line is called the ______ of a square.

diagnoal
(fun fact: in Harry Potter, Diagon Alley is a pun on "diagonally")
What tools are used to draw circles and lines
compass and straightedge
What are each of these? Name them.

Line AB
Ray CD
Line Segment EF
Fill in the blanks:
Point C is the _____ of segment DE
AB is the _________ of DE
DE is _______ by AB
The little square means Angle ACD is _____ and that AB is ______ to DE

wordbank: right, midpoint, bisected, perpendicular, perpendicular bisector
Point C is the midpoint of segment DE
AB is the perpendicular bisector of DE
DE is bisected by AB
The little square means angle ACD is right and that AB is perpendicular to DE
How do we know a quadrilateral is a square?

4 equal sides and 4 right angles
The square is _____ in the circle

Segment OC is an ________ _________
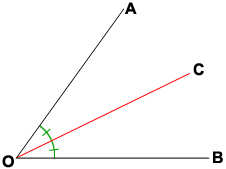
inscribed
angle bisector
What are the 3 undefined terms in geometry
Point, Line, Plane
Here is the first step of drawing a line perpendicular to m through point C.
What is the purpose of this step? Why do we draw Circle C?

Circle C provides 2 intersection points with line m. Because CF = CG, they are both radii of circle C and are equidistant from point C.
This is an unfinished square construction. What is the purpose of the large circle A with radius AB?

Segment AB is one side of the square. By drawing circle A with radius AB, we can create an equal length segment to be the left side of the square.
Why are segments FH an GH equal in length?

Circles F and G both share a radius with circle C
Any radius of circle F and G will be equal in length.
FH is a radius of circle F and GH is a radius of circle G, therefore FH = GH
What are two important features of a circle? What information about the circle do they tell you?
What is the importance of this set of points?
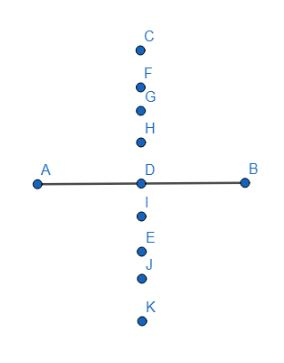
Each point is equidistant from both A and B
This is an unfinished square construction. What is the purpose of these aspects of the construction?

These are a variation of a perpendicular bisector construction. They create the right angle corners which are to be a part of the square.
Triangle ABC is an equilateral triangles because all its sides have the same length. How do we know the sides triangle ABC are equal in length?

Circle A, B, C share radii with each other, which means all radii of each circle are equal in length.
The sides of Triangle ABC are all radii of Circles A, B, C, therefore all the sides are equal in length.