A food chain shows the flow of _______ from one organism to another.
energy
Which two processes add carbon to the environment?
respiration and combustion
State the two major greenhouse gases.
carbon dioxide and methane
Give two reasons why organisms become endangered.
climate change, habitat destruction, hunting, overharvesting, pollution, introduced species
What is the name of this stage?
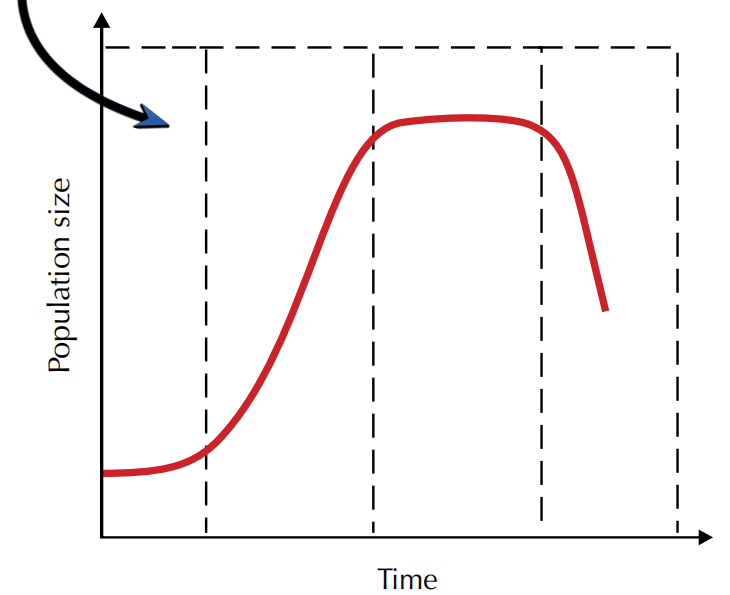
Lag phase
Define the term "trophic level"
the position of an organism in a food chian, food web, or ecological pyramid.
Exchange!
Answer the question below correctly and team gets the skill to exchange their score with any group (or not).
What changes take place during deamination?
Excess amino acids are converted into urea.
Describe the term "biodiversity".
the number of different species that live in an area
Share!
Answer the question below correctly and team gets the skill to combine their score with another group, then split it (or not).
Describe the term "sustainable resource".
a resource which is produced as rapidly as it is removed from the environment so that it does not run out.
All of the individuals of different species in an ecosystem is called a _________.
community
Bomb!
Cut your current score by half
Describe the process "decomposition" in carbon cyle.
Decomposers feed on dead bodies and waste materials, when they respire, CO2 is returned to the atmosphere.
Bonus! - Double the score of this question.
Describe reasons for habitat destruction.
increased area for human activities, extraction of natural resources, pollution
State three ways that fish stocks can be conserved.
closed seasons, protected areas, controlled net types and mesh size, quotas, monitoring, education
Double!
Answer the question below correctly and team gets the skill to double their score.
Describe the two aspects that human increases food production by using 'insecticides'.
to improve quality and yield
Describe which type of pyramid can sometimes be inverted(颠倒的) and explain how it happens?
pyramid of numbers, because sometimes one producer can feed a lot of primary consumers.
Outline the importance of "nitrogen fixation".
It converts nitrogen gas, which most organisms cannot use, into more reactive ammonium or nitrate ions, which they can use.
Describe three negative effects of deforestation.
reducing biodiversity, extinction, loss of soil, flooding and increase of carbon dioxide
Describe two reasons for conservation programmes.
(a) maintaining or increasing biodiversity
(b) reducing extinction
(c) protecting vulnerable ecosystems
(d) maintaining ecosystem functions
State three factors affecting the rate of population growth.
food supply, competition, predation, disease
State three ways that energy can be lost in a food chain.
heat (stay a live, such as respiration...), uneaten parts of food, indigestible parts of food (faeces)
State the four processes that involve microorganisms in the nitrogen cycle.
nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decomposition
Explain the process of eutrophication.
• increased availability of nitrate and other ions
• increased growth of producers
• increased decomposition after death of producers
• increased aerobic respiration by decomposers
• reduction in dissolved oxygen
• death of organisms requiring dissolved oxygen in water
Describe the method "in vitro fertilisation" (IVF).
egg and sperm are combined outside the body in a laboratory dish, after an embryo is developed, it's transferred into the uterus of a female to grow.
Describe two disadvantages of large-scale monoculture of crop plants.
reduction in biodiversity, increase in pests, reduction in soil fertility