Wernicke's aphasia is characterized by intact:
A) Naming
B) Comprehension
C) Repetition
D) Fluency
D) Fluency
Which of the following may be helpful for a traumatic brain injury (TBI) patient with bladder and bowel dysfunctions?
A) Frequent toileting
B) Anticholinergics
C) Condom catheter for men and absorbent pads for women
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
Of the following ocular muscles and cranial nerve combinations, which one is incorrect?
A) Medial rectus-III
B) Lateral rectus-VI
C) Superior oblique-IV
D) Inferior oblique-V
D) Inferior oblique-V
A popular mnemonic to remember the cranial nerves associated with the ocular muscles is “SO4 LR6 AO3”
Which of the following are characteristics of osteoarthritis (OA)?
A) Dull, aching pain better with activity
B) Joint stiffness lasting 30 minutes and improving as the day progresses
C) Typically involves the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints in the hands
D) Infrequently involves the spine
B) Joint stiffness lasting 30 minutes and improving as the day progresses
The most common error in the realm of neurodiagnostic testing is typically related to which of the following?
A) Computer analysis failure
B) Excessive ambient temperature/room temperature
C) Lack of repeat calibration of the testing probe with each measurement
D) Operator error
E) Patient's inability to fully relax
D) Operator error
Of all of the possible mistakes that can lead to false-positive or false-negative electrodiagnostic results, the most common one is due to the person performing the test.
These include not performing the test correctly, not interpreting the test correctly, not testing the appropriate nerves or muscles, failing to account for anomalous innervation, improper technique, or performing the test too early (before findings would be apparent on neurodiagnostic testing).
Shoulder subluxation after stroke:
A) Occurs late in the recovery phase
B) Is always associated with pain
C) Is associated with flaccid hemiplegia
D) Will need radiological studies for diagnosis
C) Is associated with flaccid hemiplegia
Which is the most commonly injured cranial nerve (CN)?
A) CNI
B) CN II
C) CN VII
D) CN VIII
A) CNI
The olfactory nerve is the most commonly injured nerve due to the shearing forces that damage the small nerves on the cribiform plate.

Hill-Sachs lesion of the shoulder:
A) May be associated with posterior dislocations
B) May cause shoulder instability if it accounts for 10% of the articular surface
C) Is a compression fracture of the posterolateral aspect of humeral head caused by abutment against the anterior rim of the glenoid fossa
D) Is evaluated by Speed's test
C) Is a compression fracture of the posterolateral aspect of humeral head caused by abutment against the anterior rim of the glenoid fossa
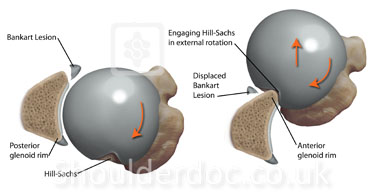
It occurs when the humeral head (the ball of the upper arm bone) is forcefully impacted against the edge of the shoulder socket (glenoid) during an anterior shoulder dislocation. This impact creates a dent or compression fracture in the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head.
Which of the following exercises is recommended for rheumatoid arthritis?
A) Isotonic
B) Concentric
C) Isokinetic
D) Isometric
D) Isometric
Allows the joint to rest.
Which of the following does the nerve conduction component of the neurodiagnostic study fail to assess or give information about?
A) Autonomic nerve
B) Integrity of myelin
C) Motor nerve
D) Sensory nerve
E) Speed of transmission
A) Autonomic nerve
Except for somatosensory evoked potentials, electrodiagnostic testing only assesses the peripheral nervous system.
Testing is possible of both the motor and the sensory fibers. Assessment can be made about the integrity of the myoneural junction, the axon, and the myelin. However, the autonomic nervous system is not evaluated by conventional nerve studies and EMG.
In a patient with transcortical mixed aphasia, the patient will have:
A) Fluent speech
B) Good comprehension
C) Preserved repetition (echolalia)
D) None of the above
C) Preserved repetition (echolalia)
Transcortical mixed aphasia, also known as isolation aphasia, is a rare and severe form of aphasia. It is characterized by:
- Reduced or absent spontaneous speech: Individuals have significant difficulty initiating speech.
- Severely impaired language comprehension: Understanding spoken or written language is greatly affected.
- Preserved repetition: Despite other impairments, the ability to repeat words and phrases remains intact.
This condition often results from extensive brain damage, typically due to a stroke or traumatic brain injury, affecting both the motor and sensory language areas while sparing the areas responsible for repetition
What is considered the most effective method for the prevention of heterotopic ossification (HO)?
A) Radiation of bone tissue
B) Range of motion
C) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
D) Diphosphonates
B) Range of motion
Radiation would include the whole body. NSAID's and biphosphonates have a role in treatment but not in prevention.
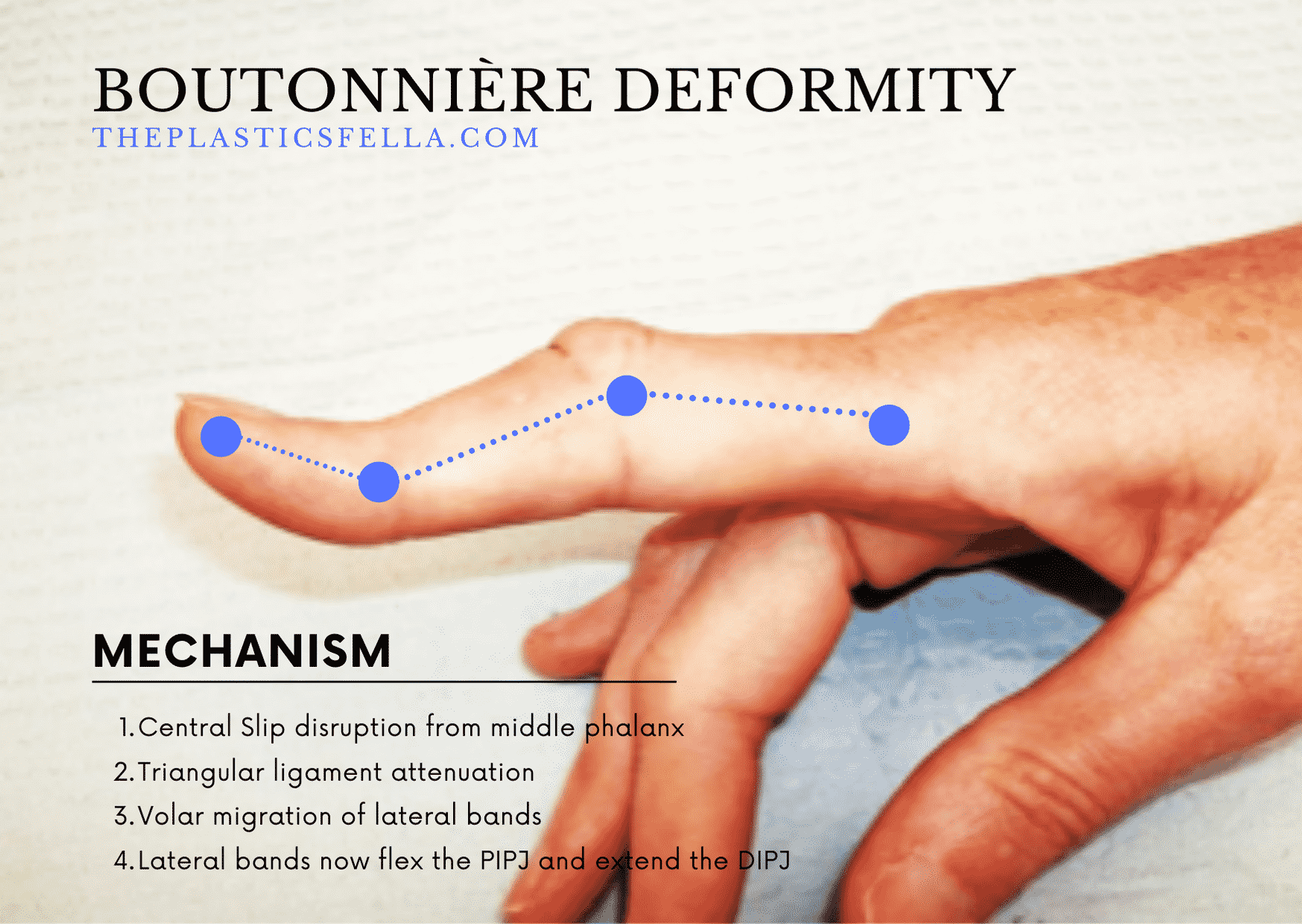
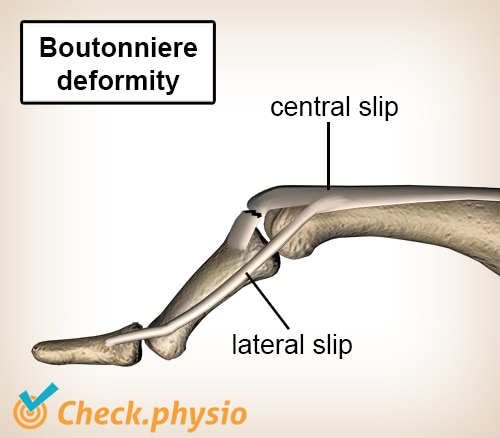
What causes Boutonnière deformity?
A) Ruptured flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendon
B) Thickening and nodule formation in the flexor tendon sheath
C) Median nerve entrapment
D) Rupture of the central slip and volar migration of lateral bands
D) Rupture of the central slip and volar migration of lateral bands
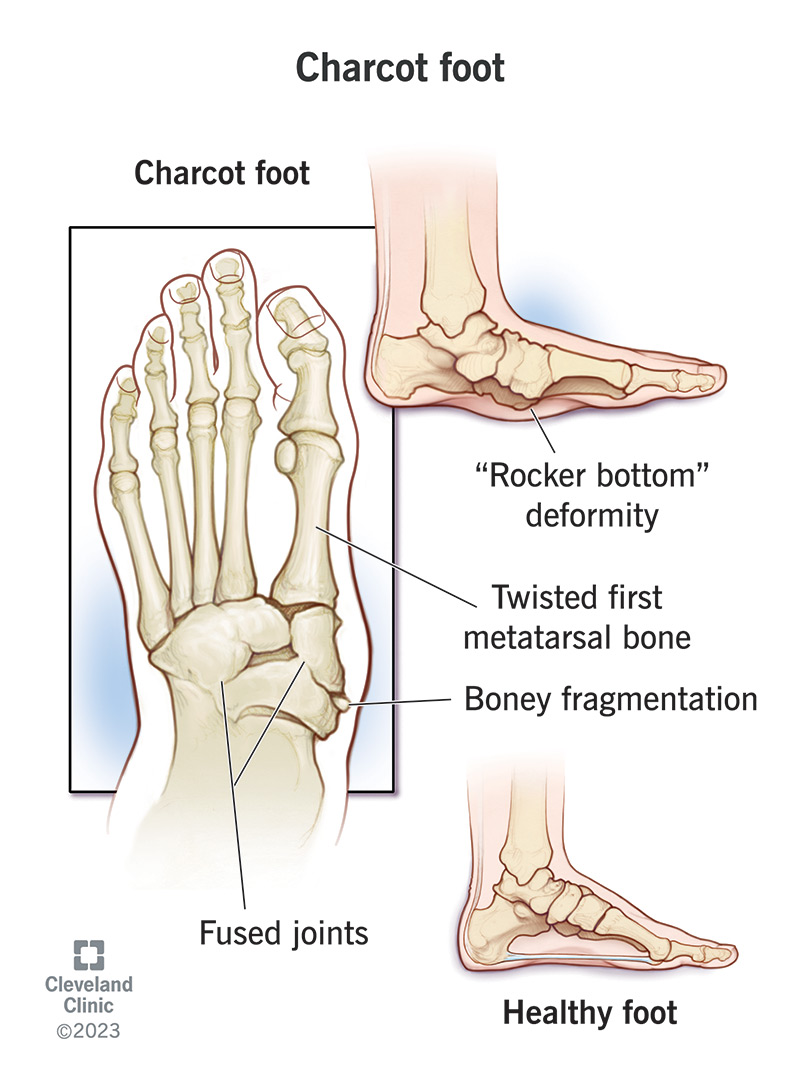
What is the most common cause of neuropathic arthropathy?
A) Osteoarthritis
B) Septic arthritis
C) Systemic lupus
D) Diabetes
D) Diabetes
In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), the sensory nerve action potential (SNAP) will be:
A) Normal
B) Decreased amplitude distally and proximally
C) Decreased amplitude distally
D) Increased
A) Normal
ALS is a disorder of the motor nerves. As such, the motor fibers, but not the sensory fibers, would be affected. Therefore, the SNAPs should be normal, whereas the compound motor action potentials might show decreased amplitudes.
Baclofen is an antispasticity agent that is:
A) A structural analogue of gamma amino butyric acid (GABA)
B) An alpha-2 adrenergic agonist
C) A hydantoin derivative
D) An imidazoline derivative
A) A structural analogue of gamma amino butyric acid (GABA)
Baclofen binds to these receptors, which are inhibitory, leading to a decrease in the release of excitatory neurotransmitters
What neurotransmitter should be enhanced to improve cognitive recovery in patients with a traumatic brain injury (TBI)?
A) Norepinephrine
B) Dopamine
C) Histamine
D) Acetylcholine
B) Dopamine
Dopamine agonists assist in improving attention and cognition function. Histamine has no role in cognitive recovery and norepinephrine has a limited role in the treatment of cognition in TBI.
Which ligament is affected in Gamekeeper's thumb?
A) Tear of the ulnar collateral ligament of the thumb metacarpophalangeal (MCP)
B) Rupture of the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendon
C) Rupture of the extensor tendon from the distal phalanx
D) Tear of the triangular fibrocartilage complex
A) Tear of the ulnar collateral ligament of the thumb metacarpophalangeal (MCP)
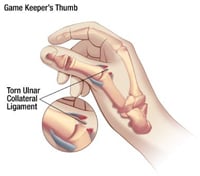
Skier's or gamekeeper's thumb is a tear of the ulnar collateral ligament. This injury happens when your thumb is pulled back or to the side, away from your fingers. It often happens when skiers fall on an outstretched hand while holding a ski pole.
What type of hypersensitivity reaction is noted in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)?
A) Type I
B) Type II
C) Type III
D) Type IV
C) Type III


In SLE, these immune complexes often target nuclear antigens, which can result in widespread effects throughout the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and central nervous system.
In myopathies, the motor unit action potentials (MUAPs) may demonstrate all of the following except:
A) Low amplitude
B) Long duration
C) Polyphasicity
D) Early recruitment
B) Long duration
In myopathies, motor units usually have low amplitude (less than 1 millivolt when using a monopolar needle), short duration, polyphasicity, and early recruitment.
Low Amplitude: In myopathies, muscle fibers are often damaged or lost. Since MUAP amplitude is proportional to the number of muscle fibers within a motor unit, the loss of muscle fibers results in lower amplitude potentials.
Short Duration: The duration of MUAPs is related to the size and number of muscle fibers. In myopathies, the muscle fibers are smaller and fewer, leading to shorter duration potentials.
Polyphasicity: Polyphasic MUAPs (having more than four phases) occur due to asynchronous firing of muscle fibers within a motor unit. This is often a result of muscle fiber regeneration and reinnervation, which is common in myopathies.
Early Recruitment: In myopathies, the remaining muscle fibers are weak, so the body compensates by recruiting more motor units at lower levels of effort. This leads to early recruitment of motor units during muscle contraction.
All of the following are features of lateral medullary syndrome except:
A) Hemiplegia
B) Dysphagia
C) Ipsilateral facial hemisensory deficit
D) Palate and vocal cord paralysis
A) Hemiplegia
Lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome) typically does not cause motor paralysis because the areas of the brainstem affected by the condition do not include the corticospinal tract, which is responsible for voluntary motor control.
A 28-year-old woman after motor vehicle accident sustained a traumatic brain injury. The impact of injury was to the right side of her head, and she now has visual changes consistent with an oculomotor cranial nerve dysfunction. What would the ocular exam demonstrate?
A) Dilation of the ipsilateral pupil
B) Constriction of the ipsilateral pupil
C) Dilation of the contralateral pupil
D) Constriction of the contralateral pupil
A) Dilation of the ipsilateral pupil
Normally, CN III constricts the ipsilateral pupil with light exposure.
What is a Rockwood type II acromioclavicular (AC) joint injury?
A) Sprain of the AC and coracoacromial (CC) ligaments
B) Torn CC ligament and intact AC ligament
C) Torn AC ligament and sprained CC ligament
D) Torn AC and CC ligaments
C) Torn AC ligament and sprained CC ligament

Which of the following is not a feature of Scheuermann kyphosis?
A) Vertebral body wedging of at least 5 degrees
B) Flattening of curvature with extension
C) Involvement of at least three vertebral bodies
D) Anterior wedging
B) Flattening of curvature with extension
Scheuermann's Kyphosis is a rigid form of spinal kyphosis caused by anterior wedging of >5 degrees across three consecutive vertebrae, most commonly in the thoracic spine.


Which of the following can result in a prolongation of the H-reflex?
A) S1 radiculopathy
B) Sacral plexopathy
C) Polyneuropathy
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
The H-reflex, or Hoffmann’s reflex, is a diagnostic tool used in electromyography (EMG) to assess the integrity of the spinal cord and peripheral nerves.
It is similar to the monosynaptic stretch reflex (like the knee-jerk reflex) but is elicited electrically rather than mechanically.
Although the H-reflex is very sensitive, it is not specific. Any of the above conditions can result in a prolongation of the H-reflex.