A 50-year-old woman is evaluated for a 6-month history of pain and swelling in the hands, knees, and feet. She reports 1 hour of joint stiffness in the morning.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. The thumb and second and third fingers on the right hand are diffusely swollen, with tenderness and swelling at the metacarpophalangeal and proximal and distal interphalangeal joints. There are similar findings on the thumb and second finger on the left hand. Several of the affected proximal interphalangeal joints have a slight purple discoloration. There is a right knee effusion. The second and fourth toes on the right foot are diffusely swollen, as are the first and third toes on the left foot. Two small psoriatic plaques—one in the umbilicus and one on the scalp—are noted.
Laboratory evaluation reveals a negative rheumatoid factor result.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Psoriatic arthritis
OA
Seronegative RA
SLE
67 yo with malaise, arthralgia, rash, fatigue, cough, painless red eye, dyspnea x 8 weeks.

Erythrocyte sedimentation rate 87 mm/h
Creatinine 2.1 mg/dL (185.6 µmol/L)
ANCA Pending
Urinalysis 3+ blood; 2+ protein; 20-30 dysmorphic erythrocytes/hpf; 5-10 leukocytes/hpf; erythrocyte casts
Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next?
Kidney biopsy
Lung biopsy
Skin biopsy
Sinus biopsy
A 36-year-old woman is evaluated during a routine wellness visit. She is asymptomatic and has no medical problems. She works as an accountant and rarely engages in physical activity. She drinks a glass of red wine with dinner five times weekly. Her diet is rich in protein and starches and low in fruits, vegetables, and nuts. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for 5 years. Her mother has rheumatoid arthritis, and the patient is concerned that she might also develop the disease. Her only medication is a combined oral contraceptive.
Physical examination, including vital signs, is normal.
Which of the following is most likely to reduce this patient's risk for developing rheumatoid arthritis?
Smoking cessation
Alcohol cessation
Discontinuation of OCP
Increased physical activity
Mediterranean diet
A 68-year-old man is evaluated for recent onset of mild pain and significant swelling of his left knee. He lives in eastern Pennsylvania and is an avid golfer. Several months ago he had an illness characterized by an enlarging erythematous annular skin lesion in the left popliteal fossa associated with fever, arthralgia, and myalgia that spontaneously resolved after several days.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. Joint examination shows diffuse swelling of the left knee with minimal warmth but no erythema, slight reduction in full flexion of the knee but pain-free range of motion, and a popliteal cyst.
Results of serologic testing are positive for Borrelia burgdorferi.
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Doxycycline
CTX
MTX
Hydroxychloroquine
A 56-year-old woman is evaluated at a follow-up visit. She has polyarticular tophaceous gout affecting her hands, feet, and knees bilaterally. She is receiving a tapering dose of prednisone following an acute gout flare. She had previously received allopurinol but discontinued it after developing a rash. She has hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Current medications are losartan and prednisone, 5 mg/d.
Laboratory studies show a serum creatinine level of 1.8 mg/dL (159.1 μmol/L), a serum urate level of 10.1 mg/dL (0.60 mmol/L), and an estimated glomerular filtration rate of 31 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Which of the following is the most appropriate additional treatment?
Febuxostat
Colchicine
Allopurinol
Pegloticase
Probenecid
A 25-year-old woman is evaluated for a 3-year history of joint pain involving her hands with more than 1 hour of morning stiffness. She also has intermittent photosensitive facial rash, fatigue, and intermittent subjective fever.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. There is tenderness to palpation with swelling of the second and third metacarpophalangeal joints bilaterally.
Complete blood count, serum creatinine level, and urinalysis are normal. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is 35 mm/h.
Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next?
ANA
Anti–double-stranded DNA antibodies
Anti-Ro/SSA, anti-La/SSB antibodies
Anti-Smith antibodies
Anti–U1-ribonucleoprotein antibodies
A 43-year-old woman is evaluated for fibromyalgia. She continues to be symptomatic with poor sleep quality and diffuse stiffness despite her participation in cognitive behavioral therapy, land and aquatic therapy, and tai chi. She also has depression, treated with escitalopram.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. There is tenderness at multiple soft-tissue sites with soft palpation. All other findings are normal.
Which of the following is the most appropriate additional treatment?
Pregabalin
Duloxetine
Cannabis
Oxycodone
Prednisone
A 62-year-old man is evaluated for worsening exertional dyspnea and nonproductive cough over the past year. He has a 6-year history of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Current medications are tofacitinib, methotrexate, and folic acid.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. Cardiac examination reveals normal jugular venous pressure and S2 without extra sounds. There are reduced breath sounds throughout the lung fields, with bibasilar inspiratory crackles. Lung percussion is resonant throughout. Joint examination shows advanced changes of rheumatoid arthritis involving the hands and wrists. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's exertional dyspnea?
ILD
Heart failure
PAH
RA pleural effusion
A 75-year-old man is evaluated for facial redness and hand, elbow, and knee rash that have progressed over the past 6 months. He has no other medical problems and takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. There is an erythematous, slightly elevated, irregular rash over both cheeks, forehead, and chin, sparing the nasolabial folds. Eyelids also appear pink and swollen. There is faint erythema over the dorsal hands. An indurated rash with faint scale is present over the extensor surfaces of the elbows and knees. Muscle strength and the remainder of the examination are normal.
Complete blood count, comprehensive metabolic panel, and serum aldolase and creatine kinase levels are normal.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Amyopathic dermatomyositis
Acute cutaneous SLE
Psoriasis
Rosacea

An 85-year-old woman is evaluated for a 10-day history of right knee pain and swelling, which is impairing her ability to walk and climb stairs. She has a history of similar symptoms over the past 2 years. Each episode has lasted about 3 weeks and resolves with rest and ice.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. She has moderate swelling of the right knee, with warmth and tenderness, and decreased range of motion related to pain. No skin lesions or tophi are noted.
Vitals normal. ESR 65. CBC, CMP, and rate normal.
Diagnosis?
Pseudogout
Gout
Infectious arthritis
RA
A 36-year-old woman is evaluated for abdominal pain and diarrhea. She has a 3-year history of ankylosing spondylitis. For the past 6 months, she has had four or five bowel movements daily and over the past month she has experienced unintentional weight loss of 3 kg (6.6 lb). The abdominal pain is poorly localized and unrelated to defecation. Stools are loose but not greasy, mucoid, or bloody. She has been taking naproxen twice daily, with good control of her ankylosing spondylitis. She reports no recent travel or antibiotic therapy. She has no other medical problems and takes no additional medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. There is mild nonlocalizing abdominal tenderness. Range of motion of cervical and lumbar spine is normal. Sacroiliac joints are not tender.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
IBD
Celiac
IBS
SIBO
A 50-year-old man is evaluated for severe pain and swelling in the left knee of 2 days' duration. He has a long history of psoriasis and polyarticular psoriatic arthritis. He reports no fever, chills, or pain in other joints. Current medications are methotrexate, folic acid, and topical clobetasol propionate.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. There are psoriatic plaques on the elbows, sacrum, and anterior shins. The left knee is swollen and warm; the patient holds it at 45 degrees of flexion, and he is unwilling to further flex or extend. There is no other joint swelling.
Arthrocentesis of the left knee reveals a synovial fluid leukocyte count of 40,000/μL (40 × 109/L) with 90% neutrophils. Gram stain is negative, and synovial fluid analysis for crystals and bacterial culture are pending.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Gout
Infectious arthritis
OA
Psoriatic arthritis

A 22-year-old woman is evaluated for a 1-month history of progressive rash on the face, chest, and arms following sun exposure.
Similar-appearing patchy skin lesions are seen over the upper chest in a V-neck distribution and the dorsal forearms. Active and passive wrist extension elicits discomfort.
Diagnosis?
Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus

Subacute cut lupus
Lupus pernio
Rosacea

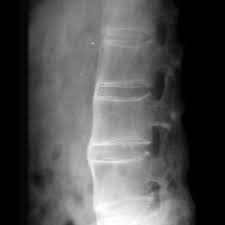
A 56-year-old man is evaluated for a 2-year history of mid to lower back pain and stiffness. He reports no buttock pain. He has tried home-based exercises, with minimal benefit.
On physical examination, there is diffuse tenderness to palpation of the lower thoracic spine and upper lumbar spine, with reduced flexion and extension. There is no sacroiliac joint tenderness.
Laboratory evaluation reveals a normal blood C-reactive protein level.
Radiograph of the spine is shown. Sacroiliac joint radiographs are normal.
Diagnosis?
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis
Spinal calcium pyrophosphate deposition dz
Spondylosis deformans
Ankylosing spondylitis
A 36-year-old woman is evaluated in the emergency department after experiencing a tonic-clonic seizure. For 1 week she has had severe headaches. Eight months ago, Raynaud phenomenon of the hands and feet developed. Current medication is sustained-release nifedipine.
On physical examination, temperature is 37.0 °C (98.6 °F), blood pressure is 240/120 mm Hg, pulse rate is 90/min, respiration rate is 18/min, and oxygen saturation is 96% with the patient breathing ambient air. The skin over the hands, forearms, trunk, lower legs, and feet is tight and appears thickened. The fingers on both hands show cyanosis. No nuchal rigidity is noted, and findings on neurologic examination are normal.
Laboratory studies:
Hematocrit : 33%
Leukocyte count : Normal
Platelet count : 90,000/μL (90 × 109/L)
Creatinine : 2.4 mg/dL (212.2 μmol/L)
Urinalysis: 2+ protein; no blood or casts
Peripheral blood smear reveals diminished platelet numbers and schistocytes.
Which of the following is the most appropriate intravenous treatment?
Captopril
Cyclophosphamide
Metoprolol
Mycophenolate
A 23-year-old man is evaluated for fever, abdominal pain, rash, and arthritis of the right knee of 3 days' duration that resolved 1 week ago. He has had more than 20 similar episodes, the last three occurring in the past year. The first episode occurred at age 5 years and presented as abdominal pain; the patient underwent appendectomy but no appendicitis was found. His paternal grandfather and maternal grandmother had a similar syndrome.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
ESR is 23 mm/h
Serum creatinine level normal
1+ protein on urinalysis
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Colchicine
Indomethacin
Prednisone
Canakinumab