Name the diagnostic criteria for Still disease
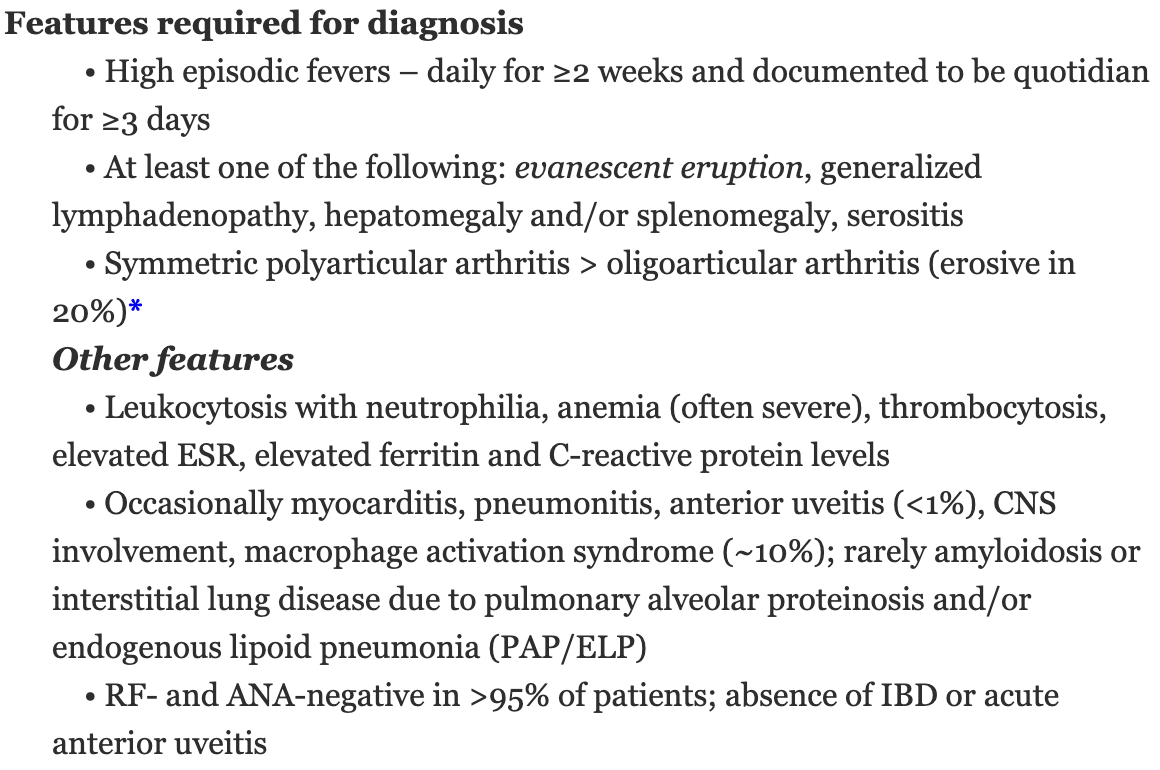
By definition, onset < 16 yo
Name the most common skin finding in Sjogrens
Most common: xerosis/pruritis (50%)
Characteristic auto-antibody for MCTD
Seniors: Cross-reactants of this autoantibody
- U1RNP (splicing of pre-mRNA to mRNA)
- antibodies of EBV and CMV cross-react to components of U1RNP
Presence of this marker is associated with transformation of MCTD to SLE
anti-dsDNA
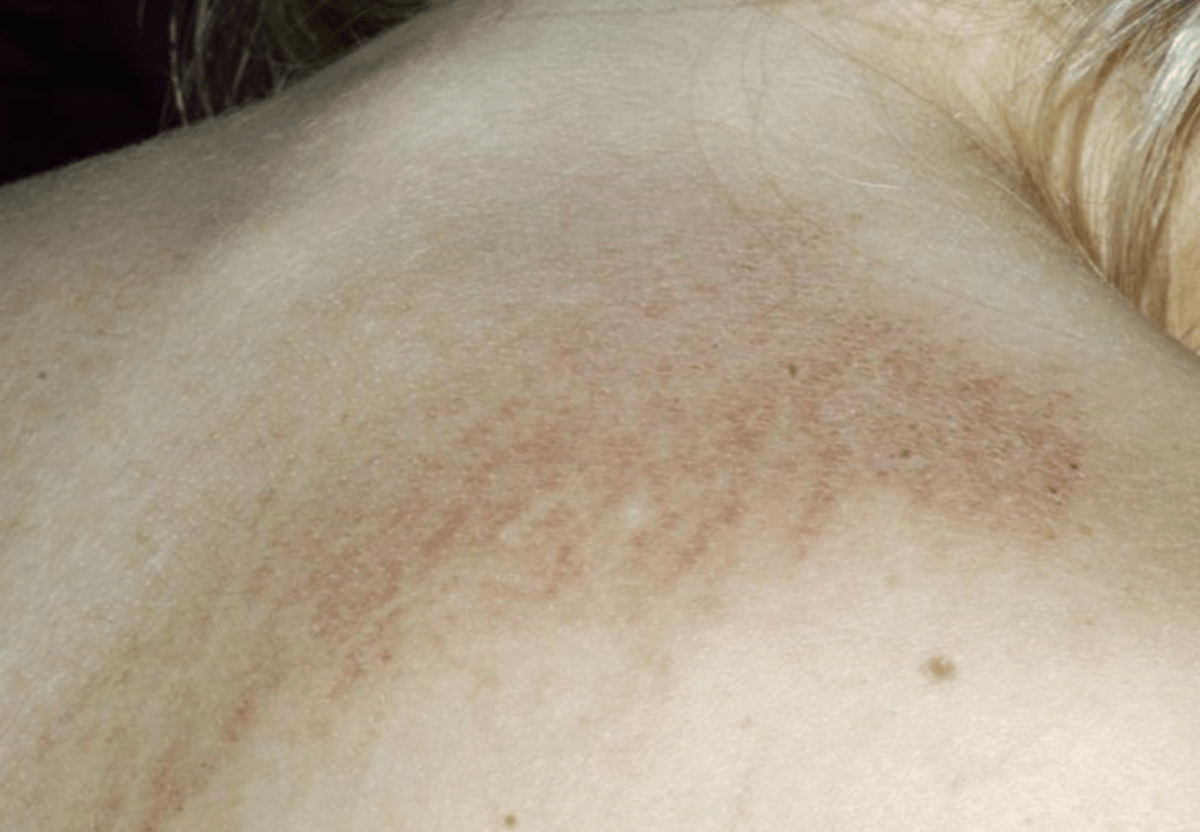
Still Disease
- Evanescent pink papules and plaques
- Persistent, often linear, plaques
Distinctive non-cutaneous feature of adult-onset Still disease
Carpal ankylosis: limited ROM with minimal pain of carpal joints
Mucosal xerosis occurs after ___% of glands have been destroyed
>50%
Name the 3 manifestations of Felty syndrome
Seropositive RA with:
- neutropenia
- splenomegaly
- refractory leg ulcers (can be multifactorial from PG, medium-sized vessel vasculitis, venous hypertension, immobilization, neuropathy, or palisaded neutrophilic and granulomatous dermatitis)
G-CSF is used to treat this complication of RA
Felty syndrome
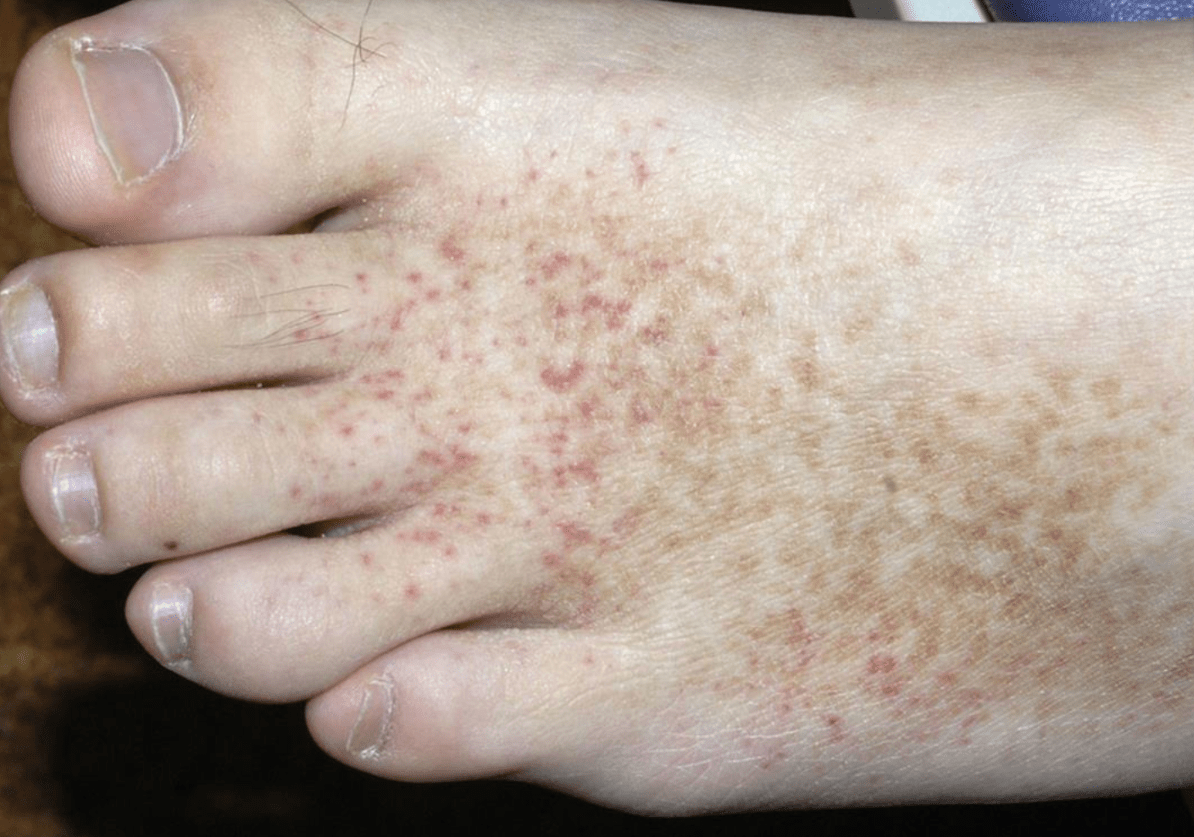
Why is this finding important in a patient with Sjogrens syndrome?
Cutaneous small vessel vasculitis (~10%), associated with increased complications
- systemic involvement
- positive serology
- B-cell lymphoma
- increased hospitalization/mortality
____% of children with Still Disease develop this potentially lethal complication
5-10% develop macrophage activation syndrome
- fever, pancytopenia, coagulopathy, hepatic dysfunction, neurologic complications, and hemophagocytosis
Another serious complication is interstitial lung disease from pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) or endogenous lipoid pneumonia (ELP)
Name the most severe complication associated with Sjogrens
Increased risk (~19 fold) in developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma (extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphomas aka MALT)
Other complications:
- Distal sensorimotor polyneuropathy, Devic syndrome (variant of MS with optic neuritis and transverse myelitis), memory loss
- Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
- Pericarditis, congential heart block
- Glomerulonephritis
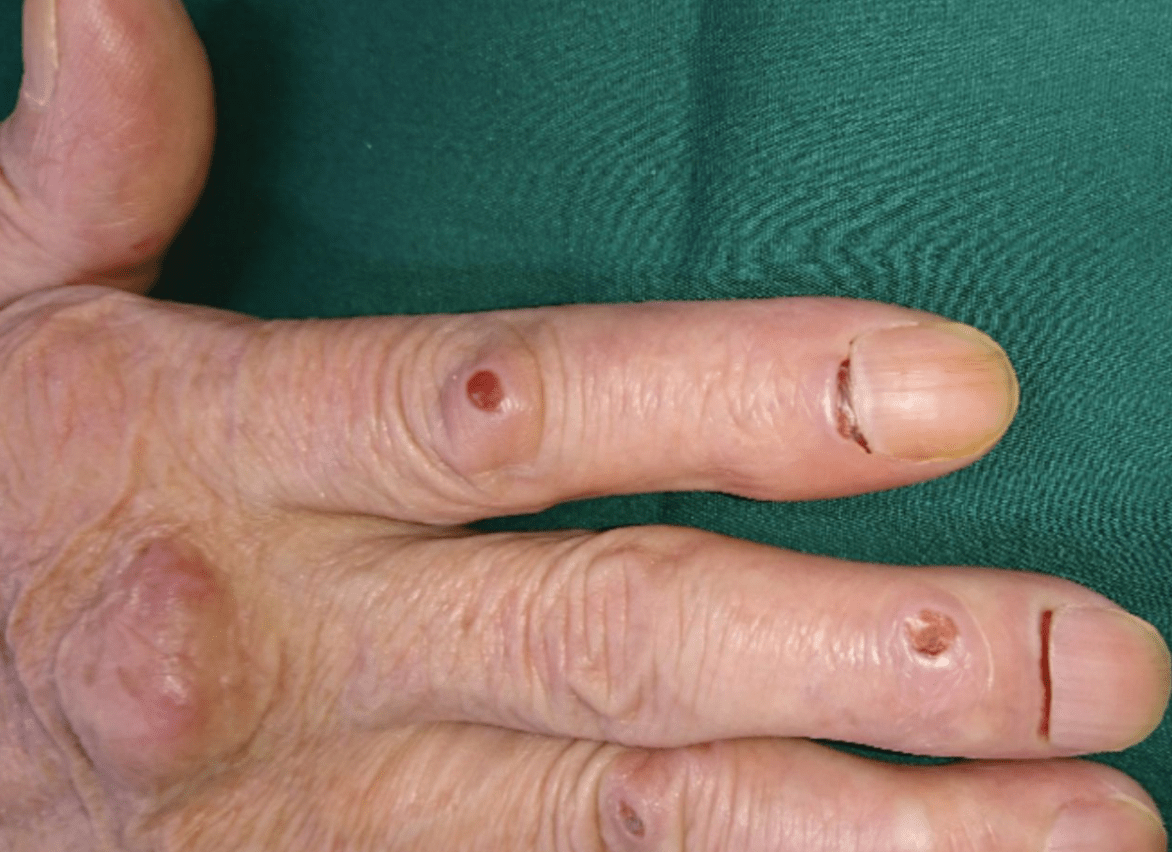
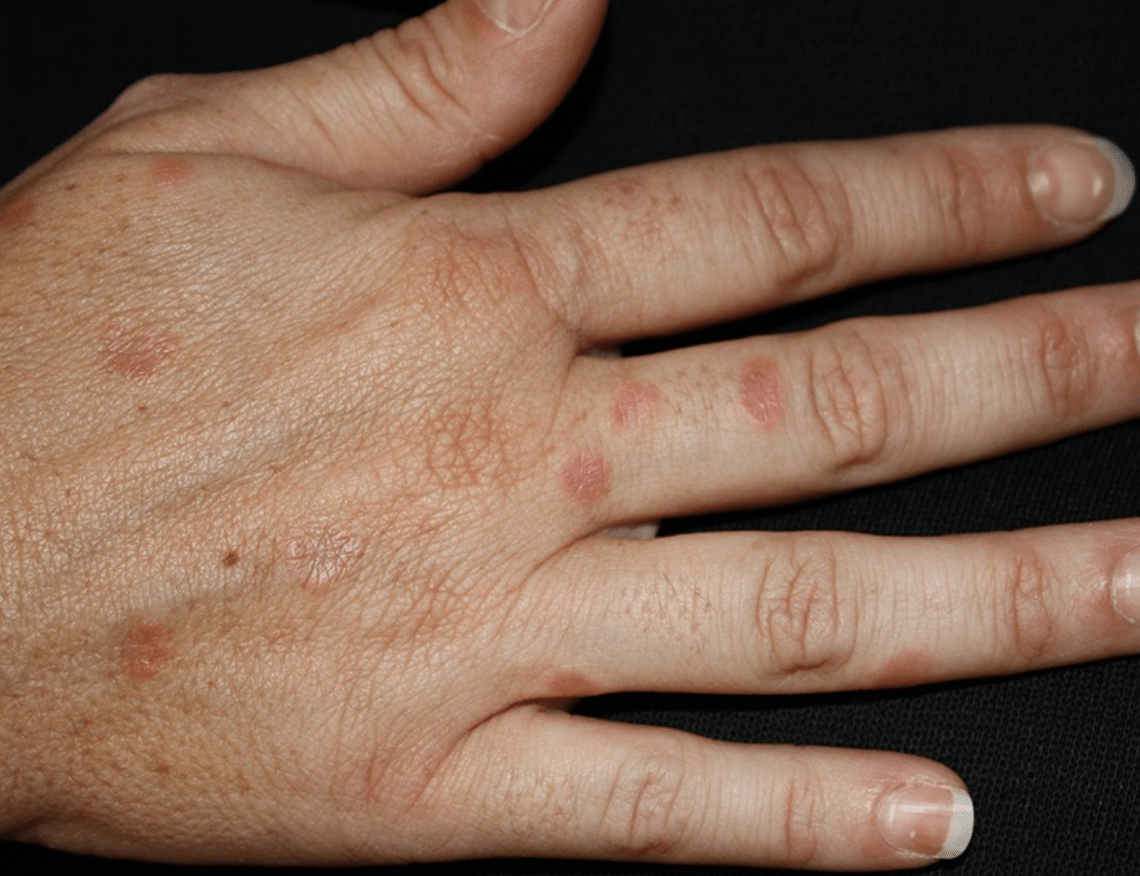
What are the nail fold changes
Bywaters' lesions from rheumatoid arthritis
This lab marker is associated with disease activity in Still disease and adult-onset Still disease
Significantly elevated ferritin level (with low circulating glycosylated ferritin)
Palisaded neutrophilic and granulomatous dermatitis
- polymorphous papules and plaques (vs rheumatoid nodules which are more periarticular skin colored nodules)
These two types of biologics have been employed as first-line therapies for Still Disease. Explain potential mechanism of why they work
- IL1/IL1R (inflammasome activation -> aberrant caspase-1 -> increase IL1 -> granulopoiesis and actives hypothalamus for thermoregulatory functions)
- IL6 (increases osteoclastogenesis and induces hepatocytes to produce acute phase reactants)
Most sensitive and specific test for Sjogrens
Seniors: Marker for increased risk for NLE
Anti-fodrin (70%)
Anti-Ro/SSA (60-70%) -> increased risk for NLE
Anti-La/SSB (20-40%)
Name the most common cause of mortality in MCTD + at least one more cause of mortality
Pulmonary artery HTN (40%) > acute cardiovascular events, TTP, HUS > infections
Distinguishing lab feature of rheumatoid vasculitis vs mixed cryoglobulinemia
Rheumatoid vasculitis: higher RF with decreased C3 and C4
Cryoglobulinemia: decreased C4 with normal C3
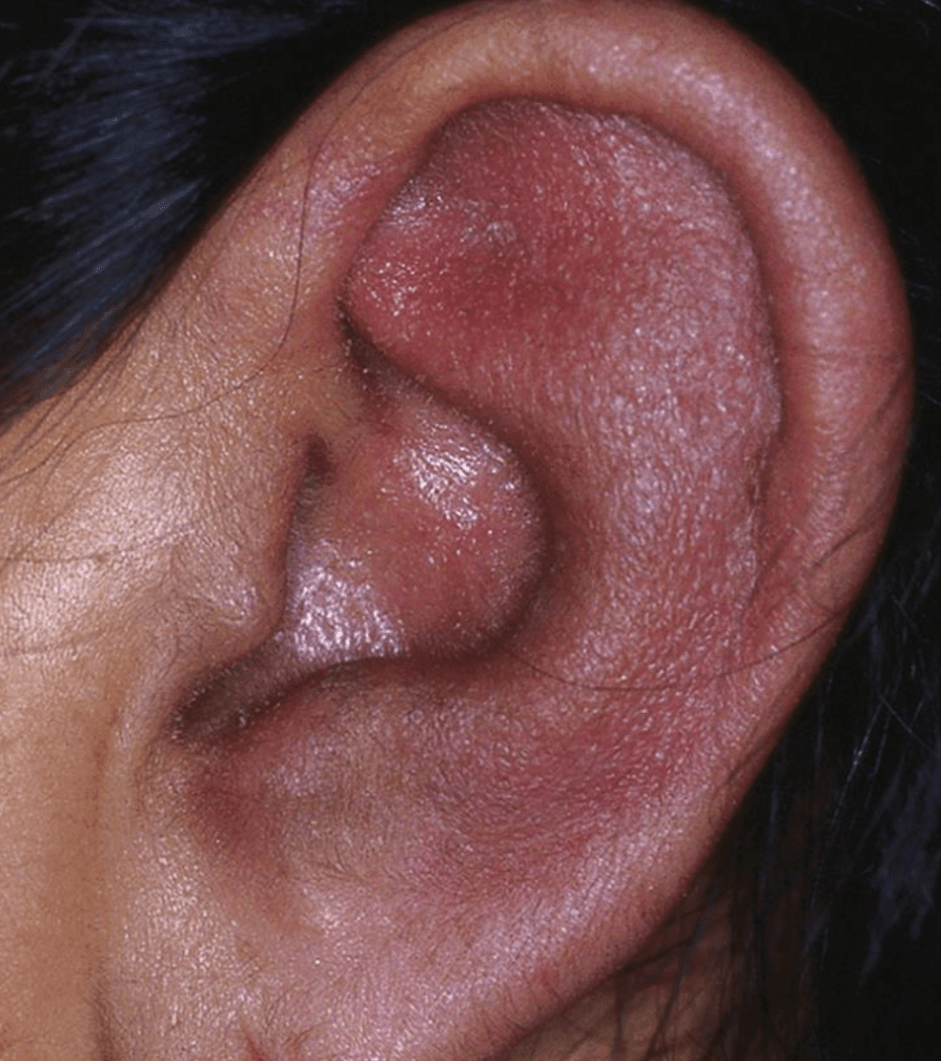
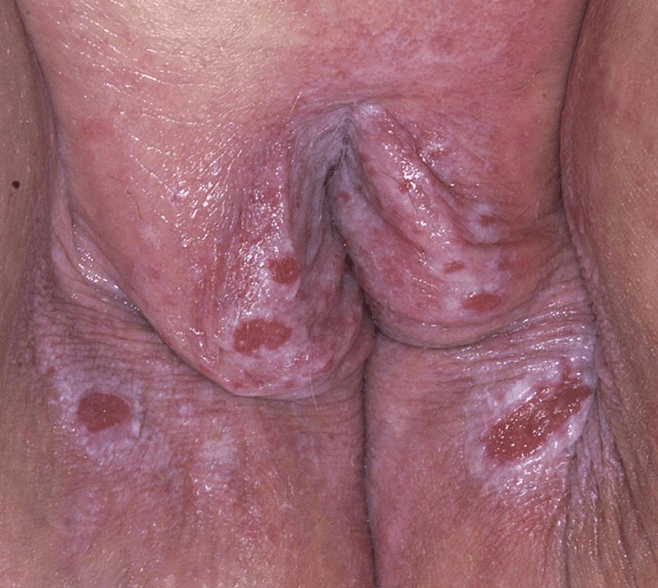
Diagnosis and name one of the leading cause of mortality
MAGIC syndrome (Mouth and Genital ulcers with Inflamed Cartilage)
- Inflammatory aortitis vs airway collapse/obstruction -> pneumonia

Name the year Shrek debuted
2001
Name at least 3 exclusion criteria for the diagnosis of primary Sjogrens
- Hx head and neck radiation treatment
- Active hepatitis C viral infection (+PCR)
- AIDS
- Sarcoidosis
- Amyloidosis
- GVHD
- IgG4 related disease
Name at least 2 triggers of rheumatoid nodulosis
- initiation of methotrexate (MTX-induced accelerated nodulosis)
- initiation fo TNF inhibitors, leflunomide, or tocilizumab
- tapering of systemic corticosteroids
Immune molecules thought to cause joint pain in rheumatoid arthritis
- RANKL binding to RANK on osteoclasts -> bony erosion
- RF and anti-CCP antibodies form immune complexes that leads to activation of complement cascade inside joints
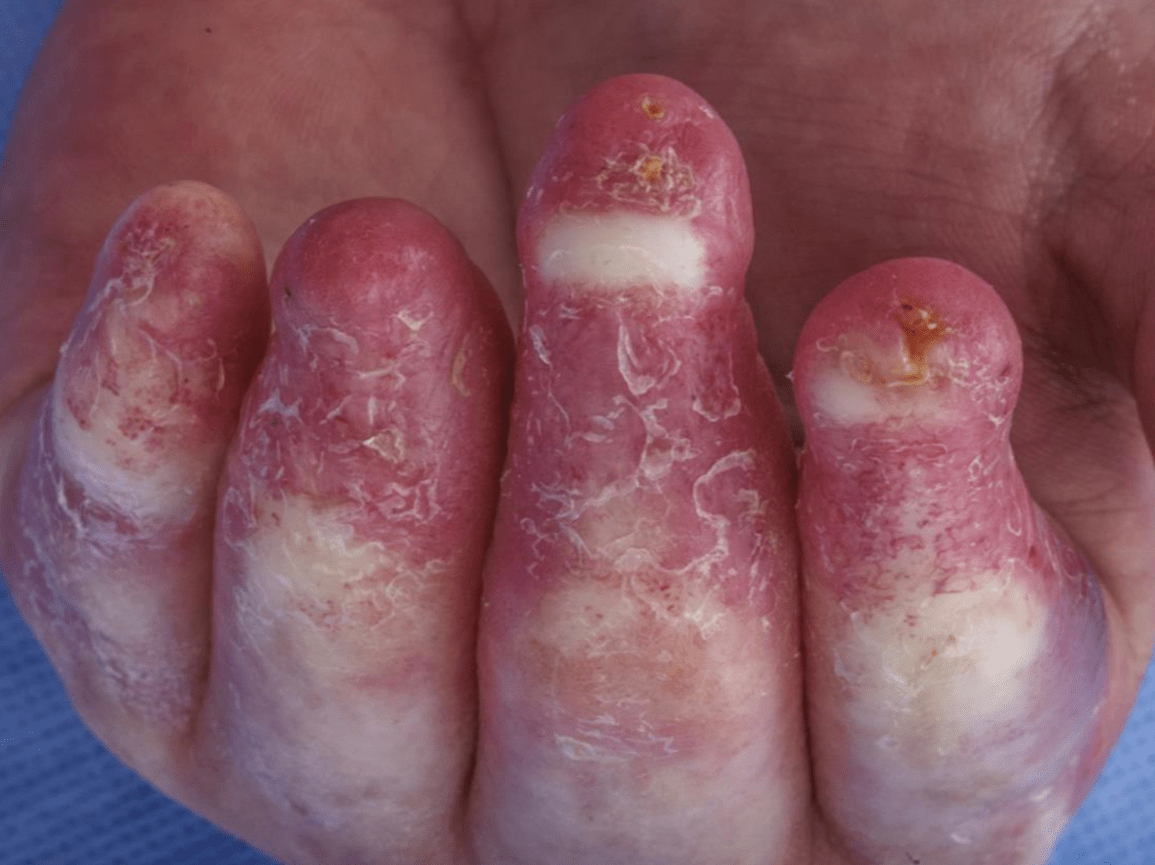
SAVI (STING [stimulator of interferon genes]-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy)
- Autosomal dominant (rarely autosomal recessive)