First-line treatment of a patient with a new diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Methotrexate
A 50-year-old man is evaluated for pain, swelling, tenderness, and redness of the right great toe that began last night. He has had several similar episodes over the past 2 years. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus and a recent diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Current medications are apixaban, metformin, and rosuvastatin.
On physical examination, the right first metatarsophalangeal joint is tender, red, warm, and swollen. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Gout
First line treatment for Polymyalgia rheumatica
Prednisone at 12.5 to 20 mg/d is appropriate treatment.
Sensetive and specific test for RA
Rheumatoid factor and anti–cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies.
- Rheumatoid factor and anti–cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibodies are approximately 70% sensitive in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis, but anti-CCP antibodies are 95% specific.
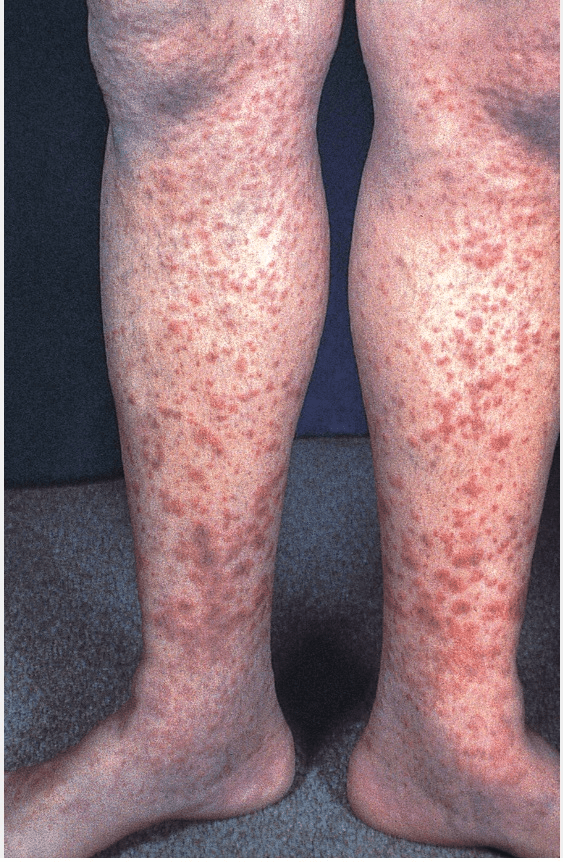
A 63-year-old woman is evaluated for fatigue and a leg rash that began 4 days ago. She has no other symptoms. She has recently diagnosed hypertension, and hydrochlorothiazide was initiated 2 weeks ago.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. The rash is shown. The larger lesions are palpable. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Hypersensitivity vasculitis
_________ is a mainstay of therapy for interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis.
Mycophenolate Mofetil
A 37-year-old woman is evaluated for a 1-year history of widespread joint and muscle pain, fatigue, poor sleep, and difficulty focusing. She also has irritable bowel syndrome and migraine headaches. Current medications are sumatriptan and topiramate.
Most soft tissue is tender to light palpation. Muscle strength is normal.
Laboratory evaluation shows a normal complete blood count, serum thyroid-stimulating hormone level, and urinalysis as well as an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 20 mm/h.
Most likely diagnosis?
Fibromylagia
________ antibodies are generally associated with diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis
Anti SCL 70
A 25-year-old woman is evaluated for a 3-year history of joint pain involving her hands with more than 1 hour of morning stiffness. She also has intermittent photosensitive facial rash, fatigue, and intermittent subjective fever. Complete blood count, serum creatinine level, and urinalysis are normal. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is 35 mm/h. the most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next?
ANA
ANA testing should be done before any subserology testing. If the ANA test result is positive, then specific subserologies are indicated on the basis of the clinical scenario. If the ANA test result is negative, then the ANA subserologic findings are typically negative. Therefore, if the initial ANA result is negative, then subserology testing is not indicated.
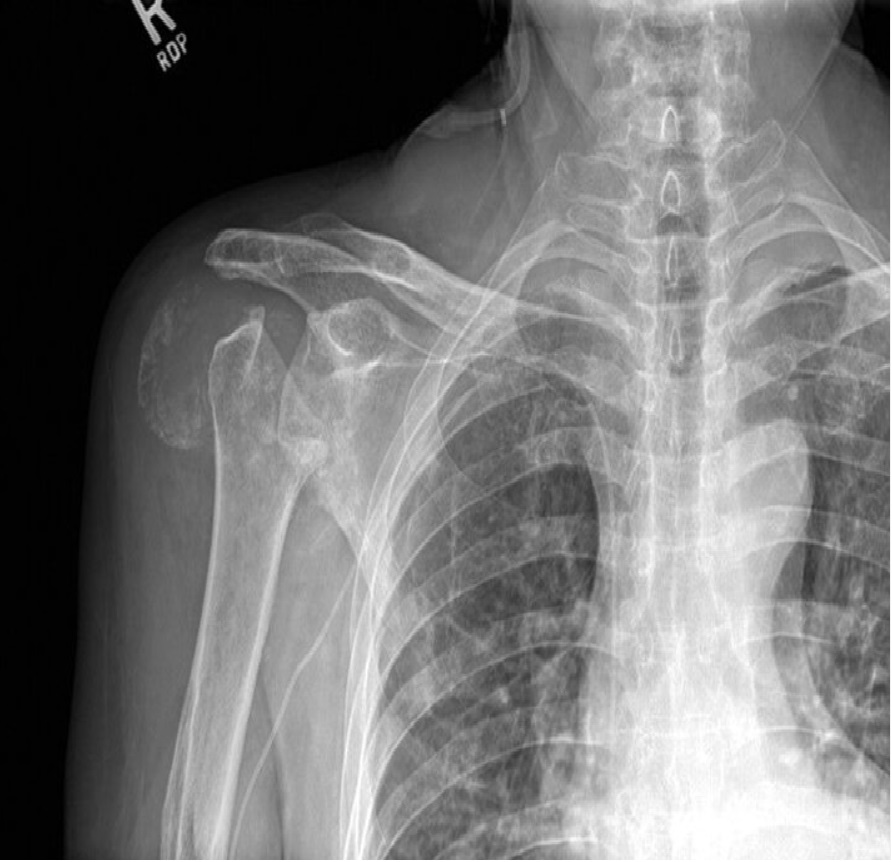
An 85-year-old woman is evaluated for worsening chronic right shoulder pain of 1 year's duration. The pain is more severe with use. She has no history of trauma to the shoulder.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. The right shoulder is swollen and tender, with no warmth or redness. There is pain-related decreased range of motion of the shoulder in all directions. Other joints are normal.
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and blood C-reactive protein level are normal.
Basic calcium phosphate–associated arthritis
Medication used for patients with gout for whom allopurinol, febuxostat, or uricosurics have failed to achieve the serum urate target and who continue to have frequent gout flares (two or more flares per year) or who have nonresolving subcutaneous tophi.
Pegloticase
Most common malignancy associated with Sjogren syndrome?
Lymphoma
- Patients with Sjögren syndrome are at high risk for lymphoma (5% lifetime risk).
- Risk factors for lymphoma in patients with Sjögren syndrome include parotid gland enlargement, depressed C4 complement level, elevated rheumatoid factor level, elevated anti-Ro/SSA and/or anti-La/SSB antibody levels, monoclonal gammopathy, and cryoglobulinemic vasculitis.
Early-onset (<3 months) and late-onset (>12 months) prosthetic joint infections are most commonly due to?
Staphylococcus Aureus
A 60-year-old woman is evaluated for achiness and fatigue. She reports dry mouth, irritated eyes, and discoloration of fingers after exposure to cold temperature that rapidly responds to rewarming.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. Parotid glands are enlarged, and salivary pooling is decreased. What is the most appropriate diagnostic test to perform next?
Anti-Ro/SSA antibodies
- Anti-Ro/SSA antibodies are the most specific laboratory test for diagnosis of Sjögren syndrome.
- Although rheumatoid factor is more common in Sjögren syndrome than in rheumatoid arthritis, it is not specific to either disease.
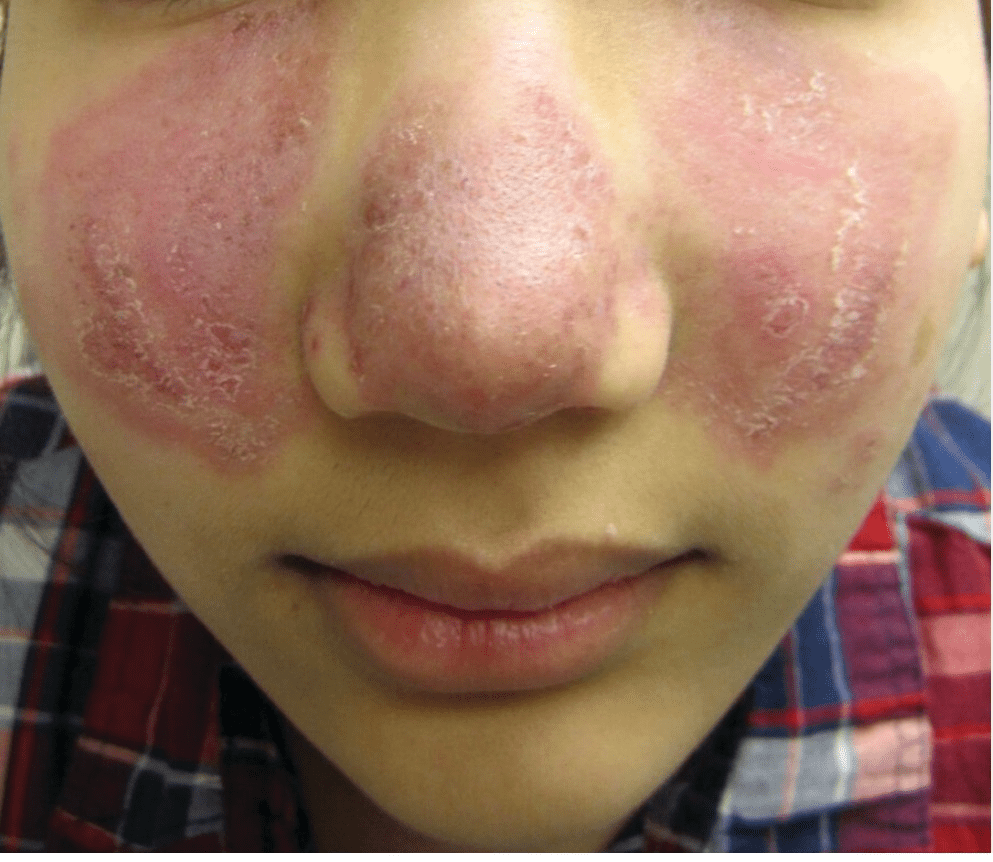
A 22-year-old woman is evaluated for a 1-month history of progressive rash on the face, chest, and arms following sun exposure. She also has experienced wrist arthralgia and malaise for the past 2 weeks.
Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus
Treatment of IgG4-related disease in patients with absolute or relative contraindications to glucocorticoid therapy.
Rituximab
A 60-year-old man is evaluated for a 1-year history of lower extremity edema. He has a 30-year history of poorly controlled ankylosing spondylitis. He also has intermittent uveitis. His only medication is naproxen; he has been reluctant to initiate biologic agents.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 158/90 mm Hg. Other vital signs are normal. He has kyphosis with immobility of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. There is decreased range of motion of the shoulders and hips with 30-degree flexion contractures at both hips. There is 2+ bilateral swelling of the lower extremities.
Labs showing Low albumin, high CRP, Creatinine of 1.8 and +3 protein on urinalysis. What's the diagnosis?
Renal amyloidosis
- Patients with long-standing, poorly controlled ankylosing spondylitis can develop renal (AA) amyloidosis, the major cause of kidney disease in these patients.
- AA amyloidosis most commonly affects the kidneys, manifesting as proteinuria and, eventually, renal insufficiency.
In the absence of chronic kidney disease, _______ at the dose of ________, followed by a single _______ dose in 1 hour, is an effective treatment of acute gout within the first 24 hours.
Colchicine, 1.2 mg, 0.6 mg
A 29-year-old man is evaluated after an episode of anterior uveitis. He has 2-year history of low back stiffness at night and in the morning that improves with activity. Current medication is meloxicam as needed.
On physical examination, he cannot touch his toes, and there is flattening of the normal lumbar lordosis. Internal rotation and flexion elicit pain in the right hip; range of motion of the right hip is diminished. Flexion, external rotation, and abduction of the hips cause pain in the right hip and low back. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable.
What is the best initial imaging test?
- Anteroposterior radiography of the pelvis is the initial imaging examination for suspected ankylosing spondylitis.
- Spondyloarthritis accounts for 40% of cases of acute anterior uveitis in the United States, and most of these patients will have ankylosing spondylitis.
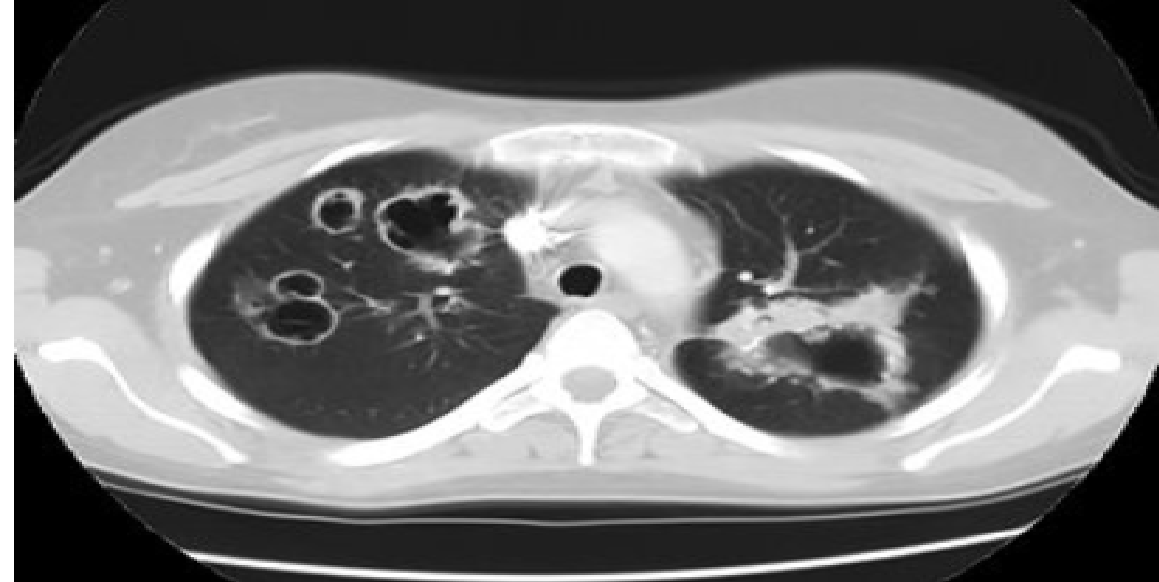
Patient has kidney disease too; Dx?
Wegner's granulomatosis
______ is reasonable alternative to colchicine as a glucocorticoid-sparing agent for recurrent oral ulcers in Behçet syndrome?
Apermilast
23 YO M is evaluated for fever, abdominal pain, rash, and arthritis of the right knee of 3 days' duration that resolved 1 week ago. He has had more than 20 similar episodes, the last three occurring in the past year. The first episode occurred at age 5 years and presented as abdominal pain; the patient underwent appendectomy but no appendicitis was found. His paternal grandfather and maternal grandmother had a similar syndrome.
Physical examination findings, including vital signs, are normal.
Labs shows an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 23 mm/h, a normal serum creatinine level, and 1+ protein on urinalysis.
Whats the diagnosis?
Familial Mediterranean fever
A 78-year-old woman is evaluated for constant bilateral headache of 1 week's duration. Two months ago, she was diagnosed with polymyalgia rheumatica.
What is most likely diagnosis?
Giant cell arteritis
______ test result in the setting of a compelling clinical picture confirms the diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis.
Positive HLA B 27
A 56-year-old man is evaluated for a 2-year history of mid to lower back pain and stiffness. He reports no buttock pain. He has tried home-based exercises, with minimal benefit.
On physical examination, there is diffuse tenderness to palpation of the lower thoracic spine and upper lumbar spine, with reduced flexion and extension. There is no sacroiliac joint tenderness.
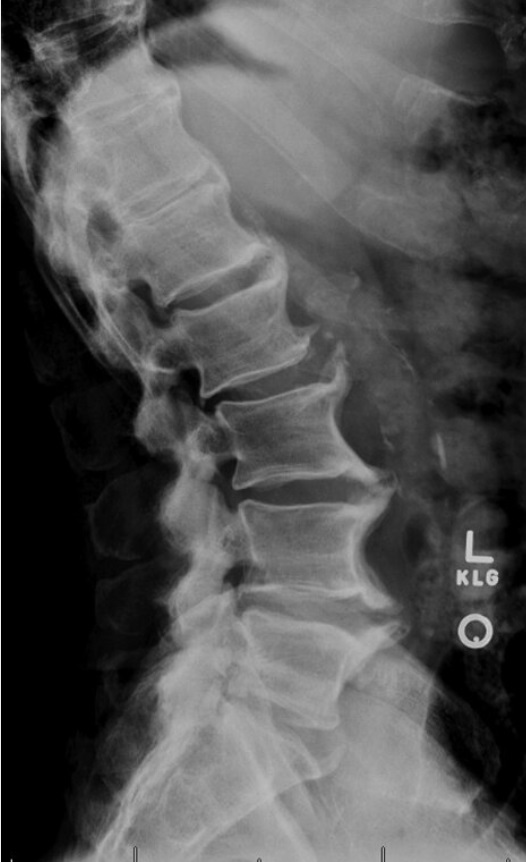
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis