disorders
leading cause of death in patients with systemic sclerosis
What is pulmonary disease (particularly interstitial lung disease)?
Name the condition and likely trigger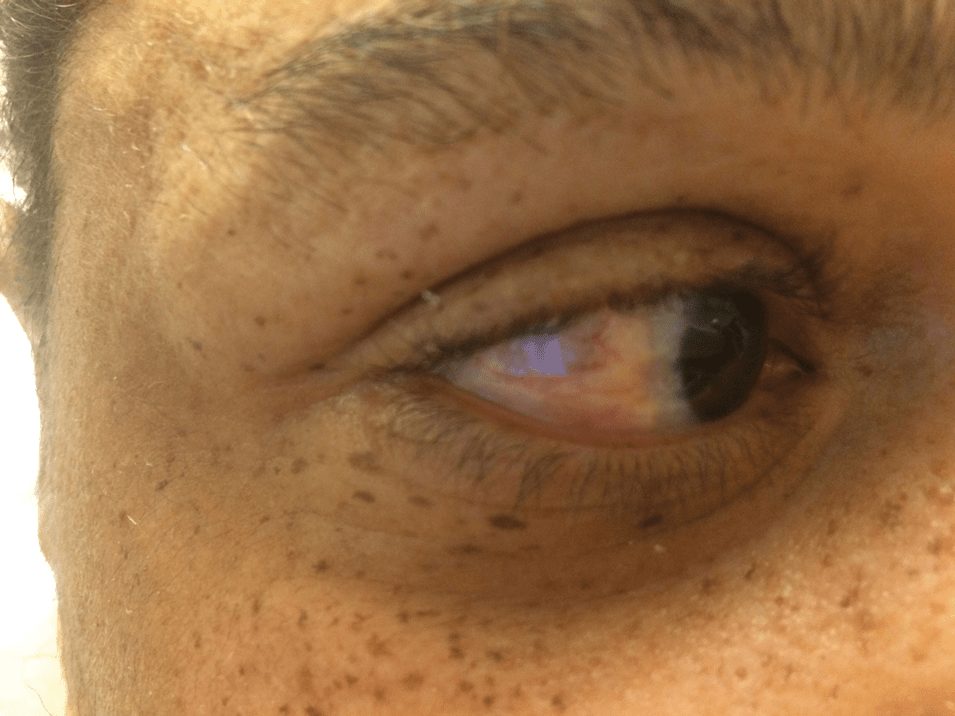
What is scleral plaque in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis?
Triggered by gadolinium contrast
most common subtype of morphea seen in adults.
What is plaque morphea?
Relapsing polychondritis has association with ___ malignancy
heme (aka myelodysplastic syndrome)
This high spiking fever pattern, accompanied by an evanescent salmon-colored rash, defines this childhood rheumatologic disorder.
What is systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (Still disease)?
High titer antibodies to this protein are typical of MCTD
anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (U1-RNP)
Major cytokines responsible for fibrosis in scleroderma.
TGF-β (>> IL-4, IL-13)
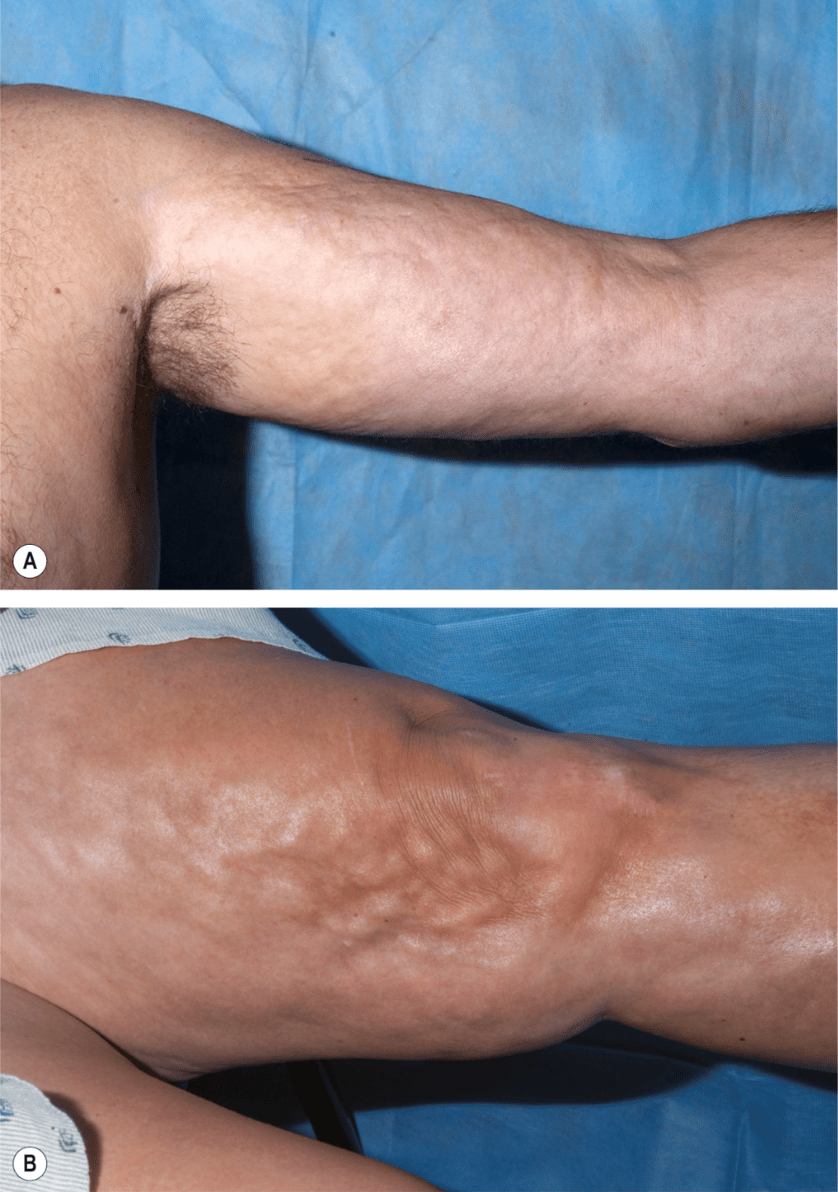
What is eosinophilic fasciitis (Shulman syndrome)?
-dry riverbed/groove sign; peripheral eosinophilia
-rapid onset, painful induration; triggered by strenuous exercise (>>borreliosis/statins)
-Good response to steroids
This subtype of morphea may cause limb shortening in children.
What is linear morphea?
Rheumatoid arthritis, splenomegaly, and neutropenia comprise this clinical triad.
What is Felty syndrome?
This potentially life-threatening complication of systemic-onset JIA is characterized by fever, cytopenias, coagulopathy, and extremely high ferritin levels.
What is macrophage activation syndrome (MAS)?
fever, cytopenias, liver dysfunction, coagulopathy, hypofibrinogenemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and very high serum levels of ferritin (treat w/ high dose steroids)
The majority of patients with Sjögren syndrome test positive for these two antibodies.
What are anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La antibodies?
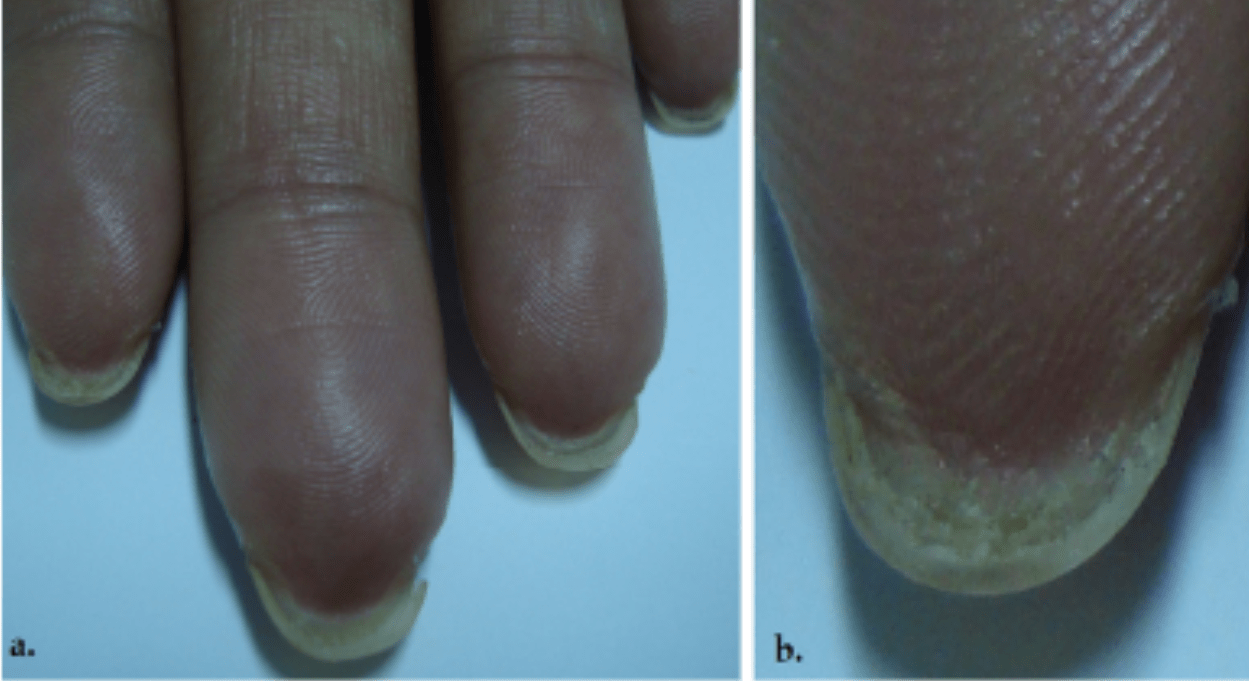
Name this finding
Pterygium inversus unguis (aka ventral pterygium)
adherence of hyponychium to ventral surface of nail plate --> obliteration of distal nail groove
Exposure to this contrast agent in patients with renal failure can trigger nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.
What is gadolinium?
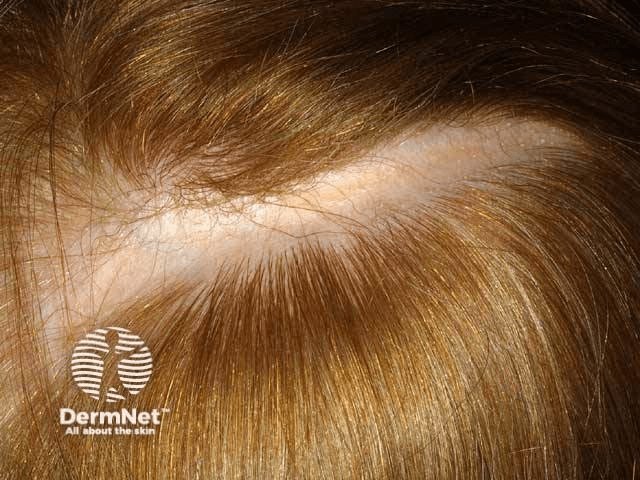 Name this finding and associated autoantibody
Name this finding and associated autoantibody
What are En Coupe de Sabre and anti-ssDNA antibody?
Tear production is assessed in Sjögren syndrome using this bedside test.
What is the Schirmer test?
This inherited autoinflammatory syndrome is characterized by periorbital edema, PAN, myelodysplastic syndrome, arthralgias, polychondritis, & pulmonary infiltrates
VEXAS syndrome
These antibodies are classically associated with the limited cutaneous form of systemic sclerosis
What are anti-centromere antibodies?
This single clinical presentation alone meets criteria by ACR for systemic sclerosis
What is skin thickening of fingers of both hands extending proximal to MCP joints (=9 points-- need 9 for diagnosis) ?
Markedly thickened, hyalinized fascia without inflammation characterizes this congenital disorder of the ECM.
What is stiff skin syndrome?
This rare, treatment-resistant morphea variant may lead to squamous cell carcinoma.
What is pansclerotic morphea?
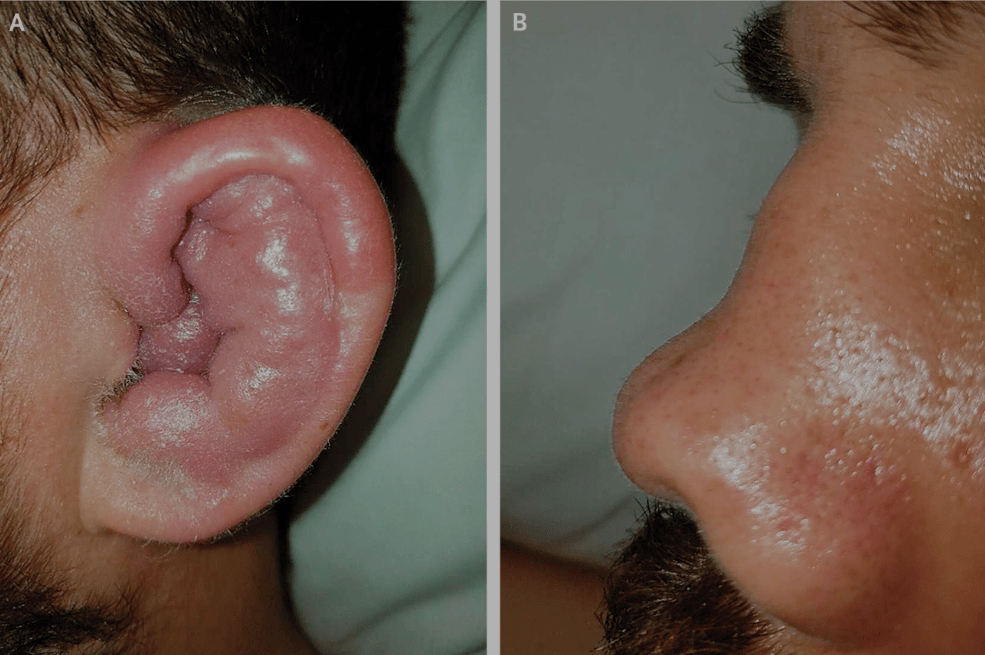 Name condition and antibody target
Name condition and antibody target
What are relapsing polychondritis and collagen 2?
What is first line treatment for JIA/Stills and other autoinflammatory syndromes?
IL-1 antagonists, e.g. anakinra, rilonacept, canakinumab
This autoantibody predicts rapidly progressive diffuse disease with renal crisis.
What is Anti-RNA polymerase III?
Name the sign
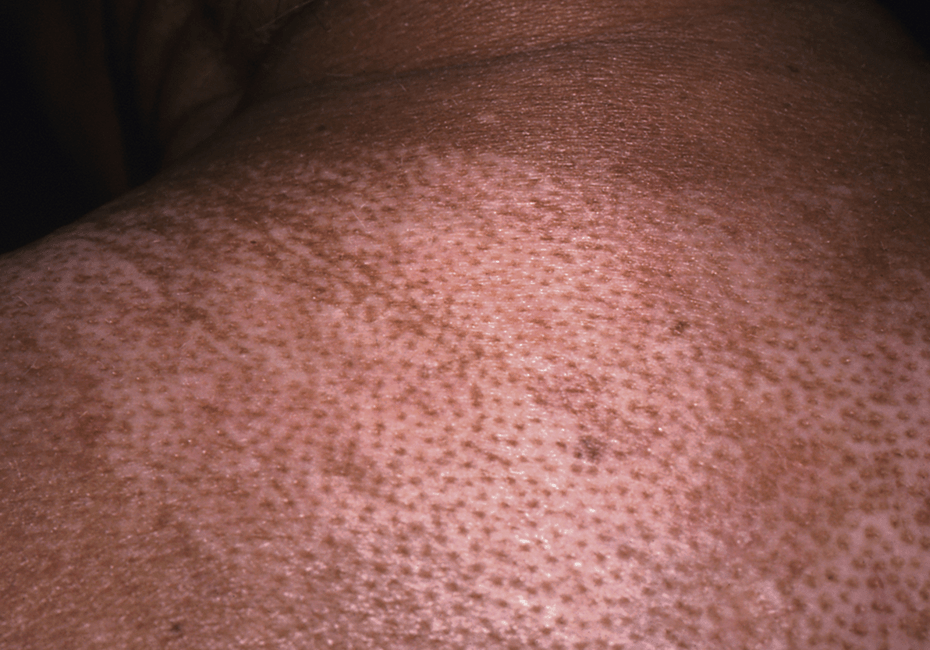
Salt and Pepper sign (aka leukoderma)
These are culprit drugs for sclerodermoid reactions
What are Bleomycin, bromocriptine, and D-penicillamine?
lichen sclerosus and lipoid proteinosis share this molecular target.
What is ECM-1 (extracellular matrix protein 1)?
Which cytokine is central to Still disease and many autoinflammatory syndromes?
(Interleukin-1) via aberrant inflammasome activation
This syndrome combines features of Behçet’s disease and relapsing polychondritis.
What is MAGIC syndrome?
Most sensitive + specific antibody for sjogren's syndrome
What is anti-fodrin?