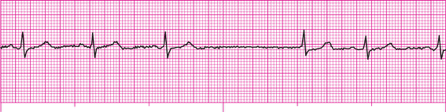
This narrow complex irregular rhythm is characterized by P waves who's shape size and direction change from beat to beat and has a rate over 100 bpm.
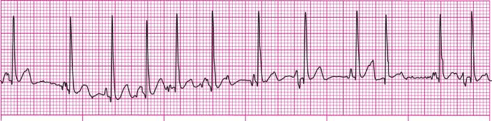
What is multifocal atrial tachycardia?
P wave may appear before, during, or after the QRS complex
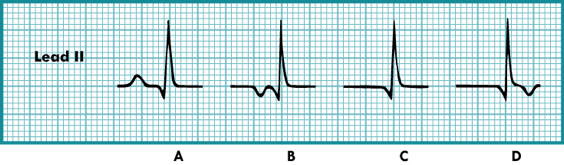
What are the P wave characteristics of a junctional rhythm?
A wide (and bizarre) complex, regular rhythm at a rate of 20-40 bpm. The P waves are usually absent or, with retrograde conduction to the atria, may appear after the QRS. T wave is frequently in the opposite direction of the QRS complex.
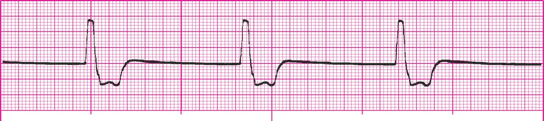
What is an idioventricular rhythm?
Symptoms of hypotension, ALOC, ischemic chest pain, signs of shock and acute heart failure.
What are the ACLS criteria of an unstable patient?
This medication is a parasympatholytic use as first line treatment for unstable bradycardia at a dose of 1 mg IVP.
What is Atropine?
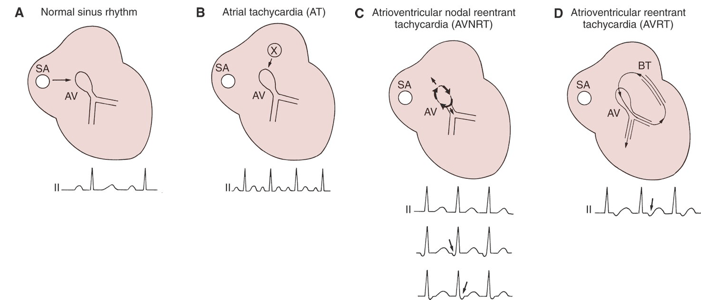
3 rhythms can be classified together as SVT.
What are atrial tachycardia, AVNRT, and AVRT?
A junctional beat that appears later in the cardiac cycle than the next expected sinus beat. This is a protective mechanism to prevent cardiac standstill.
What is a junctional escape beat?
A wide (and bizarre) complex, regular rhythm at a rate of 41-100 bpm. The P waves are usually absent or, with retrograde conduction to the atria, may appear after the QRS. T wave is frequently in the opposite direction of the QRS complex.
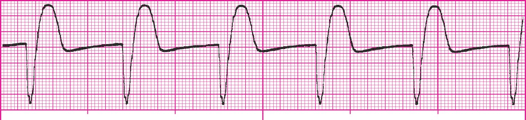
What is an accelerated idioventricular rhythm?
Delivery of an electrical shock to the heart timed to occur during QRS.
What is synchronized cardioversion?
This antiarrythmic medication slows AV conduction and may inhibit reentry pathways. It is given rapidly at a dose of 6 mg followed by 20 cc flush and may be repeated at 12 mg.
What is Adenosine?
Short PR interval, Delta wave, and QRS widening.
What are the features of WPW?
A rate of 40-60 BPM.
What is the intrinsic rate of the AV junction?
A wide (and bizarre) complex, regular rhythm at a rate of 101-250 bpm. The P waves are usually absent or, with retrograde conduction to the atria, may appear after the QRS. T wave is frequently in the opposite direction of the QRS complex.
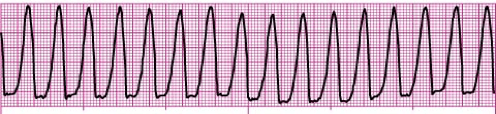
What is ventricular tachycardia?
Hypovolemia, hypoxia, hydrogen ion excess, hyper/hypokalemia, hypothermia, tamponade (cardiac), toxins, tension pneumothorax, thrombosis (pulmonary or coronary).
What are the Hs and Ts of cardiac arrest?
An antiarrythmic medication used to control of ventricular rate in A-fib and A-flutter. Second line after adenosine for narrow complex SVT. It inhibits calcium transport into the cell, decrease SA and AV node conduction, prolongs AV node refractory period. Cardiac contractility and PVR is decreased.
What is diltiazem?
A narrow complex rhythm with a regular atrial rate that may have variable ventricular conduct and is characterized by saw toothed P waves.
What is atrial flutter?
A narrow complex, regular rhythm is characterized at a rate of 61 to 100 bpm with P waves that are inverted and may appear before during or after the QRS complex.
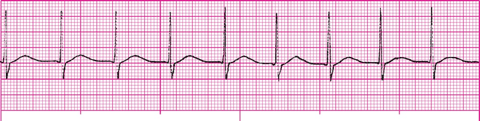
What is an accelerated junctional rhythm?
Rapid and chaotic with no pattern or regularity
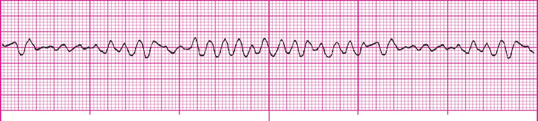
What is ventricular fibrillation?
Delivery of an electrical current across the heart muscle over a very brief period to terminate an abnormal heart rhythm. Indicated for: Pulseless monomorphic VT, Sustained polymorphic VT, VF
What is defibrillation?
A class III antiarrhythmic medication that prolongs action potential and refractory period; slows sinus rate, increasing PR interval and QT interval, decreases peripheral vascular resistant. Indicated for VF and VT.
What is amiodarone?
Dose:
Vfib/Vtach: 300mg IV/IO followed by 2nd dose of 150mg IV/IO
VT w/ Pulse: 150mg infused over 10 minutes D5W
An irregularly irregular narrow complex rhythm that has an erratic wavy baseline and loss of atrial kick.
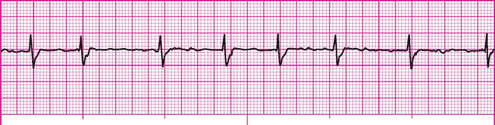
What is atrial fibrillation?
A narrow complex rhythm that is characterized at a rate of 101-180 bpm, with inverted P waves that may occur before, during, or after the QRS complex.
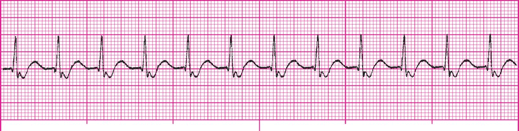
What is junctional tachycardia?
Wide QRS complexes vary in shape and amplitude from beat to beat and appear to twist from upright to negative or negative to upright and back, resembling a spindle or ribbon.
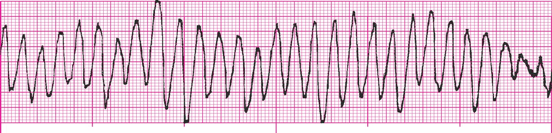
What is polymorphic VT?
The manufacturers recommendations (120-200 J) biphasic. If unknown use the maximum available or monophasic 360 J.
What is the correct j for defibrillation in cardiac arrest?
Catecholamine, adrenergic agent, vasopressor, bronchodilator. Mechanism of action: Beta 1 & 2 agonist, Alpha 1 agonist. Used for cardiac arrest or symptomatic bradycardia.
What is epinephrine?
Dose:
Cardiac arrest : 1mg (1:10,000) IV/IO q3-5mins
Symptomatic bradycardia: 2-10mcg per minute infusion