Ectopy
What is oddly placed? In other words there is wave or complex on the ECG strip that should not be there.
Complex that represents ventricular depolarization (then, cardiac contraction occurs)
What is the QRS complex?
One little box represents this time frame
What is 0.4 seconds?
Regular P wave Rhythm
P wave rate 80 bpm
No measurable PR interval
Regular QRS rhythm
QRSs wide with a rate of 30 bpm
What is third degree heart block?
There are more P waves than QRSs and no PRI, which indicates the atria and ventricles are working independently.
Regular rhythm, HR 75 bpm
P waves replaced by sawtooth waves
Narrow QRSs
What is atrial flutter?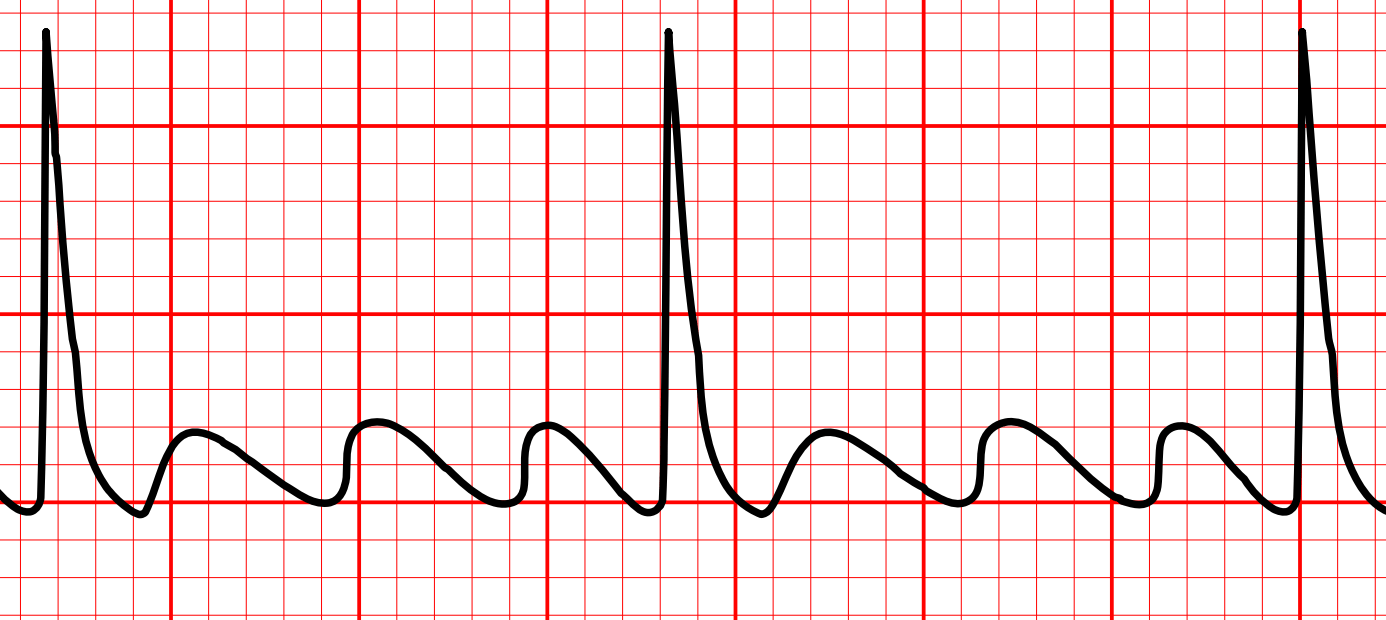
The Sinoatrial Node is known as the ______________ of the heart.
What is the pacemaker?
Nurse determines a rhythm is of supraventricular origin origin by examining this complex.
What is a QRS complex?
(Pssst the QRS is narrow in rhythms that originate above the ventricles)
Regular rhythm with 8 QRSs in 6 seconds. What is the heart rate?
What is 80 bpm?
Normal Sinus Rhythm with 2 early wide bizarre looking QRSs that look the same on the second and fifth complexes.
What are unifocal PVCs?
Regular rhythm, HR 150
No P waves
QRS complexes wide and consistent
What is ventricular tachycardia?
Premature
What is a wave or complex that came early?
How is time measured on an ECG strip?
What is horizontally?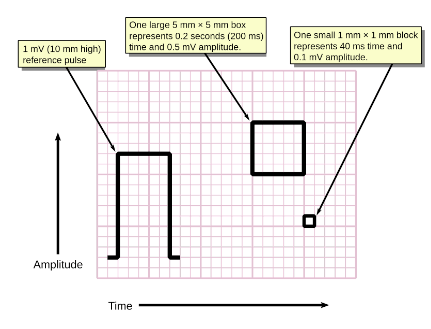
One big box represents this time frame
What is 0.2 seconds?
Regular rhythm, HR 130 bpm
P waves upright, rounded and one before each QRS
PRI 0.16 seconds, QRSs narrow
Bigger bump (t-wave) and smaller bump (p-wave) between QRSs
What is sinus tachycardia?
Regular Rhythm, HR 70 bpm
P waves upright, rounded one for each QRS
PR interval 0.24 seconds
QRS complex narrow
What is first degree block?
Isoelectric
What is a horizontal flat line between the P and T wave?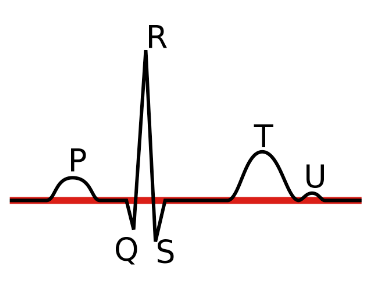
What are four characteristics of the P wave?
What are upright, rounded, look like the other P waves, and one before each QRS?
A QRS complex originating in the ventricle would be greater than how many little boxes?
What is greater than 3 little boxes?
A quivering line on ECG
No QRS complexes or P waves
What is ventricular fibrillation?
Irregularly Irregular Rhythm, Rate 120 bpm
No discernable P waves
Narrow QRS
What is atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response?
The AV node is known as the ___________ of the heart.
What is the gatekeeper?
ST segment elevation could indicate this condition
What is occlusion of a coronary artery? (MI)
Regular rhythm with 6 big boxes between QRSs
What is the heart rate?
What is 50 bpm?
300/6=50 bpm
Regular rhythm, HR 75 bpm
P wave upright, rounded, and one before each QRS
PRI is 0.18 seconds and consistent
QRS narrow
Patient pulseless
What is pulseless electrical activity (PEA)?
Regular rhythm (regular R to R intervals)
Rate 180 bpm
P wave buried in T wave
Narrow QRSs and less than 1.5 boxes between QRSs
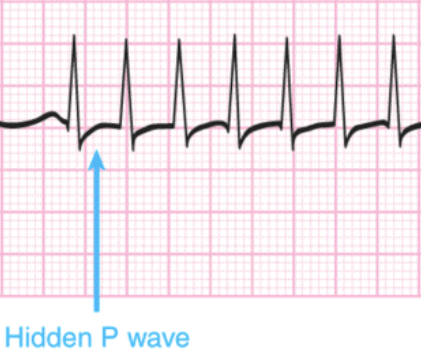 What is SVT?
What is SVT?