The creation of Sediments involves 3 processes. Name at least 2
What is Weathering, Erosion and Deposition
What does it mean to corrolate the layers

Find the index fossils that detemine those layers are the same age regardless of where the outcrops are and relative layers above or below.
What is comparative anatomy?
When you look at the similarities/differences of limb/structures of animals.
When sediments go under compacting and cementing processes they become___________
What is sedimentary rocks.
What Law states - The layers at the bottom are older then the layers at the top.
Law of super position?
State the order of the layers from oldest to youngest
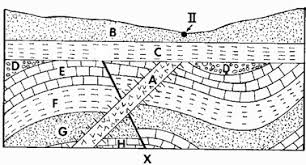
What is H,G,F,E,D,X,A,C,B
Ammonites, Trilobites and Brachiopods are examples of these types of fossils
What are Index Fossils?
Same Structure, Different Function and Shared Ancestor.
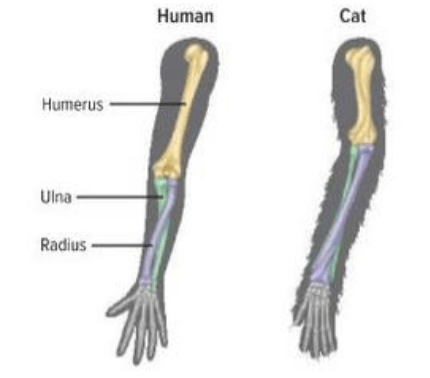
What is a Homologous Structure
When igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks go under weathering and eroding they become_________________
What is sediments?
Wide, Short
Igneous rocks are categorized as _________ or _________, depending on where the molten rock cools.
What are extrusive and intrusive.
Layers of rock is called.
What is strata?
Different Structure, Same Function, No apparent common ancestor. Also Known as Convergent Evolution.

What are Analogous Structures
The processes that turn metamorphic rocks into sediments
What are weathering and eroding?
A column or section of exposed rock is known as an____________
Outcrop?
Name the 2 Types of Dating rock layers and Fossils and how are they different
Relative dating describes the relationship of time within the layers and Absolute Dating is an exact age that is determined by Carbon or Radioactive dating.
This law states sediments fall in layers that are Flat.

What is an Vestigial Structure
_________ and ____________ turn sedimentary rocks into metamorphic rocks.
Heat and pressure
Any intrusion or fault that crosses over a layer is __________ then the layer it crosses over
Younger?
Define each of the processes in the sequence that evolve the rock to its final type.
IR = Igneous Rock, SR= Sedimentary Rock
MR = Metamorphic Rock
MR-IR-MR-SR-IR-MR-IR
MR-Heat and Pressure, IR-Melting and Solidification- MR-Heat and Pressure, SR-Weathering and Erosion, Compaction and Cementation, IR-Melting and Solidification, MR-Heat and Pressure, IR-Melting and Solidification
The difference between Homologous Structures and Analogous Structure
Homologous - Similar Structure, Different Function
Analogous- Different Structure, Similar Function
What is a common ancestor
When metamorphic and igneous rocks go under melting they turn into__________
What is magma?
This concept that states- The processes that changes the earth's land forms today are the same processes that change them millions of years ago.
What is Uniformitarianism?