Rocks form in different ways and are related to the environment in which they are formed but what common characteristic do all rocks have?
All rocks are made up of Minerals. (#2 on study guide)
Which process(es) in the rock cycle can lead to the formation of metamorphic rock?
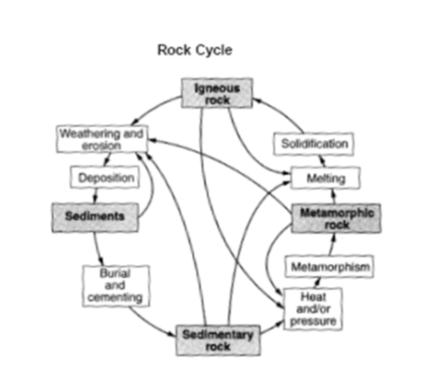
Heat and Pressure (Metamorphism) (#52 on study guide)
A presence of metamorphic rocks in an area is an indicator that the area was subjected to ...
HEAT and PRESSURE (#29 on study guide)
 By looking at the rock above, how do you know it is a sedimentary rock?
By looking at the rock above, how do you know it is a sedimentary rock?
Fossils! (#10 on study guide)
An igneous rock would most likely be formed near?
Volcanoes (#36 on study guide)
True or False - There is only one diagram that shows the rock cycle?
False (#3 on study guide)
Like most Earth materials, rocks are created and destroyed in cycles. Write the definition of the rock cycle:
THE ROCK CYCLE IS A MODEL THAT DESCRIBES THE FORMATION, BREAKDOWN, AND REFORMATION OF A ROCK AS A RESULT OF SEDIMENTARY, IGNEOUS AND METAMORPHIC PROCESSES. (#55 on study guide)
Foliated means the rocks has:
VISIBLE BANDS OR LAYERS (#33 on study guide)
Part 1: What is erosion?
Part 2: How does moving water separate big and little rocks?
a. Rocks of all sizes and shapes are heaped together, with little rocks filling in big spaces.
b. The heavier rocks are carried farther than lighter ones because they have more momentum.
c. The lighter rocks are carried farther than heavier ones because they stay suspended in water longer.
d. Rounder rocks are smoother and likely to roll farther under water then square or rectangular rocks.
Part 1: THE PROCESS THAT MOVES SEDIMENT
Part 2: c. The lighter rocks are carried farther than heavier ones because they stay suspended in water longer.
(#8 and #14 on study guide)
What are other terms for cooling/hardening?
SOLIDIFICATION and Crystallization (#49 on study guide)
To describe a rock’s texture, geologists determine?
Color, Texture, Crystal Structure (#5 on study guide)
Part 1: Which process in the rock cycle causes sediment to form?
Part 2: Which two processes result in the formation of igneous rock?
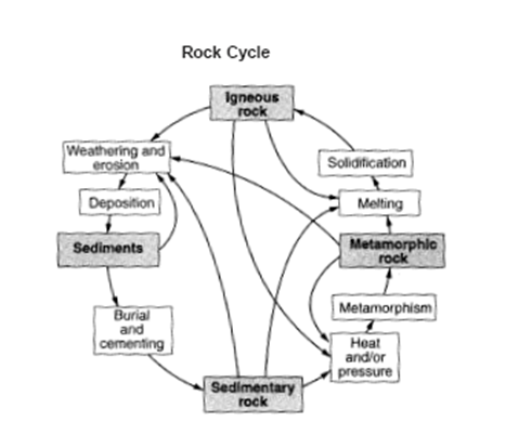
Part 1: weathering and erosion
Part 2: MELTING and SOLIDIFICATION
(#53 & #50/51 on study guide)
How are metamorphic rocks formed?
Any previously existing rocks that are exposed to Intense HEAT and PRESSURE (Metamorphism) (#35 on study guide)
What process can transform a metamorphic rock or igneous rock into a sedimentary rock?
WEATHERING/EROSION and SEDIMENTATION (COMPACTION AND CEMENTATION) .
(#13 on study guide)
Part 1: Coarse grains are an indicator that the rock cooled?
Part 2: Small or non-visible grains are an indicator that the rock cooled? (This type of cooling produces glassy textures.)
Part 1: SLOWLY
Part 2: QUICKLY
(#43 and #44 on study guide)
The most important characteristic to determine how a rock is formed is?
TEXTURE and MINERAL COMPOSITION (WHAT MINERALS ARE IN THE ROCK). (#4 on study guide)
Coal is a fossil fuel used within the US. It is found underground, compressed in a layer between other types of rock. Coal is formed by what 2 rock forming processes?
Deposition and Compaction (#56 on study guide)
Intrusive (igneous) means the rock formed:
Extrusive (igneous) means the rock formed:
Intrusive: INSIDE EARTH – COOLED SLOWLY (LARGE GRAINS/CRYSTALS)
Extrusive: OUTSIDE ON EARTH’S SURFACE (LAVA THAT HAS EXITED EARTH) – COOLED QUICKLY (SMALL GRAINS/CRYSTALS)
(#47 and #48 on study guide)
_______ rock forms when plant and animal remains formed under pressure for millions of years.
Organic
(#20 on study guide)
What is the difference between magma and lava?
MAGMA IS FOUND UNDER GROUND DEEP WITHIN THE EARTH
LAVA IS FOUND ON EARTH’S SURFACE (VOLCANO EXPELLS LAVA)
(#46 on study guide)
Unique characteristics such as rock composition, types of minerals present, mineral arrangement, mineral shape, mineral size, grain and texture are used for
IDENTIFYING ROCKS AS IGNEOUS, SEDIMENTARY OR METAMORPHIC (#6 on study guide)
Throughout our rocks and rock cycle unit, you found that rocks have many common and practical uses. List some common uses the different types of rocks that we studied.
BUILDING MATERIALS, LANDSCAPING, TOOLS, WEAPONS, COUNTERTOPS, STATUES (#57 on study guide)
Is heat and pressure a chemical or physical process?
Chemical (#30 on study guide)
______________ sedimentary rocks are composed of fragments of older rocks (i.e conglomerate).
_____________ rocks are created when water evaporates or the remains of plants and animals.
Clastic
Non- Clastic (chemical or organic)
(#17 or #18 on study guide)
Tell me everything you know about igneous rocks that form from magma and lava (cooling rate, crystal size, grain size, location (common and specific name)....
 (#39 on study guide)
(#39 on study guide)